Abstract
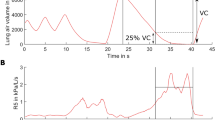
Mice deficient in surfactant protein D [SP-D (−/−)] develop progressive emphysema with age, associated with loss of parenchymal tissue, subpleural fibrosis, and accumulation of abnormal elastin fibers. We measured the changes in lung function, partitioned into components for the airways and lung parenchyma, occurring with age in SP-D (−/−) mice at three ages (n = 8 per group) (5, 8, and 13 wk). Impedance spectra between 0.25 and 19.625 Hz were calculated and a model, consisting of an airway compartment [airway resistance (Raw) and inertance (Iaw)] and a constant-phase tissue compartment [coefficients of tissue damping (G) and elastance (H)], was fitted to the data. Hysteresivity was calculated as G/H. Adult values of Raw, G, and H are reached by 8 wk of age in wild-type controls. Raw and H were lower at all ages in SP-D (−/−) compared with the wild-type controls (p = 0.006 and 0.029, respectively), and a similar trend was seen in G (p = 0.060). The patterns of change in respiratory mechanics were similar in both SP-D (+/+) and (−/−) groups. There were no changes in hysteresivity with age and no differences between wild-type and SP-D (−/−) mice. These data demonstrate that the changes in lung structure in SP-D (−/−) mice are reflected in the mechanical properties of both airway and lung parenchyma measured in vivo.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- SP-D:
-
surfactant protein D
- FOT:
-
forced oscillation technique
- Zrs:
-
respiratory input impedance
- Raw:
-
airway resistance
- Iaw:
-
airway inertance
- G:
-
coefficient of tissue damping
- H:
-
coefficient of tissue elastance
- η:
-
hysteresivity
References
Wert SE, Yoshida M, LeVine AM, Ikegami M, Jones T, Ross GF, Fisher JH, Korfhagen TR, Whitsett JA 2000 Increased metalloproteinase activity, oxidant production, and emphysema in surfactant protein D gene-inactivated mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97: 5972–5977
Wong CJ, Akiyama J, Allen L, Hawgood S 1996 Localization and developmental expression of surfactant proteins D and A in the respiratory tract of the mouse. Pediatr Res 39: 930–937
Motwani M, White RA, Guo N, Dowler LL, Tauber AI, Sastry KN 1995 Mouse surfactant protein-D. cDNA cloning, characterization, and gene localization to chromosome 14. J Immunol 155: 5671–5677
Wright JR 1997 Immunomodulatory functions of surfactant. Physiol Rev 77: 931–962
Korfhagen TR, Sheftelyevich V, Burhans MS, Bruno MD, Ross GF, Wert SE, Stahlman MT, Jobe AH, Ikegami M, Whitsett JA, Fisher JH 1998 Surfactant protein-D regulates surfactant phospholipid homeostasis in vivo. J Biol Chem 273: 28438–28443
Ikegami M, Whitsett JA, Jobe AJ, Ross G, Fisher J, Korfhagen T 2000 Surfactant metabolism in SP-D gene ablated mice. Am J Physiol 279: L468–L476
Hantos Z, Daroczy B, Suki B, Nagy S, Fredberg JJ 1992 Input impedance and peripheral inhomogeneity of dog lungs. J Appl Physiol 72: 168–178
Sly PD, Hayden MJ, Petak F, Hantos Z 1996 Measurement of low-frequency respiratory impedance in infants. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 154: 161–166
Fredberg JJ, Stamenovic D 1989 On the imperfect elasticity of lung tissue. J Appl Physiol 67: 2408–2419
Schuessler TF, Bates JHT 1995 A computer-controlled research ventilator for small animals: design and evaluation. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 42: 860–866
Tomioka S, Bates JHT, Irvin CG 2002 Airway and tissue mechanics in a murine model of asthma: alveolar capsule vs. forced oscillations. J Appl Physiol 93: 263–270
Weibel ER 1986 Functional morphology of lung parenchyma. In: Fishman AP (ed) Handbook of Physiology: The Respiratory System, Vol III. American Physiological Society, Bethesda, MD, 89–112.
Petak F, Hall GL, Sly PD 1998 Repeated measurements of airway and parenchymal mechanics in rats by using low frequency forced oscillations. J Appl Physiol 84: 1680–1696
Nagase T, Ludwig MS 1998 Antigen-induced responses in lung parenchymal strips during sinusoidal oscillation. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 76: 176–181
Hantos Z, Petak F, Adamicza A, Daroczy B, Fredberg JJ 1995 Differential responses of global airway, terminal airway, and tissue impedances to histamine. J Appl Physiol 79: 1440–1448
Petak F, Hantos Z, Adamicza A, Asztalos T, Sly PD 1997 Methacholine-induced bronchoconstriction in rats: effects of intravenous vs. aerosol delivery. J Appl Physiol 82: 1479–1787
Glasser SW, Burhans MS, Korfhagen TR, Na CL, Sly PD, Ross GF, Ikegami M, Whitsett JA 2001 Altered stability of surfactant in SP-C-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 6366–6371
Goerke J, Clements JA 1986 Alveolar surface tension and lung surfactant. In: Fishman AP (ed) Handbook of Physiology: The Respiratory System, Vol III. American Physiological Society, Bethesda, MD, 247–262.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council, Canberra, Australia (grant 961278), and the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, U.S.A. (grants HL63329 and HL61646).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Collins, R., Ikegami, M., Korfhagen, T. et al. In Vivo Measurements of Changes in Respiratory Mechanics with Age in Mice Deficient in Surfactant Protein D. Pediatr Res 53, 463–467 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000049464.46191.BF
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000049464.46191.BF
This article is cited by
-
Surfactant protein D, Club cell protein 16, Pulmonary and activation-regulated chemokine, C-reactive protein, and Fibrinogen biomarker variation in chronic obstructive lung disease
Respiratory Research (2014)
-
Adenoviral gene transfer of a mutant surfactant enzyme ameliorates pseudomonas-induced lung injury
Gene Therapy (2006)