Abstract
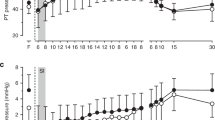
This study was designed to determine the effects of a membrane permeant phosphodiesterase-resistant analog of cGMP on lung liquid production and pulmonary blood flow at the time of birth. Experiments were performed on seven fetal sheep prepared for chronic measurements of lung liquid production (Jv), pulmonary blood flow (Qp) and pressure, as well as systemic pressure. Injection of either 8-bromo-cGMP or saline were made via a catheter inserted in the left pulmonary artery. Experiments consisted of 1 h of control, 1 h of infusion, and 2 h of recovery. Data were analyzed by ANOVA and Newman-Keuls test. After infusion of 8-bromo-cGMP, Jv was decreased by 70 and 44% from control in h 3 and 4, respectively. Qp was elevated by 100 mL/min in h 2 and 3 and continued to be elevated by 50 mL/min in h 4. Saline infused animals showed no significant changes in Qp and Jv. This study demonstrates that 8-bromo-cGMP decreases lung liquid production and increases pulmonary blood flow in near term fetal sheep. Although blood flow increased in h 2, lung liquid production did not decrease at this time, suggesting a time dissociation between changes in pulmonary blood flow and lung liquid production. Thus, it is possible that a common transduction pathway involving cGMP may be responsible for lung liquid reduction and elevation of pulmonary blood flow at birth. However, Qp and Jv may not be causally related.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- Jv:
-
net lung liquid production
- Qp:
-
pulmonary blood flow
- EDRF:
-
endothelium-derived relaxing factor
- NO:
-
nitric oxide
- PVR:
-
pulmonary vascular resistance
- PAP:
-
pulmonary arterial pressure
- PG:
-
prostaglandin
References
Strang LB 1997 Neonatal Respiration. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford, UK, 20–46
Alcorn D, Adamson TA, Lambert TF, Maloney JM, Richie BC, Robinson PM 1997 Morphological effects of chronic tracheal ligation and drainage in the fetal lamb lung. J Anat 123: 649–660
Moessinger AC, Harding R, Adamson TM, Singh M, Ku GT 1990 Role of lung fluid volume in growth and maturation of the fetal sheep lung. J Clin Invest 86: 1270–1277
Cassin S, Dawes GS, Mott JC, Ross BB, Strang LB 1964 The vascular resistance of the foetal and newly ventilated lung of the lamb. J Physiol 171: 61–79
Walters DV, Olver RE 1978 The role of catecholamines in lung liquid absorption at birth. Pediatr Res 12: 239–242
Cassin S, Demarco V, Perks AM, Kuck H, Ellis TM 1994 Regulation of lung liquid secretion in immature fetal sheep: hormonal interaction. J Appl Physiol 77: 1445–1450
Abman SH, Chatfield BA, Hall SL, McMurthy IF 1990 Role of endothelium-derived relaxing factor during transition of pulmonary circulation at birth. Am J Physiol 259:H1921–H1927
Cassin S 1993 The role of eicosanoids and endothelium-dependent factors in regulation of the fetal pulmonary circulation. J Lipid Mediators 6: 477–485
Iwamoto HS, Teitel D, Rudolph AM 1987 Effects of birth-related events on blood flow distribution. Pediatr Res 22: 634–640
Olver RE, Ramsden CA, Strang LB, Walters DV 1986 The role of amiloride-blockable sodium transport in adrenaline-induced lung liquid reabsorption in the fetal lamb. J Physiol 376: 334–340
Strang L B 1991 Fetal lung liquid: secretion and reabsorption. Physiol Rev 71: 991–1016
Cummings JJ 1995 Pulmonary vasodilator drugs decrease lung liquid production in fetal sheep. J Appl Physiol 79: 1212–1218
Ignarro LJ, Harbison RG, Wood KC, Kadowitz PJ 1986 Activation of purified soluble guanylate cyclase by endothelium-derived relaxing factor from intrapulmonary artery and vein: stimulation by acetylcholine, bradykinin and arachidonic acid. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 237: 893–900
Ignarro LJ, Burke TM, Wood KS, Wolin MS, Kadowitz PJ 1984 Association between cyclic GMP accumulation and acetylcholine-elicited relaxation of bovine intrapulmonary artery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 228: 682–690
Gryglewski RJ, Botting RM, Vane JR 1988 Mediators produced by the endothelial cell. Hypertension 12: 530–548
Griffith TM, Edwards DH, Lewis MJ, Henderson AH 1985 Evidence that cyclic GMP mediates endothelium-dependent relation. Eur J Pharmacol 112: 195–202
Kelley TJ, Al-Nakkash L, Drumm ML 1997 C-type natriuretic peptide increases chloride permeability in normal and cystic fibrosis airway cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 16: 464–470
Geary GA, Goy MF, Boucher RC 1993 Synthesis and vectorial export of cGMP in airway epithelium: expression of soluble and CNP specific guanylate cyclases. Am J Physiol 265:L598–L605
Jiang H, Colbran JL, Francis SH, Corbin JD 1992 Direct evidence for cross activation of cGMP-dependent protein kinase by cAMP in pig coronary arteries. J Biol Chem 267: 1015–1019
