Abstract
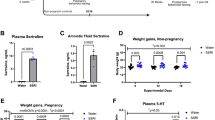
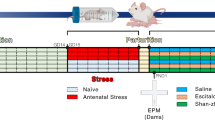
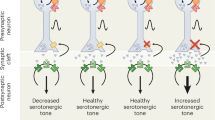
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and benzodiazepines are frequently used to treat maternal depression during pregnancy, however the effect of increased serotonin (5HT) and γ-amino-butyric acid (GABA) agonists in the fetal human brain remains unknown. 5HT and GABA are active during fetal neurologic growth and play early roles in pain modulation, therefore, if prolonged prenatal exposure alters neurodevelopment this may become evident in altered neonatal pain responses. To examine biologic and behavioral effects of prenatal exposure, neonatal responses to acute pain (phenylketonuria heel lance) in infants with prolonged prenatal exposure were examined. Facial action (Neonatal Facial Coding System) and cardiac autonomic reactivity derived from the relationship between respiratory activity and short term variations of heart rate (HRV) were compared between 22 infants with SSRI exposure (SE) [fluoxetine (n = 7), paroxetine (n = 11), sertraline (n = 4)]; 16 infants exposed to SSRIs and clonazepam (SE+) [paroxetine (n = 14), fluoxetine (n = 2)]; and 23 nonexposed infants during baseline, lance, and recovery periods of a heel lance. Length of maternal SSRI use did not vary significantly between exposure groups—[mean (range)] SE:SE+ 183 (31–281):141 (54–282) d (p > 0.05). Infants exposed to SE and SE+ displayed significantly less facial activity to heel lance than control infants. Mean HR increased with lance, but was significantly lower in SE infants during recovery. Using measures of HRV and the transfer relationship between heart rate and respiration, SSRI infants had a greater return of parasympathetic cardiac modulation in the recovery period, whereas a sustained sympathetic response continued in the control group. Prolonged prenatal SSRI exposure appears to be associated with reduced behavioral pain responses and increased parasympathetic cardiac modulation in recovery following an acute neonatal noxious event. Possible 5HT-mediated pain inhibition, pharmacologic factors and the developmental course remain to be studied.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- 5HT:
-
5 hydroxytryptamine (serotonin),
- BZ:
-
benzodiazepine
- C:
-
control (nonexposed) infants
- DA:
-
dopamine
- GABA:
-
γ-amino-butyric acid
- HFP:
-
high-frequency power
- HRV:
-
heart rate variability
- LFP:
-
low-frequency power
- NE:
-
norepinephrine
- NFCS:
-
Neonatal Facial Coding System
- NICU:
-
neonatal intensive care unit
- PKU:
-
phenylketonuria
- RP:
-
respiratory power
- RSA:
-
respiratory sinus arrhythmia
- SE:
-
SSRI-exposed infants
- SE+:
-
SSRI- and BZ-exposed infants
- SSRI:
-
selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
References
Altshuler LL, Cohen L, Szuba MP, Burt VK, Gitlin M, Mintz J 1996 Pharmacolgic management of psychiatric illness during pregnancy: dilemmas and guidelines. Am J Psychiatry 153: 529–606
Whitaker-Azmitia PM, Druse M, Walker P, Lauder JM 1996 Serotonin as a developmental signal. Behav Brain Res 73: 19–29
Lauer JA, Adams PM, Johnson KM 1987 Perinatal diazepam exposure: behavioral and neurochemical consequences. Neurotoxicol Teratol 9: 213–219
Huether G, Thomke F, Adler L 1992 Administration of tryptophan-enriched diets to pregnant rats retards the development of the serotonergic system in their offspring. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 68: 175–181
Lauder JM 1993 Neurotransmitters as growth regulatory signals: role of receptors and second messengers. Trends Neurosci 16: 233–240
De Pasqual E, Monteau R, Hilaire G 1994 Endogenous serotonin modulates the fetal respiratory rhythm: an in vitro study in the rat. Dev Brain Res 80: 222–232
Smith D, Gallager D 1987 GABA, benzodiazepine and serotonergic receptor development in the dorsal raphe nucleus: electrophysiological studies. Dev Brain Res 35: 191–198
Lauder JM, Han VK, Henderson P, Verdoorn T, Towle AC 1986 Prenatal ontogeny of the GABAergic system in the rat brain. Neuroscience 19: 36–38
Kellogg CK 1995 Perinatal benzodiazepine modulation of GABAA receptor function: influence on adaptive responses. NIDA Res Monogr 158: 202–226
