Abstract
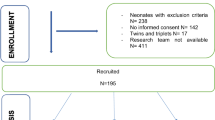
Many attempts have been made to obtain safe and effective analgesia in newborns. Oral glucose-water has been found to have analgesic properties in neonates. We investigated whether other sensory stimulation added to oral glucose provided more effective analgesia than oral glucose alone. In a randomized prospective double-blind trial, we studied 120 term newborns during heel prick. The babies were divided randomly into six groups of 20, and each group was treated with a different procedure during heel prick:A) control;B) 1 mL 33% oral glucose given 2 min before the heel prick;C) sucking;D) 1 mL 33% oral glucose plus sucking;E) multisensory stimulation including 1 mL 33% oral glucose (sensorial saturation);F) multisensory stimulation without oral glucose. Sensorial saturation consisted in massage, voice, eye contact, and perfume smelling during heel prick. Each heel prick was filmed and assigned a point score according to the Douleur Aiguë du Nouveau-né (DAN) neonatal acute pain scale. Camera recording began 30 s before the heel prick, so it was impossible for the scorers to distinguish procedure A (control) from B (glucose given 2 min before), C (sucking water) from D (sucking glucose), and E (multisensory stimulation and glucose) from F (multisensory stimulation and water) from the video. Procedure E (multisensory stimulation and glucose) was found to be the most effective procedure, and the analgesia was even more effective than that produced by procedure D (sucking glucose). We conclude that sensorial saturation is an effective analgesic technique that potentiates the analgesic effect of oral sugar. It can be used for minor painful procedures on newborns.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Anand KJ, Hickey PR 1987 Pain and its effects in the human neonate and fetus. N Engl J Med 317: 1321–1326
Fitzgerald M, Millard C, MacIntosh N 1988 Hyperalgesia in premature infants. Lancet 1: 292
McIntosh N 1997 Pain in the newborn, a possible new starting point. Eur J Pediatr 156: 173–177
Menon G, Anand KJ, McIntosh N 1998 Practical approach to analgesia and sedation in the neonatal intensive care unit. Semin Perinatol 22: 417–424
Anand KJ, Scalzo FM 2000 Can adverse neonatal experiences alter brain development and subsequent behavior?. Biol Neonate 77: 69–82
Richard T 1985 Can a fetus feel pain?. BMJ 291: 1220–1221
Beyer JE, DeGood DE, Ashley LC, Russell GA 1983 Patterns of postoperative analgesic use with adults and children following cardiac surgery. Pain 17: 71–81
Anand KJ 1998 Clinical importance of pain and stress in preterm neonates. Biol Neonate 73: 1–9
Stevens BJ, Johnston CC 1994 Physiological responses of premature infants to a painful stimulus. Nurs Res 43: 226–231
Tsuji M, Saul P, du Plessis A, Eichenwald E, Sobh J, Crocker R, Volpe JJ 2000 Cerebral intravascular oxygenation correlates with mean arterial pressure in critically ill premature infants. Pediatrics 106: 625–632
Canadian Pediatric Society. Fetus and Newborn Committee 2000 Prevention and management of pain and stress in the neonate. Pediatrics 104: 454–458
Spaeth JP, O'Hara IB, Kurth CD 1998 Anesthesia for the micropremie. Semin Perinatol 22: 390–401
Stevens B, Gibbins S, Franck LS 2000 Treatment of pain in the neonatal intensive care unit. Pediatr Clin North Am 47: 633–640
Carbajal R, Simon N 1995 Sédation et analgésie chez l'enfant. Arch Pediatr 2: 1089–1096
Anand KJ 2001 Consensus statement for the prevention and management of pain in the newborn. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 155: 173–180
