Abstract
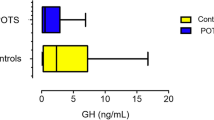
To overcome the difficulties of studying hormone pulsatility in the newborn, we have developed an automated microsampling system that permits the measurement of hormones in small prediluted samples of blood (40 μL) taken at 10-min intervals over 12 h. The system has been validated in adult volunteers, and the error attributable to the dilution was <4%. Using this method in 10 preterm babies, we have been able to describe pulsatile changes in GH and have demonstrated a clear postprandial elevation in GH levels peaking 60 min after a feed. Fourier transform analysis indicated a pulse periodicity of 180 min in babies who were appropriate for gestational age(n = 6), but faster, co-dominant pulse periodicities of 90-100 and 140 min in babies who were small for gestational age (weight and length below the 10th centile) (n = 4). There was no significant difference between mean, peak, and baseline GH levels between the two groups.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- CV:
-
coefficient of variation
- SGA:
-
small of gestational age
- AGA:
-
appropriate for gestational age
- OC:
-
observed concentration
References
Veldhuis JD, Faria A, Vance ML, Evans WS, Thorner MO, Johnson ML 1988 Contemporary tools for the analysis of episodic growth hormone secretion in clearance in vivo. Acta Paediatr Scand Suppl 347: 63–82.
Matthews DR 1988 Time series analysis in endocrinology. Acta Paediatr Scand Suppl 347: 55–62.
Shaywitz BA, Finklestein J, Hellman L, Weitzman ED 1971 Growth hormone in newborn infants during sleep wake periods. Pediatrics 48: 103–109.
Cornblath M, Parker ML, Reisner SH, Forbes AE, Daughaday WH 1965 Secretion and metabolism of growth hormone in premature and full term infants. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 25: 209–218.
Finklestein JW, Anders TF, Sachar EJ, Roffwarg HP, Hellman LD 1971 Behavioural state, sleep stage and growth hormone levels in human infants. J Clin Endocrinol 32: 368–371.
Miller JD, Wright NM, Esparza, Jansons R, Yang HC, Mosier HD 1992 Spontaneous pulsatile GH release in male and female premature infants. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 75: 1508–1513.
Wright NM, Northington FJ, Miller JD, Veldhuis JD, Rogol AD 1992 Elevated growth hormone secretory rate in premature infants: deconvolutional analysis of pulsatile growth hormone secretion in the neonate. Pediatr Res 32: 286–290.
De Zegher F, Devlieger H, Veldhuis JD 1993 Properties of growth hormone and prolactin hypersecretion by the human infant on the day of birth. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 76: 1177–1181.
De Zegher F, Van den Berghe G, Devlieger H, Eggermont E, Veldhuis 1993 Dopamine inhibits growth hormone and prolactin secretion in the human newborn. Pediatr Res 34: 642–645.
de Zegher F, Kimpen J, Raus J, Vanderschueren-Lodeweyckx M 1990 Hypersomatotropism in the dysmature infant at term and preterm birth. Biol Neonate 58: 188–191.
Deiber M, Chatelain P, Naville D, Putet G, Salle B 1989 Functional somatotropism in small for gestational age (SGA) newborn infants. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 68: 232–233.
Clark RG, Chambers G, Lewin J, Robinson ICAF 1986 Automated repetitive microsampling of blood: growth hormone profiles in conscious male rats. J Endocrinol 111: 27–35.
Tomlinson PR, Smellie JM, Prescod N, Dalton RN, Chantler C 1994 Differential excretion of urinary proteins in children with vesicoureteric reflux and reflux nephropathy. Paediatr Nephrol 8: 21–25.
Dalton RN, Turner C 1987 A sensitive and specific method for measurement of inulin. Ann Clin Biochem 24( suppl 1): 51–231.
Matthews DR, Hindmarsh PC, Pringle PJ, Brook CJD 1991 A distribution method for analysing the baseline pulsatile endocrine signals as exemplified by 24 hour growth hormone profiles. Clin Endocrinol 35: 245–252.
Lang DA, Matthews DR, Burnett M, Ward GM, Turner RC 1982 Pulsatile, synchronous basal insulin and glucagon secretion in man. Diabetes 31: 22–26.
Fairhall KM, Mynett A, Smith RG, Robinson ICAF 1995 Consistent GH responses to repeated injections of GH-releasing hexapeptide(GHRP-6) and the non-peptide GH secretagogue, L-692,585. J Endocrinol 145: 417–426.
Miller JD, Tannenbaum GS, Collle E, Guyda HJ 1982 Daytime pulsatile growth hormone secretion during childhood and adolescence. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 55: 989–994.
Adrian TE, Lucas A, Bloom SR, Aynsley-Green A 1983 Growth hormone response to feeding in term and preterm neonates. Acta Paediatr Scand 72: 251–254.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Neil Dalton from the Children Nationwide Research Laboratory, Guy's Hospital in London, for performing the inulin and albumin assays and Phillip Sutton for his technical advice. Our thanks also to the nurses of the Neonatal Unit.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adcock, C., Ogilvy-Stuart, A., Robinson, I. et al. The Use of an Automated Microsampling System for the Characterization of Growth Hormone Pulsatility in Newborn Babies. Pediatr Res 42, 66–71 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199707000-00011
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199707000-00011
This article is cited by
-
Measuring luteinising hormone pulsatility with a robotic aptamer-enabled electrochemical reader
Nature Communications (2019)
-
An updated view of hypothalamic–vascular–pituitary unit function and plasticity
Nature Reviews Endocrinology (2017)