Abstract
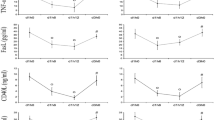
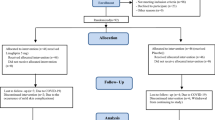
It has been shown that patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus have elevated von Willebrand factor (vWF) plasma concentrations. Plasma fibrinogen, vWF, and its propeptide concentrations have been evaluated in 102 children with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus to determine whether an increase of vWF and its propeptide levels precedes and may predict the development of persistent microalbuminuria. The patients have been divided into two groups according to the presence or absence of microalbuminuria at the end of follow-up. They have been followed up for at least 8 y. Control group consisted of 80 age- and sex-matched healthy volunteers. At the beginning of the study there was no significant difference in fibrinogen, vWF, and its propeptide levels between patients and control subjects. During the follow-up, a significant increase of plasma vWF and its propeptide has been observed in the group of patients who later developed microalbuminuria but not in those who remained normoalbuminuric. This increase started 3 y and become statistically significant (p < 0.01) 2 y before the onset of microalbuminuria, persisting until the end of the study. During the entire follow-up plasma values of fibrinogen persisted in the normal range. In conclusion, an increase in plasma concentration of vWF and its propeptide precedes microalbuminuria and, therefore, can be useful to identify children with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus at risk to develop incipient nephropathy later in life.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- AER:
-
albumin excretion rate
- IDDM:
-
insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus
- vWF:
-
von Willebrand factor
- vWF propeptide:
-
von Willebrand factor propeptide
- HbA1c:
-
glycated Hb
References
Parving HH 1996 Microalbuminuria in essential hypertension and diabetes mellitus. J Hypertens 14( suppl 2): 89–94
Jensen T 1991 Albuminuria: a marker of renal and generalized vascular disease in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Dan Med Bull 38: 134–144
Messent JWC, Elliott TG, Hill RD, Jarrett RJ, Keen H, Viberti GC 1992 Prognostic significance of microalbuminuria in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: a twenty-three year follow-up study. Kidney Int 41: 836–839
Huvers FC, De Leeuw PW, Houben AJHM, De Haan CHA, Hamulyak K, Schouten H, Wolffenbuttel BHR, Schaper NC 1999 Endothelium dependent vasodilatation, plasma markers of endothelial function, and adrenergic vasoconstrictor responses in type I diabetes under near-normoglycemic conditions. Diabetes 47: 1300–1307
Vane JR, Anggard EE, Botting RM 1990 Mechanism of disease: regulatory functions of the vascular endothelium. N Engl J Med 323: 27–36
Ross R 1993 The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: a perspective for the 1990s. Nature 362: 801–809
Remuzzi G, Benigni A 1993 Endothelins in the control of cardiovascular and renal function. Lancet 342: 589–593
Deckert T, Feldt-Rasmussen B, Borch-Johnsen K, Jensen T, Kofoed-Enevoldsen A 1989 Albuminuria reflects widespread vascular damage: the Steno hypothesis. Diabetologia 32: 219–226
Elliott TG, Cockcroft JR, Groop PH, Viberti GC, Ritter JM 1993 Inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis in forearm vasculature in insulin-dependent diabetic patients: blunted vasoconstriction in patients with microalbuminuria. Clin Sci 83: 687–693
Collier A, Leach JP, McLellan A, Jardine A, Morton JJ, Small M 1992 Plasma endothelinlike immunoreactivity levels in IDDM patients with microalbuminuria. Diabetes Care 15: 1038–1040
Jensen T, Bjerre-Knudsen J, Feldt-Rasmussen B, Deckert T 1989 Features of endothelial dysfunction in early diabetic nephropathy. Lancet 1: 461–463
Gruden G, Cavallo-Perin P, Bazzab M, Stella S, Vuolo A, Pagano G 1994 PAI-1 and factor VII activity are higher in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus patients with microalbuminuria. Diabetes 43: 426–429
Stehouwer CDA, Stroes ESG, Hackeng WHL, Mulder PGH, den Ottolander GJH 1991 von Willebrand factor and development of diabetic nephropathy in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 40: 971–976
Stehouwer CDA, Fischer HRA, van Kuijk AWR, Polak BCP, Donker AJM 1995 Endothelial dysfunction precedes development of microalbuminuria in IDDM. Diabetes 44: 561–564
Greaves M, Malia RG, Goodfellow K, Mattock M, Stevens LK, Stephenson JM, Fuller JH, Eurodiab IDDM Complications Study Group 1997 Fibrinogen and von Willebrand factor in IDDM: relationships to lipid vascular risk factor, blood pressure, glycaemic control and urinary albumin excretion rate: the Eurodiab IDDM Complications Study. Diabetologia 40: 698–705
Myrup B, Mathiesen ER, Ronn B, Deckert T 1994 Endothelial function and serum lipids in the course of developing microalbuminuria in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res 26: 33–39
Jensen JS, Myrup B, Borch-Johnsen K, Jensen G, Jensen T, Feldt-Rasmussen B 1995 Aspects of haemostatic function in healthy subjects with microalbuminuria—a potential atherosclerotic risk factor. Thromb Res 77: 423–430
Vischer UM, Emeis JJ, Bilo HJG, Stehouwer CDA, Thomsen C, Rasmussen O, Hermansen K, Wollheim CB, Ingerslev J 1998 von Willebrand factor (vWf) as a plasma marker of endothelial activation in diabetes: improved reliability with parallel determination of the vWf propeptide (vWf: AgII). Thromb Haemost 80: 1002–1006
Feldt-Rasmussen B, Dinesen B, Deckert M 1985 Enzyme immunoassay: an improved determination of urinary albumin excretion in diabetics with incipient nephropathy. Scand J Lab Clin Invest 45: 539–544
Ford I, Malik RA, Newrick PG, Preston FE, Ward JD, Greaves M 1992 Relationships between haemostatic factors and capillary morphology in human diabetic neuropathy. Thromb Haemost 68: 628–633
Vischer UM, Ingerslev J, Wollheim CB, Mestries JC, Tsakiris DA, Haefeli WE, Kruithof EK 1997 Acute von Willebrand factor secretion from the endotheliumin vivo: assessment through plasma propeptide (vWf:AgII) levels. Thromb Haemost 77: 387–393
Stehouwer CDA, Donker AJM 1993 Urinary albumin excretion and cardiovascular disease risk in diabetes mellitus: is endothelial dysfunction the missing link?. J Nephrol 6: 72–92
Stehouwer CDA, Nauta JJP, Zeldenrust GC, Hackeng WHL, Donker AJM, den Ottolander GJH 1992 Urinary albumin excretion, cardiovascular disease, and endothelial dysfunction in non–insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Lancet 340: 319–323
Pedrinelli R, Giampietro O, Carnassi F, Mellilo E, Dell'Omo G, Catapano G, Matteuci E, Talarico L, Morale M, de Negri F, di Bello V 1994 Microalbuminuria and endothelial dysfunction in essential hypertension. Lancet 344: 14–18
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verrotti, A., Greco, R., Basciani, F. et al. von Willebrand Factor and Its Propeptide in Children with Diabetes. Relation between Endothelial Dysfunction and Microalbuminuria. Pediatr Res 53, 382–386 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000049509.65496.BF
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000049509.65496.BF
This article is cited by
-
Cross-sectional relations of serum aldosterone and urine sodium excretion to urinary albumin excretion in a community-based sample
Kidney International (2006)
-
Renal functional reserve in patients with Type 1 diabetes mellitus
Wiener Klinische Wochenschrift (2004)