Jin JG, Murthy KS, Grider JR, Makhlouf GM 1993 Activation of distinct cAMP- and cGMP-dependent pathways by relaxant agents in isolated gastric muscle cells. Am J Physiol 264:G470–G477
Kindler PM, Ziabakhsh S, Perks AM 1992 Effect of cAMP, its analogues, and forskolin on lung liquid production by in vitro lung preparations from fetal guinea pits. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 70: 330–338
Cassin S, Dawes GS, Ross BB 1964 Pulmonary blood flow and vascular resistance in immature foetal lambs. J Physiol 171: 80–89
Davis TA, Gause G, Perks AM, Cassin S 1992 Effect of intravenous saline infusion on fetal ovine lung liquid secretion. Am J Physiol 262:R1117–R1120
Perks AM, Cassin S 1985 The rate of production of lung liquid in fetal goats and the effect of expansion of the lungs. J Dev Physiol 7: 149–160
Normand ICS, Olver RE, Reynolds EOR, Strang LB 1971 Permeability of lung capillaries and alveoli to non-electrolytes in foetal lamb. J Physiol 219: 303–320
Olver RE, Ramsden CA, Strang LB, Walters DV 1986 The role of amiloride blockable sodium transport in adrenaline-induced lung liquid reabsorption in the fetal lamb. J Physiol 376: 334–340
Cassin S, Perks AM 1982 Studies of factors which stimulate lung liquid secretion in fetal goats. J Dev Physiol 4: 311–325
Winer BJ 1971 Statistical Principles in Experimental design. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 205–260
Heymann MA, Soifer JS 1989 Control of the fetal and neonatal pulmonary circulation. Lung Biol Health Dis 38: 33–50
Accurso FJ, Abman SH, Wilkoning RB, Worthen GS, Henson P 1991 Fetal pulmonary vasodilation after exogenous platelet-activating factor. J Appl Physiol 70: 778–787
Tiktinski MH, Cummings JJ, Morin FC 1992 Acetylcholine increases pulmonary blood flow in intact fetuses via endothelium-dependent vasodilation. Am J Physiol 262:H406–H410
Bellan JA, Minkes RK, McNamara DB 1991 Nω-Nitro-L-arginine selectively inhibits vasodilator responses to acetylcholine and bradykinin in cats. Am J Physiol 260:H1025–H1029
Zapol WM, Rimar S, Gillis N, Marletta M, Bosken C 1994 Nitric oxide and the lung. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 149: 1375–1380
Webber SE, Morikawa T, Widdicombe JG 1992 Platelet-activating factor relaxes ferret tracheal smooth muscle and reduces transepithelial potential differences in vitro. Br J Pharmacol 105: 223–229
Kinsella JP, MaQuerton JA, Rosenberg AA, Abman SA 1992 Hemodynamic effects of exogenous nitric oxide in ovine transitional pulmonary circulation. Am J Physiol 263:H875–H880
Barker PM, Brown MJ, Ramsden CA, Strang LB, Walters DV 1988 The effect of thyroidectomy in the fetal sheep on lung liquid reabsorption induced by adrenaline. J Physiol 407: 373–383
Walters DV, Ramsden CA, Olver RE 1990 Dibutyryl cAMP induces a gestation-dependent absorption of fetal lung liquid. J Appl Physiol 68: 2054–2059
Cook NS 1988 The pharmacology of potassium channels and their therapeutic potential. Trends Pharmacol Sci 9: 21–28
Archer SL, Huang JMC, Hampl V, Nelson DP, Schultz PJ 1994 Nitric oxide and cGMP cause vasorelaxation by activation of a charybdotoxin-sensitive K channel by cGMP dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: 7583–7587
Smith JA, Francis SH, Walsh KA, Kumar S, Corbin JD 1996 Auto-phosphorylation of type Iβ cGMP-dependent protein kinase increases basal catalytic activity and enhances allosteric activation by cGMP or cAMP. J Biol Chem 271: 20756–20762
Komalavilas P, Lincoln TM 1996 Phosphorylation of the inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor. J Biol Chem 271: 21933–21938
Harrison S, Reifsnyder DH, Gallis B, Cadd GG, Beavo JA 1986 Isolation and characterization of bovine cardiac muscle cGMP-inhibited phosphodiesterase: a receptor for new cardiotonic drugs. Mol Pharmacol 29: 506–514
Haynes JJ, Kithas PA, Taylor AE, Strada SJ 1991 Selective inhibition of cGMP-inhibitable cAMP phosphodiesterase decreases pulmonary vasoreactivity. Am J Physiol 261:H487–H492
Perks AM, Ruiz T, Chua B, Vonder Muhl LI, Kindler PM, Blair W 1993 Reabsorption of lung liquid produced by 2,4-Dinitrophenol inin-vitro lungs from fetal guinea pigs. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 71: 1–11
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Hilken Kuck for his excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported in part by National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Grant HL-10834, Children's Miracle Network, and from Division of Sponsored Research.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kabbani, M., Cassin, S. The Effects of cGMP on Fetal Sheep Pulmonary Blood Flow and Lung Liquid Production. Pediatr Res 43, 325–330 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199803000-00003
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199803000-00003