Abstract
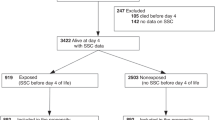
The relationship between skin color and illness severity in the newborn remains untested. We have evaluated the predictive value of skin color readings for illness severity in a population of high-risk newborn infants. A prospective study was conducted on 107 white newborns in the intensive care unit, which were categorized as either high or low severity of illness, defined by the presence of severe neonatal morbidity. Illness severity was also determined using a Score for Neonatal Acute Physiology (SNAP). Color readings were obtained at 10 different body sites using a portable tristimulus colorimeter during the first 24 h, and color was expressed using the standard CIE L*a*b* system. Skin CIE b* values were significantly lower in the high severity group (p < 0.0001), and a significant inverse correlation with SNAP was observed (rs range, −0.37 to −0.71, p < 0.0001). In particular a low b* value for the abdomen was found to be a significant predictor of illness severity (92.6% sensitivity; 96.6% specificity; 96% positive predictive value; 93.7% negative predictive value; adjusted odds ratio, 14.7; 95% confidence interval, 6.4 to 33.8). Our findings indicate that skin color reflects clinical severity in the newborn and that skin colorimetry can accurately identify higher risk infants.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- SNAP:
-
Score for Neonatal Acute Physiology
- CIE:
-
Commission Internationale de L'Eclairage
- NICU:
-
Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
- ROC:
-
Receiver-Operating Characteristic
References
Wiswell TE 1996 Examination of the critically ill neonate. In: Spitzer AR (ed) Intensive Care of the Fetus and Neonate. CV Mosby, St. Louis, pp 337–344
Rubaltelli FF, Gourley GR, Loskamp N, Modi N, Roth-Kleiner M, Sender A, Vert P 2001 Transcutaneous bilirubin measurement: a multicenter evaluation of a new device. Pediatrics 107: 1264–1271
Apgar V 1953 Proposal for a new method of evaluation of the newborn infant. Anesth Analg 32: 260–267
Spector SA, Ticknor W, Grossman BS 1981 Study of the usefulness of clinical and hematologic findings in the diagnosis of neonatal bacterial infections. Clin Pediatr 20: 385–392
Ramenofsky ML 1993 Early assessment and management of trauma. In: Ashcraft KW, Holder TM (eds) Pediatric Surgery, 2nd Ed. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 110–121
Van Cleve L, Johnson L, Andrews S, Hawkins S, Newbold J 1995 Pain responses of hospitalized neonates to venipuncture. Neonatal Network 14: 31–36
Garner JS, Jarvis WR, Emori TG, Horan TC, Hughes JM 1988 CDC definitions for nosocomial infections. Am J Infect Control 16: 128–140
Moro ML, De Toni A, Stolfi I, Carrieri MP, Braga M, Zunin C 1996 Risk factors for nosocomial sepsis in newborn intensive and intermediate care units. Eur J Pediatr 155: 315–322
Bancalari E, Abdenour GE, Feller R, Gannon J 1979 Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: clinical presentation. J Pediatr 95: 819–823
Kliegman RM, Fanaroff AA 1984 The necrotizing enterocolitis. N Engl J Med 310: 1093–1103
[No authors listed] 1984 An international classification of retinopathy of prematurity. The Committee for the Classification of Retinopathy of Prematurity. Arch Ophthalmol 102: 1130–1134
De Felice C, Toti P, Laurini RN, Stumpo M, Picciolini E, Todros T, Tanganelli P, Buonocore G, Bracci R 2001 Early neonatal brain damage in histologic chorioamnionitis. J Pediatr 138: 101–104
Richardson DK, Gray JE, McCormick MC, Workman K, Goldmann DA 1993 Score for neonatal acute physiology: a physiologic severity index for neonatal intensive care. Pediatrics 91: 617–623
Gray JE, Richardson DK, McCormick MC, Workman-Daniels K, Goldmann DA 1992 Neonatal Therapeutic Intervention Scoring System, a therapy-based severity-of-illness index. Pediatrics 90: 561–567
Zollinger H 1999 Colorimetry. In: Zollinger H (ed) Color: A Multidisciplinary Approach. Verlag Helvetica Chimica Acta, Zurich, pp 63–78
Robertson AR 1977 The CIE 1976 color-difference formulae. Color Res Appl 2: 7–11
Zweig MH, Campbell G 1993 Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) plots: a fundamental evaluation tool in clinical medicine. Clin Chem 39: 561–577