Lauder JM 1995 Ontogeny of neurotransmitter systems: substrates for developmental disabilities?. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev 1: 151–168
Fitzgerald M 1995 Pain in infancy: some unanswered questions. Pain Rev 2: 77–91
Fitzgerald M 1997 Neonatal pharmacology of pain. In: Dickenson AH, Besson J-MR, Appleton I (eds) The Pharmacology of Pain. Springer, New York
Waagepetersen HS, Sonnewald U, Schousboe A 1999 The GABA paradox: multiple roles as metabolite, neurotransmitter, and neurodifferentiative agent. J Neurochem 73: 1335–1342
Gaiarsa JL, McLean H, Congar P, Leinekugel X, Khazipov R, Tseeb V, Ben-Ari Y 1995 Postnatal maturation of gamma-aminobutyric acid A and B-mediated inhibition in the CA3 hippocampal region of the rat. J Neurobiol 26: 339–349
Vorhees CV, Acuff-Smith KD, Schilling MA, Fisher JE, Moran MS, Buelke-Sam J 1994 A developmental neurotoxicity evaluation of the effects of prenatal exposure to fluoxetine in rats. Fundam Appl Toxicol 23: 194–205
De Ceballos ML, Benedi A, Urdin C, Del Rio J 1985 Prenatal exposure of rats to antidepressant drugs down-regulates beta-adrenoceptors and 5-HT2 receptors in cerebral cortex: lack of correlation between 5-HT2 receptors and serotonin-mediated behaviour. Neuropharmacology 24: 947–952
Montero D, De Ceballos ML, Del Rio J 1990 Down-regulation of 3H-imipramine binding sites in rat cerebral cortex after prenatal exposure to antidepressants. Life Sci 46: 1619–1626
Cabrera TM, Battaglia G 1994 Delayed Decreases in brain 5-hydroxytryptamine 2A/2C receptor density and function in male rat progeny following prenatal fluoxetine. J Pharma Experi Therapeutics 269: 637–645
Pastuszak A, Schick-Boschetto B, Zuber C, Feldkamp M, Pinelli M, Sihn S, Donnenfeld A, McCormack M, Leen-Mitchell M, Woodland C et al 1993 Pregnancy outcome following first-trimester exposure to fluoxetine (Prozac). JAMA 269: 2246–2248
Goldstein DJ 1991 Fluoxetine-exposed pregnancies. Clin Res 39: 768A
Vendittelli F, Alain J, Nouaille Y, Brosset A, Tabaste JL 1995 A case of lipomeningocele with fluoxetine (and alprazolam, vitamins B1 and B6, heptaminol) prescribed during pregnancy. Eur J Obstet Gynecol 58: 85–86
Stanford MS, Patton JH 1992 In utero exposure to fluoxetine HCI increases hematoma frequency at birth. Pharmacol Biochem 45: 959–962
Nulman I, Rovet J, Stewart DE, Wolpin J, Gardner HA, Theis JG, Kulin N, Koren G 1997 Neurodevelopment of children exposed in uteroto antidepressant drugs. N Engl J Med 336: 258–262
Koren G, Nulman I, Addis A 1998 Outcome of children exposed in utero to fluoxetine: a critical review. Depress Anxiety 8: 827–31
Kulin NA, Pastuszak A, Koren G 1998 Are the new SSRIs safe for pregnant women?. Can Fam Physician 44: 2081–2083
Spencer MJ 1993 Fluoxetine hydrochloride (Prozac) toxicity in a neonate. Pediatrics 92: 721–722
Lester BM, Cucca J, Andreozzi L, Flanagan P, Oh W 1993 Possible association between fluoxetine hydrochloride and colic in an infant. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 32: 1253–1255
Nordeng H, Lindemann R, Perminov KV, Reikvam A 2001 Neonatal withdrawal syndrome after in utero exposure to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Acta Paediatr 90: 288–291
Cohen LS, Heller VL, Bailey JW, Grush L, Ablon JS, Bouffard SM 2000 Birth outcomes following prenatal exposure to fluoxetine. Biol Psychiatry 48: 996–1000
Chambers CD, Johnson KA, Dick LM, Felix RJ, Jones KL 1996 Birth outcomes in pregnant women taking fluoxetine. N Engl J Med 335: 1010–1015
Prechtl HF 1974 The behavioral states of the newborn infant (a review). Brain Res 76: 185–212
Grunau RE, Craig KD 1987 Pain expression in neonates: facial action and cry. Pain 28: 395–410
Grunau RVE, Johnston CC, Craig KD 1990 Neonatal facial and cry responses to invasive and non-invasive procedures. Pain 42: 295–305
Craig KD, Whitfield MF, Grunau RV, Linton J, Hadjistavropoulos HD 1993 Pain in the preterm neonate: behavioural and physiological indices. Pain 52: 287–299
Grunau RVE, Oberlander TF, Holsti L, Whitfield MF 1998 Bedside application of the Neonatal Facial Coding System in pain assessment of premature neonates. Pain 76: 277–286
Lilley CM, Craig KD, Grunau RE 1997 The expression of pain in infants and toddlers: developmental changes in facial action. Pain 72: 161–170
