Abstract
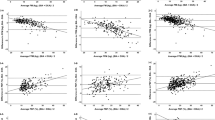
The purpose of this study was to determine the ability of air displacement plethysmography (ADP) to estimate body fatness in prepubertal and early pubertal African American and white children. One hundred nineteen nonoverweight and overweight boys (N = 56) and girls (N = 63), age (mean ± SD) 9.8 ± 1.7 y, body mass index 25.9 ± 7.6 kg/m2 (range, 14.2–47.0 kg/m2), and mean percent body fat (%BF) by dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) 39.2 ± 11.7% (range, 12.2–57.5%), were studied. %BF by ADP was compared with DXA %BF estimates and with body fat by several field methods: skinfold thicknesses using the Slaughter et al. equations (Hum Biol 60: 709–723, 1988), bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) using the Houtkooper et al. equation (J Appl Physiol 72: 366–373, 1992), and a predictive equation using skinfold thicknesses, BIA, and weight (Goran et al.: Am J Clin Nutr 63: 299–305, 1996). All methods used to estimate %BF were significantly correlated with DXA (all p < 0.0001), with r2 ranging from 0.85 (skinfold measurements) to 0.95 (ADP). ADP using the Siri equation underestimated %BF by −1.9% (p < 0.001); the Bland-Altman limits of agreement (defined as ±2 SD) were ±7.4%. %BF by ADP-Siri underestimated %BF by DXA by 3.0% for girls (p < 0.001) and by 0.6% for boys (NS). Agreement between body fat estimation by ADP and DXA did not vary with age, race, or pubertal stage. Application of the age-adjusted Lohman model to ADP significantly increased the magnitude of the underestimation to −6.9% (p < 0.0001). Prediction of %BF by the Slaughter skinfold thickness equation showed no significant mean bias for the overall data, but significantly underestimated %BF in girls (−3.7%) while overestimating %BF in boys (+2.4%) with wide limits of agreement (±17.7%, p < 0.01 versus ADP). %BF by the Houtkooper BIA equation or Goran model underestimated %BF to a significantly greater degree than ADP (Houtkooper, −8.1%; Goran, −10.1%; both p < 0.0001 versus DXA or ADP). Determination of %BF from ADP using the Siri model slightly underestimates %BF as determined by DXA in girls, but appears to be superior to existing field methods both in accuracy and limits of agreement. Because of the ease with which it can be performed, ADP may prove useful for investigations of adiposity in children.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- DXA:
-
dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry
- ADP:
-
air displacement plethysmography
- BIA:
-
bioelectrical impedance analysis
- BF:
-
percent body fat
- VTG:
-
thoracic gas volume
- FFM:
-
fat-free mass
References
Troiano RP, Flegal KM 1998 Overweight children and adolescents: description, epidemiology, and demographics. Pediatrics 101: 497–504
[No authors listed] 1997 Update: prevalence of overweight among children, adolescents, and adults—United States, 1988–1994. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 46: 198–202
Freedman DS, Srinivasan SR, Valdez RA, Williamson DF, Berenson GS 1997 Secular increases in relative weight and adiposity among children over two decades: the Bogalusa Heart Study. Pediatrics 99: 420–426
Roche AF 1993 Methodological considerations in the assessment of childhood obesity. Ann NY Acad Sci 699: 6–17
Van den Broeck J, Wit JM 1997 Anthropometry and body composition in children. Horm Res 48: 33–42
Lohman TG, Harris M, Teixeira PJ, Weiss L 2000 Assessing body composition and changes in body composition. Another look at dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry. Ann NY Acad Sci 904: 45–54
Dempster P, Aitkens S 1995 A new air displacement method for the determination of human body composition. Med Sci Sports Exerc 27: 1692–1697
McCrory MA, Gomez TD, Bernauer EM, Mole PA 1995 Evaluation of a new air displacement plethysmograph for measuring human body composition. Med Sci Sports Exerc 27: 1686–1691
Levenhagen DK, Borel MJ, Welch DC, Piasecki JH, Piasecki DP, Chen KY, Flakoll PJ 1999 A comparison of air displacement plethysmography with three other techniques to determine body fat in healthy adults. J Parenter Enteral Nutr 23: 293–299
Dewit O, Fuller NJ, Fewtrell MS, Elia M, Wells JC 2000 Whole body air displacement plethysmography compared with hydrodensitometry for body composition analysis. Arch Dis Child 82: 159–164
Nunez C, Kovera AJ, Pietrobelli A, Heshka S, Horlick M, Kehayias JJ, Wang Z, Heymsfield SB 1999 Body composition in children and adults by air displacement plethysmography. Eur J Clin Nutr 53: 382–387
Lockner DW, Heyward VH, Baumgartner RN, Jenkins KA 2000 Comparison of air-displacement plethysmography, hydrodensitometry, and dual x-ray absorptiometry for assessing body composition of children 10 to 18 years of age. Ann NY Acad Sci 904: 72–78
Yanovski JA, Yanovski SZ, Filmer KM, Hubbard VS, Avila N, Lewis B, Reynolds JC, Flood M 1996 Differences in body composition of black and white girls. Am J Clin Nutr 64: 833–839
[No authors listed] 1992 Obesity and cardiovascular disease risk factors in black and white girls: the NHLBI Growth and Health Study. Am J Public Health 82: 1613–1620
Morrison JA, Barton B, Biro FM, Sprecher DL, Falkner F, Obarzanek E 1994 Sexual maturation and obesity in 9- and 10-year-old black and white girls: the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Growth and Health Study. J Pediatr 124: 889–895