Suresh S, Anand KJ 1998 Opioid tolerance in neonates: mechanisms, diagnosis, assessment, and management. Semin Perinatol 22: 425–433
Jacqz-Aigrain E, Burtin P 1996 Clinical pharmacokinetics of sedatives in neonates. Clin Pharmacokinet 31: 423–443
Levene M 1995 Pain relief and sedation during neonatal intensive care. Eur J Pediatr 154: S22–S23
Law RMT, Halpern S, Martins RF, Reich H, Innanen V, Ohlsson A 1996 Measurement of methemoglobin after EMLA analgesia for newborn circumcision. Biol Neonate 70: 213–217
Gourrier E, Karoubi P, El Hanache A, Merbouche S, Mouchnino G, Dhabhi S, Leraillez J 1995 Utilisation de la crème EMLA chez le nouveau-né à terme et prématuré. Etude d'efficacité et de tollerance. Arch Pediatr 2: 1041–1046
Lemmen RJ, Semmekrot BA 1996 Muscle rigidity causing life-threatening hypercapnia following fentanyl administration in a premature infant. Eur J Pediatr 155: 1067
Blass EM 1997 Milk-induced hypoalgesia in human newborns. Pediatrics 99: 825–829
Balon-Perin S, Kolanowski J, Berbinschi A, Franchimont P, Ketelslegers JM 1991 The effects of glucose ingestion and fasting on plasma immunoreactive beta-endorphin, adrenocorticotropic hormone, and cortisol in obese subjects. J Endocrinol Invest 14: 919–925
Tropeano G, Lucisano A, Liberale I, Barini A, Vuolo IP, Martino G, Menini E, Dell'Acqua S 1994 Insulin, C-peptide, androgens, and beta-endorphin response to oral glucose in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 78: 305–309
Blass EM, Fitzgerald E 1988 Milk-induced analgesia and comforting in 10-day-old rats: opioid mediation. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 29: 9–13
Shide DJ, Blass EM 1989 Opioidlike effects in intraoral infusions of corn oil and polycose on stress reactions in 10-day-old rats. Behav Neurosci 103: 1168–1175
Blass E, Fitgerald E, Kehoe P 1987 Interactions between sucrose pain and isolation distress. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 26: 483–489
Ramenghi LA, Evans DJ, Levene MI 1999 “Sucrose analgesia”: absorptive mechanism or taste perception?. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 80: F146–F147
Bellieni CV, Buonocore G, Nenci A, Franci N, Cordelli DM, Bagnoli F 2001 Sensorial saturation: an effective analgesic tool for heel-prick in preterm infants. A prospective randomized trial. Biol Neonate 80: 15–18
Prechtl HF, Beintema DJ 1964 The neurological examination of the full term newborn infant. In: Clinics in Developmental Medicine N. 12 Heinemann Ed., London
Carbajal R, Chauvet X, Courdec S, Olivier-Martin M 1999 Randomized trial of analgesic effects of sucrose, glucose, and pacifiers in term neonates. BMJ 319: 1397–1402
Carbajal R, Paupe A, Hoenn E, Lenclen R, Olivier-Martin M 1997 DAN: une échelle comportamentale d'évaluation de la douleur aigue du nouveau-né. Arch Pediatr 4: 623–628
Overgaard C, Knudsen A 1999 Pain relieving effect of sucrose in newborns during heel prick. Biol Neonate 75: 279–284
Bucher HU, Baumgartner R, Bucher N, Seiler M, Fauchère JC 2000 Artificial sweetener reduces nociceptive reaction in term newborn infants. Early Hum Dev 59: 51–60
Ramenghi LA, Griffith GC, Wood CM, Levene MI 1996 Effect of non-sucrose sweet tasting solution on neonatal heel prick responses. Arch Dis Child 74: F129–F131
Skogsdal Y, Eriksson M, Schollin J 1997 Analgesia in newborns given oral glucose. Acta Paediatr 86: 217–220
Haouari N, Wood C, Griffiths G, Levene M 1995 The analgesic effect of sucrose in full term infants: a randomised controlled trial. BMJ 310: 1498–1500
Rushforth JA, Levene MI 1993 Effect of sucrose on crying in response to heel stab. Arch Dis Child 69: 388–389