Saul JP, Berger RD, Albrecht P, Stein SP, Chen MH, Cohen RJ 1991 Transfer function analysis of the circulation: unique insights into cardiovascular regulation. Am J Physiol 261: H1231–H1245
Fox NA, Porges SW 1985 The relation between neonatal heart period patterns and developmental outcome. Child Dev 59: 28–37
Porter FL, Porges SW, Marshall RE 1988 Newborn pain cries and vagal tone: parallel changes in response to circumcision. Child Dev 59: 495–505
Litvack DA, Oberlander TF, Carney LH, Saul JP 1995 Time and frequency domain methods for heart rate variability analysis: a methodological comparison. Psychophysiology 32: 492–504
Oberlander TF, Berde CB, Lam KH, Rappaport LA, Saul JP 1995 Infants tolerate spinal anesthesia with minimal overall autonomic changes: transfer function analysis of respiratory sinus arrhythmia in former premature infants undergoing hernia repair. Anesth Analg 80: 20–27
Oberlander TF, Berde CB, Lam KH, Saul JP 1996 Halothane causes withdrawal of cardiac sympathetic modulation in infants: transfer function analysis of respiratory sinus arrhythmia. Pediatr Res 40: 710–717
Hanna BD, Saul JP, Cohen RJ, Stark AR 1990 Transfer function analysis of respiratory sinus arrhythmia: developmental changes in sleeping premature infants. Circulation 82 ( suppl III): 334
Oberlander TF, Grunau RE, Whitfield MF, Fitzgerald C, Pitfield S, Saul JP 2000 Biobehavioral pain responses in former extremely low birth weight infants at four months' corrected age. Pediatrics 105: 6e
Brouillette RT, Morrow AS, Weese-Mayer DE, Hunt CE 1987 Comparison of respiratory inductive plethysmography and thoracic impedance for apnea monitoring. J Pediatr 111: 377–383
Berger RD, Akselrod S, Gordon D, Cohen RJ 1986 An efficient algorithm for spectral analysis of heart rate variability. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 33: 900–904
Berger RD, Saul JP, Cohen RJ 1989 Transfer function analysis of autonomic regulation. I. canine atrial rate response. Am J Physiol 256: H142–H152
Kim J, Misri S, Kent N, Oberlander T, Rurak DW, Riggs KW 1999 Comparison of fetal and neonatal fluoxetine and paroxetine exposure during the perinatal period in humans. AAPS PharmSci 1: S96
Hiemke C, Härtter S 2000 Pharmacokinetics of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Pharmacol Ther 85: 11–28
Öhman R, Hägg S, Carleborg L, Spigset O 1999 Excretion of paroxetine into breast milk. J Clin Psychiatry 60: 519–523
Stowe ZN, Owens MJ, Landry JC, Kilts CD, Ely T, Llewellyn A, Nemeroff CB 1998 Sertraline and desmethylsertraline in human breast milk and nursing infants. Am J Psychiatry 155: 1643–1644
Tuddin A, Ito S, Koren G 1996 Excretion of fluoxetine and its metabolite, norfluoxetine, in human breast milk. J Clin Pharmacol 36: 42–47
Neville MC 1999 Physiology of lactation. Clin Perinatol 26: 251–279
Jenness R 1979 The composition of human milk. Semin Perinatol 3: 225–239
Birnbaum CS, Cohen LS, Bailey JW, Grush LR, Robertson LM, Stowe ZN 1999 Serum concentrations of antidepressants and benzodiazepines in nursing infants: a case series. Pediatrics 104: e11
Mayes LC, Grillon C, Granger R, Schottenfeld R 1998 Regulation of arousal and attention in preschool children exposed to cocaine prenatally. Ann N Y Acad Sci 846: 126–143
Cabrea-Vera TM, Battaglia G 1998 Prenatal exposure to fluoxetine (Prozac) produces site-specific and age-dependent alterations in brain serotonin transporters in rat progeny: evidence from autoradiographic studies. J Pharm Exp Therapeutics 286: 1474–1481
Cabrea-Vera TM, Garcia F, Battaglia G 1997 Effect of prenatal fluoxetine (Prozac) exposure on brain serotonin in prepubescent and adult male rat offspring. J Pharm Exp Therapeutics 280: 138–45
Borella A, Bindra M, Whitaker-Azmitia PM 1997 Role of the 5-HT1A receptor in development of the neonatal rat brain: preliminary behavioral studies. Neuropharmacology 36: 445–450
Whitaker-Azmitia PM 1998 Role of the neurotropic properties of serotonin in the delay of brain maturation induced by cocaine. Ann N Y Acad Sci 846: 158–164
Akbari HM, Kramer HK, Whitaker-Azmitia PM, Spear LP, Azmitia EC 1992 Prenatal cocaine exposure disrupts the development of the serotonergic system. Brain Res 572: 57–63
Mayes LC 1999 Developing brain and in utero cocaine exposure: effects on neural ontogeny. Dev Psychopathol 11: 685–714
