Abstract
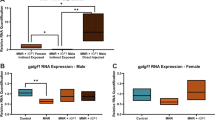
In the human, intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR) can result in persistent postnatal growth failure, which may be attributable, in part, to abnormal GH secretion. Whether putative alterations in GH secretion are the result of abnormalities intrinsic to the pituitary or reflect changes in the production of GH-releasing hormone or somatostatin (SS) is unknown. We tested the hypothesis that growth failure associated with IUGR or early postnatal food restriction (FR) is caused by a central defect in hypothalamic SS gene expression. Both models displayed persistent growth failure postnatally without any catch-up growth. We measured levels of SS mRNA levels in rats experimentally subjected to IUGR or FR. SS mRNA levels were measured by semiquantitative in situ hybridization throughout development. Levels of SS mRNA in the periventricular nucleus were significantly higher in both male and female IUGR rats in the juvenile and adult stages compared with matched controls (p ≤ 0.05). FR was associated with higher SS mRNA levels only in neonatal female rats (p ≤ 0.05). These results suggest that intrauterine malnutrition induces a persistent increase in the expression of SS mRNA in the periventricular nucleus, whereas early postnatal FR results in only a transient increase in SS gene expression. Because IGF-I levels were normal in juvenile IUGR and FR rats, central dysregulation of SS neurons does not appear to be the cause of early postnatal growth failure in either model. However, these observations are consistent with the hypothesis that nutritional stress at critical times during development can have persistent and potentially irreversible effects on organ function.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- FR:
-
food restriction
- GHRH:
-
GH, releasing hormone
- IUGR:
-
intrauterine growth retardation
- NPY:
-
neuropeptide Y
- PeN:
-
periventricular nucleus
- SS:
-
somatostatin
References
Wigglesworth JS 1964 Experimental growth retardation in the foetal rat. J Pathol Bacteriol 88: 1–13.
Barker DJP 1996 Growth in utero and coronary heart disease. Nutr Rev 54: S1–S7.
Gluckman PD, Harding JE 1997 The physiology and pathophysiology of intrauterine growth retardation. Horm Res 48: 11
Barker DJP, Gluckman PD, Godfrey KM, Harding JE, Owens JA, Robinson JS 1993 Fetal nutrition and cardiovascular disease in adult life. Lancet 341: 938–941.
Barker DJP, Hales CN, Fall CHD, Phipps K, Clarck PMS 1993 Type 2 (non–insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus, hypertension and hyperlipidaemia (syndrome X): relation to reduced fetal growth. Diabetologia 36: 62–67.
Boersma B, Wit JM 1997 Catch-up growth. Endocr Rev 18: 646–661.
Woodall SM, Breier BH, Johnston BM, Gluckman PD 1996 A model of intrauterine growth retardation caused by chronic maternal undernutrition in the rat: effects on the somatotrophic axis and postnatal growth. J Endocrinol 150: 231–242.
Tannenbaum GS 1991 Neuroendocrine control of growth hormone secretion. Acta Paediatr Suppl 372: 5–16.
Ackland FM, Stanhope R, Eyre C, Hamill G, Jones J, Preece MA 1988 Physiological growth hormone secretion in children with short stature and intra-uterine growth retardation. Horm Res 30: 241–245.
Widdowson EM, McCance RA 1963 The effect of finite periods of undernutrition at different ages on the composition and subsequent development of the rat. Proc R Soc Lond 185: 329–342.
Hughes P, Tanner J 1970 A longitudinal study of the growth of the blackhooded rat: methods of measurement and rates for growth for skull, limbs pelvis, nose-rump and tail lengths. J Anat 106: 349–370.
Paxinos G, Watson C 1986 The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 2nd Ed. Academic Press, London
Rogers KV, Vician L, Steiner RA, Clifton DK 1987 Reduced preprosomatostatin messenger ribonucleic acid in the periventricular nucleus of hypophysectomized rats determined by quantitative in situ hybridization. Endocrinology 121: 90–93.
Gluckman PD, Cutfield W, Harding JE, Milner D, Jensen E, Woodall SM, Gallaher BH, Bauer MK, Breier BH 1996 Metabolic consequences of intrauterine growth retardation. Acta Paediatr Suppl 417: 3–6.
Sadiq HF, Das UG, Tracy TF, Devaskar SU 1999 Intrauterine growth restriction differentially regulates perinatal brain and skeletal muscle glucose transporters. Brain Res 823: 96–103.
Rajakumar PA, He J, Simmons RA, Devaskar SU 1998 Effect of uteroplacental insufficiency upon brain neuropeptide Y and corticotropin-releasing factor gene expression and concentrations. Pediatr Res 44: 168–174.
Thissen JP, Ketelslegers JM, Underwood LE 1994 Nutritional regulation of the insulin-like growth factors. Endocr Rev 15: 80–101.
Plagemann A, Harder T, Rake A, Waas T, Melchior K, Ziska T, Rohde W, Dorner G 1999 Observations on the orexigenic hypothalamic neuropeptide Y-system in neonatally overfed weanling rats. J Neuroendocrinol 11: 541–546.
Chan YY, Clifton DK, Steiner RA 1996 Role of NPY neurones in GH-dependent feedback signalling to the brain. Horm Res 45: 12
Rettori V, Milenkovic L, Aguila MC, McCann SM 1990 Physiologically significant effect of neuropeptide Y to suppress growth hormone release by stimulating somatostatin discharge. Endocrinology 126: 2296–2301.
Lucas A 1994 Role of nutritional programming in determining adult morbidity. Arch Dis Child 71: 288–290.
Widdowson EM, McCance RA 1974 The determinants of growth and form. Proc R Soc Lond 185: 1–17.
Engelbregt MJT, Houdijk ECAM, Popp-Snijders C, Delemarre-van de Waal HA 1997 Persistent growth impairment despite normal growth hormone secretion and normal serum IGF-I levels in male and female intra-uterine growth retarded rats. Horm Res 48: Abstr 277
Edén S 1979 Age- and sex-related differences in episodic growth hormone secretion in the rat. Endocrinology 105: 555–560.
Tonshof B, Mehls O 1996 Interaction between glucocorticoids and the somatotrophic axis. Acta Paediatr Suppl 417: 72–75.
Ramos S, Goya L, Alvarez C, Pascual-Leone AM 1998 Mechanism of hypothyroidism action on insulin-like growth factor-I and -II from neonatal to adult rats: insulin mediates thyroid hormone effects in the neonatal period. Endocrinology 139: 4782–4792.
Patel YC, Srikant CB 1986 Somatostatin mediation of adenohypophysial secretion. Annu Rev Physiol 48: 551–567.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge Dr. C. Popp-Snijders and her staff for measurement of the IGF-I.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by Ferring, The Netherlands.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huizinga, C., Oudejans, C., Steiner, R. et al. Effects of Intrauterine and Early Postnatal Growth Restriction on Hypothalamic Somatostatin Gene Expression in the Rat. Pediatr Res 48, 815–820 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-200012000-00019
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-200012000-00019