Abstract
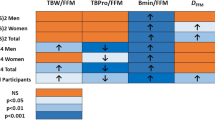
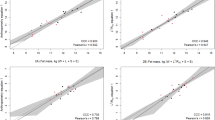
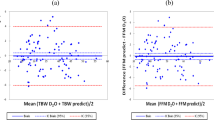
Normative body composition during the first 2 y of life was derived from a prospective study of 76 children. We present 1) fat free mass (FFM) and its components, and fat mass (FM), 2) incremental growth rates partitioned into chemical components, and 3) age-specific and gender-specific constants for converting chemical and physical components into FFM for children during the first 2 y of life. A multicomponent model based on measurements of total body water (TBW), total body potassium (TBK) and bone mineral content (BMC) was used to estimate FFM and FM at 0.5, 3, 6, 9, 12, 18, and 24 mo of age. TBW was determined by deuterium dilution, TBK by whole body counting, and BMC by dual energy x-ray absorptiometry. FFM was higher in boys than girls between 0.5–18 mo of age (p ≤ 0.05). Percent FM increased on average from 13 to 31% between 0.5 and 3–6 mo, and then gradually declined. Percent FM was significantly higher in girls than in boys at 6 and 9 mo of age (p ≤ 0.02). The components of FFM on a percentage basis changed with age (p = 0.001), but not gender. The protein content of FFM increased gradually with age, while TBW declined (p = 0.001). As a percentage of FFM, osseous mineral increased from 2.0 to 3.4% in boys and from 2.1 to 3.3% in girls between 0.5 and 24 mo (p = 0.001). Density and potassium content of FFM increased gradually with age (p = 0.001). These normative body composition data provide an updated reference upon which to assess normal growth and nutritional status of pediatric populations representative of mixed feeding groups during the first 2 y of life.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- FFM:
-
fat free mass
- FM:
-
fat mass
- %FM:
-
percent fat mass
- TBW:
-
total body water
- TBK:
-
total body potassium
- TOBEC:
-
total body electrical conductivity
- DXA:
-
dual energy x-ray absorptiometry
- BMC:
-
bone mineral content
- ECW:
-
extracellular water
- ICW:
-
intracellular water
References
Fomon SJ, Haschke F, Ziegler EE, Nelson SE 1982 Body composition of reference children from birth to age 10 years. Am J Clin Nutr 35: 1169–1175.
Butte NF, Heinz C, Hopkinson JM, Wong WW, Shypailo R, Ellis KJ 1999 Fat mass in infants and toddlers: comparability of total body water, total body potassium, total body electrical conductivity and dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 29: 184–189.
Wang ZM, Heshka S, Pierson RN, Heymsfield SB 1995 Systematic organization of body-composition methodology: an overview with emphasis on component-based methods. Am J Clin Nutr 61: 457–465.
Wong WW, Lee LS, Klein PD 1987 Deuterium and oxygen-18 measurements on microliter samples of urine, plasma, saliva, and human milk. Am J Clin Nutr 45: 905–913.
Wong WW, Cochran WJ, Klish WJ, Smith EO, Lee LS, Klein PD 1988 In vivo isotope-fractionation factors and the measurement of deuterium- and oxygen-18-dilution spaces from plasma, urine, saliva, respiratory water vapor, and carbon dioxide. Am J Clin Nutr 47: 1–6.
Ellis KJ, Shypailo RJ 1993 Whole-body potassium measurements independent of body size. In: Human Body Composition: In Vivo Methods, Models, and Assessment. Plenum Press, New York, 371–375.
Ellis KJ, Shypailo RJ, Pratt JA, Pond WG 1994 Accuracy of dual energy x-ray absorptiometry for body composition measurements in children. Am J Clin Nutr 60: 660–665.
Heymsfield SB, Wang ZM, Withers RT 1996 Multicomponent molecular level models of body composition analysis. In: Roche AF, Heymsfield SB, Lohman TG (eds) Human Body Composition. Human Kinetics, Champaign, 129–148.
Schoeller DA 1996 Hydrometry. In: Roche AF, Heymsfield SB, Lohman TG (eds) Human Body Composition. Human Kinetics, Champaign, 25–44.
Salazar G, Infante C, Vio F 1994 Deuterium equilibration time in infant's body water. Eur J Clin Nutr 48: 475–481.
Trowbridge FL, Graham GG, Wong WW, Mellits ED, Rabold JD, Lee LS, Cabrera MP, Klein PD 1984 Body water measurements in premature and older infants using H218O isotopic determinations. Pediatr Res 18: 524–527.
Romahn A, Burmeister W 1977 Die Körperzusammensetzung während der ersten zwei Lebensjahre Bestimmungen mit der Kalium-40-Methode. Klin Pädiat 189: 321–327.
Forbes GB 1962 Methods for determining composition of the human body. Pediatrics 29: 477
Christiansen C, Rödbro P, Thöger NC 1975 Bone mineral content and estimated total body calcium in normal children and adolescents. Scand J Clin Lab 35: 507–510.
Christiansen C, Rödbro P 1975 Estimation of total body calcium from the bone mineral content of the forearm. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 35: 425–431.
McGowan A, Jordan M, MacGregor J 1975 Skinfold thickness in neonates. Biol Neonate 25: 66–84.
Karlberg P, Taranger J 1976 The somatic development of children in a Swedish urban community. Acta Paediatr Scand Suppl 258: 1–148.
de Bruin NC, van Velthoven KAM, de Ridder M, Stijnen T, Juttmann RE, Degenhart HJ, Visser HKA 1996 Standards for total body fat and fat-free mass in infants. Arch Dis Child 74: 386–399.
Forbes GB 1987 Human Body Composition. Growth, Aging, Nutrition, and Activity. Springer-Verlag, New York, 1–350.
Ziegler EE, O'Donnell AM, Nelson SE, Fomon SJ 1976 Body composition of the reference fetus. Growth 40: 329–341.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work is a publication of the US Department of Agriculture/Agricultural Research Service (USDA/ARS) Children's Nutrition Research Center, Department of Pediatrics, Baylor College of Medicine and Texas Children's Hospital, Houston, Texas.
This project was funded in part with federal funds from the USDA/ARS under Cooperative Agreement 58–6250-6001.
The contents of this publication do not necessarily reflect the views or policies of the USDA, nor does mention of trade names, commercial products, or organizations imply endorsement by the US Government.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Butte, N., Hopkinson, J., Wong, W. et al. Body Composition during the First 2 Years of Life: An Updated Reference. Pediatr Res 47, 578–585 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-200005000-00004
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-200005000-00004
This article is cited by
-
Infant growth and body composition from birth to 24 months: are infants developing the same?
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2024)
-
Adiposity and feeding practices in the first two years of life among toddlers in Guadalajara, Mexico
BMC Pediatrics (2023)
-
Body composition from birth to 2 years
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2023)
-
Differential associations between body composition indices and neurodevelopment during early life in term-born infants: findings from the Pakistan cohort: Multi-Center Body Composition Reference Study
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2023)
-
Body composition of infants at 6 months of age using a 3-compartment model
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2023)