Roumell N, Wille D, Abramson L, Delaney V 1997 Facial expressivity to acute pain in cocaine exposed toddlers. Infant Mental Health Journal 18: 274–281
Chesley S, Lumpkin M, Schatzki A, Galpern WR, Greenblatt DJ, Shader RI, Miller LG 1991 Prenatal exposure to benzodiazepine–I. Prenatal exposure to lorazepam in mice alters open-field activity and GABAA receptor function. Neuropharmacology 30: 53–58
Livezey GT, Marczynski TJ, Isaac L 1986 Enduring effects of prenatal diazepam on the behavior, EEG, and brain receptors of the adult cat progeny. Neurotoxicology 7: 319–333
Livezey GT, Radulovacki M, Isaac L, Marczynski TJ 1985 Prenatal exposure to diazepam results in enduring reductions in brain receptors and deep slow wave sleep. Brain Res 334: 361–365
Pankaj V, Brain PF 1991 Effects of prenatal exposure to benzodiazepine-related drugs on early development and adult social behaviour in Swiss mice, I: agonists. Gen Pharmacol 22: 33–41
Gai N, Grimm VE 1982 The effect of prenatal exposure to diazepam on aspects of postnatal development and behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology 78: 225–229
Kellogg CK 1988 Benzodiazepines: influence on the developing brain. Prog Brain Res 73: 207–228
Schlumpf M, Parmar R, Schreiber A, Ramseier HR, Butikofer E, Abriel H, Barth M, Rhyner T, Lichtensteiger W 1992 Nervous and immune systems as targets for developmental effects of benzodiazepines. A review of recent studies. Dev Pharmacol Ther 18: 145–158
Inglefield JR, Bitran D, Olschowka JA, Kellogg CK 1993 Selective effects on CRF neurons and catecholamine terminals in two stress-responsive regions of adult rat brain after prenatal exposure to diazepam. Brain Res Bull 31: 353–359
Gillberg C 1977 “Floppy infant syndrome” and maternal diazepam. [letter]. Lancet 2: 244
Besunder JB, Reed MD, Blumer JL 1988 Principles of drug biodisposition in the neonate. A critical evaluation of the pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic interface. Clin Pharmacokinet 14: 261–286
Fisher JB, Edgren BE, Mammel MC, Coleman JM 1985 Neonatal apnea associated with maternal clonazepam therapy: a case report. Obstet Gynecol 66: 34S–35S
Mazzi E 1977 Possible neonatal diazepam withdrawal: a case report. Am J Obstet Gynecol 129: 583–587
Rementeria JL, Bhatt K 1977 Withdrawal symptoms in neonates form intrauterine exposure to diazepam. J Pediatrics 90: 123–126
Whitelaw AGL, Cummings AJ, McFadyen IR 1981 Effect of maternal lorazepam on the neonate. BMJ 282: 1106–1108
Grunau RE 2000 Long-term consequences of pain in human neonates. In: Anand KJS, Stevens BJ, McGrath PJ (eds) Pain in Neonates, 2nd Ed. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam
Dahl RE 1996 The regulation of sleep and arousal. Dev Psychopathol 8: 3–27
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Sandy Pitfield, MSc, MD, who assisted in editing and analysis of the heart rate signals, for his invaluable contribution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by funding from the British Columbia Medical Services Foundation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oberlander, T., Eckstein Grunau, R., Fitzgerald, C. et al. Prolonged Prenatal Psychotropic Medication Exposure Alters Neonatal Acute Pain Response. Pediatr Res 51, 443–453 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-200204000-00008
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-200204000-00008
This article is cited by
-
The development of a patient decision aid to reduce decisional conflict about antidepressant use in pregnancy
BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making (2022)
-
Prenatal Effects of Fluoxetine on Adaptive Behavior and the Cognitive Domain in Male Rats During the Prepubertal Period of Development
Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology (2019)
-
Effect of Fluoxetine in Prenatal Period on Nociceptive System Reactivity and Psychoemotional Behavior in Young Female Rats
Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine (2018)
-
A patient decision aid for antidepressant use in pregnancy: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Trials (2016)
-
Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) for treatment of major depression during pregnancy: study protocol for a pilot randomized controlled trial
Trials (2014)