Blass EM, Hoffmeyer LB 1991 Sucrose as an analgesic for newborn infants. Pediatrics 87: 215–218
Blass EM, Watt LB 1999 Suckling and sucrose-induced analgesia in human newborns. Pain 83: 611–623
Als H, Duffy FH, McAnulty GB 1996 Effectiveness of individualised neurodevelopmental care in the newborn intensive care unit. Acta Paediatr 416: S21–S30
Als H, Gilkerson L 1997 The role of relationship-based developmentally supportive newborn intensive care in strengthening outcome of preterm infants. Semin Perinatol 21: 178–189
Johnston CC, Stremler R, Horton L, Friedman A 1999 Effect of repeated doses of sucrose during heel stick procedure in preterm neonates. Biol Neonate 75: 160–166
Lindahl S 1997 Calming minds or killing pain in newborn infants?. Acta Paediatr 86: 787 787–788
Melzack R, Wall PD 1965 Pain mechanisms: a new theory. Science 150: 971–979
Wall PD 1978 The gate control theory of pain mechanism. A re-examination and re-statement. Brain 101: 1–18
Melzack R 1999 From the gate to the neuromatrix. Pain 6: S121–S126
Relier JP 1996 Importance of fetal perceptions in the organization of the mother-fetus interactions. Biol Neonate 69: 165–212
Robin M 2000 Premier regards, premiers échanges. In: Herbinet E, Busnel MC (eds) L'Aube des Sens. Stock, Paris, 55–64
Herbinet E, Busnel MC 2000 L'Aube des Sens. Stock, Paris
Franck LS, Lawhon G 1998 Environmental and behavioral strategies to prevent and manage neonatal pain. Semin Perinatol 22: 434–443
Korner AF, Kraemer HC, Haffner ME, Cosper LM 1975 Effects of waterbed flotation on premature infants: a pilot study. Pediatrics 56: 361–367
Gray L, Watt L, Blass EM 2000 Skin-to-skin contact is analgesic in healthy newborns. Pediatrics 105: e14
Locsin RG 1981 The effect of music on the pain of selected post-operative patients. J Adv Nurs 6: 19–25
McIntosh N, van Veen L, Brameyer H 1994 Alleviation of the pain of heel prick in preterm infants. Arch Dis Child 70: F177–F181
Stevens B, Ohlsson A 2001 Sucrose for analgesia in newborn infants undergoing painful procedures (Cochrane Review). In: The Cochrane Library, Issue 4, Oxford
Abad F, Diaz NM, Domenech E, Robayna M, Rico J 1996 Oral sweet solution reduces pain-related behaviour in preterm infants. Acta Paediatr 85: 854–858
Bucher HU, Moser T, Von Siebental K, Keel M, Wolf M, Duc G 1995 Sucrose reduces pain reaction to heel lancing in preterm infants: a placebo-controlled, randomized and masked study. Pediatr Res 38: 332–335
Johnston CC, Stremler RL, Stevens BJ, Horton LJ 1997 Effectiveness of oral sucrose and simulated rocking on pain response in preterm neonates. Pain 72: 193–199
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bellieni, C., Bagnoli, F., Perrone, S. et al. Effect of Multisensory Stimulation on Analgesia in Term Neonates: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Pediatr Res 51, 460–463 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-200204000-00010
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-200204000-00010
This article is cited by
-
Music for pain relief of minor procedures in term neonates
Pediatric Research (2024)
-
The role of time interval elimination on pain control of preterm infants by sucrose administration
European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology (2023)
-
A Guide to Pain Assessment and Management in the Neonate
Current Emergency and Hospital Medicine Reports (2016)
-
Pain…. from analgesic care to decennal experience
Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2015)
-
Non-pharmacological intervention for neonatal pain control
Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2014)