Hosmer DW, Lemeshow S 1989 Applied Logistic Regression. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Takiwaki H, Overgaard L, Serup J 1994 Comparison of narrow-band reflectance spectrophotometric and tristimulus colorimetric measurements of skin color: twenty-three anatomical sites evaluated by the Dermaspectrometer and the Chroma Meter CR-200. Skin Pharmacol 7: 217–225
Rubegni P, Cevenini G, Flori ML, Fimiani M, Stanghellini E, Molinu A, Barbini P, Andreassi L 1997 Relationship between skin color and sun exposure history: a statistical classification approach. Photochem Photobiol 65: 347–351
Walsh RJ 1964 Variation in the melanin content of the skin of New Guinea natives at different ages. J Invest Dermatol 42: 261–265
Ballowitz L, Avery ME 1970 Reflectance of the skin. Studies on infant and adult humans, Wistar and Gunn rats. Biol Neonate 15: 348–360
Post PW, Krauss AN, Waldman S, Auld PAM 1976 Skin reflectance of newborn infants from, 25 to 44 weeks gestational age. Hum Biol 48: 541–557
Grande R, Gutierrez E, Latorre E, Argueles F 1994 Physiological variations in the pigmentation of newborn infants. Hum Biol 66: 495–507
Horbar JD, Onstad L, Wright E 1993 Predicting, mortality risk for infants weighing 501 to, 1500 grams at birth: a National Institutes of Health Neonatal Research Network report. Crit Care Med 21: 12–18
[No authors listed] 1995 CRIB (clinical risk index for babies), mortality, and impairment after neonatal intensive care. Scottish Neonatal Consultants' Collaborative Study Group and the International Neonatal Network. Lancet 345: 1020–1022
Richardson DK, Phibbs CS, Gray JE, McCormick MC, Workman-Daniels K, Goldmann DA 1993 Birth weight and illness severity: independent predictors of neonatal mortality. Pediatrics 91: 969–975
Karesen PI, Dohlen G, Fundingsrud HP, Dahl LB 1998 The use of CRIB (clinical risk index for babies) score in auditing the performance of one neonatal intensive care unit. Acta Paediatr 87: 195–200
Bührer C, Grimmer I, Metze B, Obladen M 2000 The CRIB (Clinical Risk Index for Babies) score and neurodevelopmental impairment at one year corrected age in very low birth weight infants. Intensive Care Med 26: 325–329
Richardson DK, Corcoran JD, Escobar GJ, Kee SK 2001 for the Canadian NICU Network, the Kaiser Permanente Neonatal Minimum Data Set Wide Area Network, and the SNAP-II Study Group, SNAP-II and SNAPPE-II: simplified newborn illness severity and mortality risk scores. J Pediatr 138: 92–100
Zipursky A 2000 Erythropoietin therapy for premature infants: cost without benefit?. Pediatr Res 48: 136
Ruda MA, Ling Q-D, Hohmann AG, Peng YB, Tachibana T 2000 Altered nociceptive neuronal circuits after neonatal peripheral inflammation. Science 289: 628–630
Kopola H, Lahti A, Myllylä RA, Hannuksela M 1993 Two-channel fiber optic skin erythema meter. Opt Eng 32: 222–226
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Katie Henry (editorial assistance); Laura Bianciardi (online research); Alessandra Lombardi and Chiara Ginanneschi (data collection); Dr. Gordon B. Avery, Dr. Maurizio Costantini, and Dr. Giuseppe Latini (critical reading of the manuscript), Dr. Eduardo Bancalari (helpful discussion), and Prof. Enzo Ballatori and Dr. Luigi Ferrante (statistical advice), as well as the medical and nursing staff of the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit, Azienda Ospedaliera Senese, for their kind collaboration during the course of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported in part by a grant from the Italian Ministry of Education MURST (funding for research of National Interest).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Felice, C., Flori, M., Pellegrino, M. et al. Predictive Value of Skin Color for Illness Severity in the High-Risk Newborn. Pediatr Res 51, 100–105 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-200201000-00018
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-200201000-00018
This article is cited by
-
Foot Pulse Oximeter Perfusion Index Correlates with Calf Muscle Perfusion Measured by Near-Infrared Spectroscopy in Healthy Neonates
Journal of Perinatology (2005)
-
The pulse oximeter perfusion index as a predictor for high illness severity in neonates
European Journal of Pediatrics (2002)