Meuller EH 1987 Ethnic differences in fat distribution during growth. In: Bouchard C, Johnston FE (eds) Fat Distribution During Growth and Later Health Outcomes. Alan R. Liss, New York, pp 127–145
Goran MI, Driscoll P, Johnson R, Nagy TR, Hunter G 1996 Cross-calibration of body-composition techniques against dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry in young children. Am J Clin Nutr 63: 299–305
Must A, Dallal GE, Dietz WH 1991 Reference data for obesity: 85th and 95th percentiles of body mass index (wt/ht2) and triceps skinfold thickness [published erratum appears in Am J Clin Nutr 1991;54:773]. Am J Clin Nutr 53: 839–846
Siri WE 1961 Body composition from fluid spaces and density: analysis of methods. In: Brozek J, Henschel A (eds) Techniques for Measuring Body Composition. National Academy of Sciences/National Research Council, Washington, DC, pp 223–224
Boileau RA, Lohman TG, Slaughter MH, Ball TE, Going SB, Hendrix MK 1984 Hydration of the fat-free body in children during maturation. Hum Biol 56: 651–666
Hewitt MJ, Going SB, Williams DP, Lohman TG 1993 Hydration of the fat-free body mass in children and adults: implication for body composition assessment. Am J Physiol 265: E88–E95
Lohman TG 1986 Applicability of body composition techniques and constants for children and youths. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 14: 325–357
Lohman TG 1989 Assessment of body composition in children. Pediatr Exerc Sci 1: 19–30
Figueroa-Colon R, Mayo MS, Treuth MS, Aldridge RA, Weinsier RL 1998 Reproducibility of dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry measurements in prepubertal girls. Obes Res 6: 262–267
Pintauro SJ, Nagy TR, Duthie CM, Goran MI 1996 Cross-calibration of fat and lean measurements by dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry to pig carcass analysis in the pediatric body weight range. Am J Clin Nutr 63: 293–298
Brunton JA, Bayley HS, Atkinson SA 1993 Validation and application of dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry to measure bone mass and body composition in small infants. Am J Clin Nutr 58: 839–845
Ellis KJ, Shypailo RJ, Pratt JA, Pond WG 1994 Accuracy of dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry for body-composition measurements in children. Am J Clin Nutr 60: 660–665
Chan GM 1992 Performance of dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry in evaluating bone, lean body mass, and fat in pediatric subjects. J Bone Miner Res 7: 369–374
Hicks VL, Heyward VH, Baumgartner RN, Flores AJ, Stolarczyk LM, Wotruba EA 1993 Body composition of Native-American women estimated by dual-energy x- ray absorptiometry and hydrodensitometry. Basic Life Sci 60: 89–92
Lohman TG, Roche AF, Martorel R (eds) 1988 Anthropometric Standardization Manual Human Kinetics, Champaign, IL
Slaughter MH, Lohman TG, Boileau RA, Horswill CA, Stillman RJ, Van Loan MD, Bemben DA 1988 Skinfold equations for estimation of body fatness in children and youth. Hum Biol 60: 709–723
Houtkooper LB, Going SB, Lohman TG, Roche AF, Van Loan M 1992 Bioelectrical impedance estimation of fat-free body mass in children and youth: a cross-validation study. J Appl Physiol 72: 366–373
Bland J, Altman D 1986 Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1: 307–310
Fields D, Goran M 2000 Body composition techniques and the four-compartment model in children. J Appl Physiol 89: 613–620
Fields DA, Hunter GR, Goran MI 2000 Validation of the BOD POD with hydrostatic weighing: influence of body clothing. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 24: 200–205
McCrory MA, Mole PA, Gomez TD, Dewey KG, Bernauer EM 1998 Body composition by air-displacement plethysmography by using predicted and measured thoracic gas volumes. J Appl Physiol 84: 1475–1479
Roemmich JN, Clark PA, Weltman A, Rogol AD 1997 Alterations in growth and body composition during puberty. I. Comparing multicompartment body composition models. J Appl Physiol 83: 927–935
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by Z-01-HD-04-00641 (J.A.Y.) and the Office of Research on Minority Health.J. Yanovski, M. Michael, and N. Sebring are Commissioned Officers in the United States Public Health Service.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nicholson, J., McDuffie, J., Bonat, S. et al. Estimation of Body Fatness by Air Displacement Plethysmography in African American and White Children. Pediatr Res 50, 467–473 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-200110000-00008
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-200110000-00008
This article is cited by
-
Analysis of variants and mutations in the human winged helix FOXA3 gene and associations with metabolic traits
International Journal of Obesity (2015)
-
Serum leptin and loss of control eating in children and adolescents
International Journal of Obesity (2014)
-
Air-displacement plethysmography for the measurement of body composition in children aged 6–48 months
Pediatric Research (2012)
-
Physical Activity Intensity and Risk of Overweight and Adiposity in Children
Obesity (2008)
-
Validity of new child-specific thoracic gas volume prediction equations for air-displacement plethysmography
BMC Pediatrics (2006)