Abstract
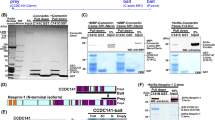
The channel proteins responsible for the cardiac transient outward K+ current (Ito) of human and rodent heart are composed, in part, of pore-forming Kv4.3 or Kv4.2 principal subunits. Recent reports implicate K+ channel interacting proteins (members of the neuronal Ca2+-binding protein family) as subunits of the Ito channel complex. We reported that another Ca2+-binding protein, frequenin [or neuronal calcium center protein-1 (NCS-1)], also functions as a Kv4 auxiliary subunit in the brain. By examining cardiac expression of NCS-1, the aim of this study was to examine the potential physiologic relevance of this protein as an additional regulator of cardiac Ito. Immunoblot analysis demonstrates NCS-1 protein to be expressed in adult mouse ventricle at levels comparable to that found in some brain regions. Cardiac NCS-1 protein expression levels are much higher in fetal and neonatal mouse hearts when compared with the adult. Immunocytochemical analysis of isolated neonatal mouse ventricular myocytes demonstrates co-localization of NCS-1 and Kv4.2 proteins at the sarcolemma. Given its high levels of expression in the heart, NCS-1 should be considered an important potential Kv4 regulatory subunit, particularly in the immature heart.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- Ito:
-
transient outward K+ current
- KChIPs:
-
K+ channel interacting proteins
- NCS-1:
-
neuronal calcium center protein-1 (also known as frequenin)
References
Coetzee WA, Amarillo Y, Chiu J, Chow A, Lau D, McCormack T, Moreno H, Nadal MS, Ozaita A, Pountney D, Saganich M, Vega-Saenz DM, Rudy B 1999 Molecular diversity of K+ channels. Ann N Y Acad Sci 868: 233–285
Nakahira K, Shi G, Rhodes KJ, Trimmer JS 1996 Selective interaction of voltage-gated K+ channel beta-subunits with alpha-subunits. J Biol Chem 271: 7084–7089
Kuryshev YA, Wible BA, Gudz TI, Ramirez AN, Brown AM 2001 KChAP/Kvbeta1.2 interactions and their effects on cardiac Kv channel expression. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 281: C290–C299
Zhang M, Jiang M, Tseng GN 2001 minK-Related peptide 1 associates with Kv4.2 and modulates its gating function: potential role as beta subunit of cardiac transient outward channel?. Circ Res 88: 1012–1019
Petrecca K, Miller DM, Shrier A 2000 Localization and enhanced current density of the Kv4.2 potassium channel by interaction with the actin-binding protein filamin. J Neurosci 20: 8736–8744
An WF, Bowlby MR, Betty M, Cao J, Ling HP, Mendoza G, Hinson JW, Mattsson KI, Strassle BW, Trimmer JS, Rhodes KJ 2000 Modulation of A-type potassium channels by a family of calcium sensors. Nature 403: 553–556
Kuo HC, Cheng CF, Clark RB, Lin JJ, Lin JL, Hoshijima M, Nguyen-Tran VT, Gu Y, Ikeda Y, Chu PH, Ross J, Giles WR, Chien KR 2001 A defect in the Kv channel-interacting protein 2 (KChIP2) gene leads to a complete loss of Ito and confers susceptibility to ventricular tachycardia. Cell 107: 801–813
Nakamura TY, Pountney DJ, Ozaita A, Nandi S, Ueda S, Rudy B, Coetzee WA 2001 A role for frequenin, a Ca2+-binding protein, as a regulator of Kv4 K+-currents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98: 12808–12813
Roth MB, Zahler AM, Stolk JA 1991 A conserved family of nuclear phosphoproteins localized to sites of polymerase II transcription. J Cell Biol 115: 587–596
Burgoyne RD, Weiss JL 2001 The neuronal calcium sensor family of Ca2+-binding proteins. Biochem J 353: 1–12
Dixon JE, McKinnon D 1994 Quantitative analysis of potassium channel mRNA expression in atrial and ventricular muscle of rats. Circ Res 75: 252–260
Takeuchi S, Takagishi Y, Yasui K, Murata Y, Toyama J, Kodama I 2000 Voltage-gated K+ Channel, Kv4.2, localizes predominantly to the transverse-axial tubular system of the rat myocyte. J Mol Cell Cardiol 32: 1361–1369
Rosati B, Pan Z, Lypen S, Wang HS, Cohen I, Dixon JE, McKinnon D 2001 Regulation of KChIP2 potassium channel beta subunit gene expression underlies the gradient of transient outward current in canine and human ventricle. J Physiol 533: 119–125
Guo W, Malin SA, Johns DC, Jeromin A, Nerbonne JM 2002 Modulation of Kv4-encoded K+ currents in the mammalian myocardium by neuronal calcium sensor-1. J Biol Chem 277: 26436–26443
Xu H, Dixon JE, Barry DM, Trimmer JS, Merlie JP, McKinnon D, Nerbonne JM 1996 Developmental analysis reveals mismatches in the expression of K+ channel alpha subunits and voltage-gated K+ channel currents in rat ventricular myocytes. J Gen Physiol 108: 405–419
Colucci WS 1997 Molecular and cellular mechanisms of myocardial failure. Am J Cardiol 80: 15L–25L
Osawa M, Tong KI, Lilliehook C, Wasco W, Buxbaum JD, Cheng HY, Penninger JM, Ikura M, Ames JB 2001 Calcium-regulated DNA binding and oligomerization of the neuronal calcium-sensing protein, calsenilin/DREAM/KChIP3. J Biol Chem 276: 41005–41013
Haddock PS, Coetzee WA, Cho E, Porter L, Katoh H, Bers DM, Jafri MS, Artman M 1999 Subcellular [Ca2+]igradients during excitation-contraction coupling in newborn rabbit ventricular myocytes. Circ Res 85: 415–427
Hendricks KB, Wang BQ, Schnieders EA, Thorner J 1999 Yeast homologue of neuronal frequenin is a regulator of phosphatidylinositol-4-OH kinase. Nat Cell Biol 1: 234–241
Pongs O, Lindemeier J, Zhu XR, Theil T, Engelkamp D, Krah-Jentgens I, Lambrecht HG, Koch KW, Schwemer J, Rivosecchi R 1993 Frequenin—a novel calcium-binding protein that modulates synaptic efficacy in the Drosophila nervous system. Neuron 11: 15–28
Weiss JL, Archer DA, Burgoyne RD 2000 Neuronal Ca2+ sensor-1/frequenin functions in an autocrine pathway regulating Ca2+ channels in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem 275: 40082–40087
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Institutes of Health (Grant 1 R01 HL71058-01 to W.A.C.), the American Heart Association (Scientist Development Award 013019N to T.Y.N.), and by the Seventh District Association, Inc. E.S. was the recipient of a medical student research fellowship from the Society for Pediatric Research.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakamura, T., Sturm, E., Pountney, D. et al. Developmental Expression of NCS-1 (Frequenin), a Regulator of Kv4 K+ Channels, in Mouse Heart. Pediatr Res 53, 554–557 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000057203.72435.C9
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000057203.72435.C9
This article is cited by
-
Interleukin-11: A Multifunctional Cytokine with Intrinsically Disordered Regions
Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics (2016)
-
Multiple Roles for Frequenin/NCS-1 in Synaptic Function and Development
Molecular Neurobiology (2012)
-
Ncs-1
AfCS-Nature Molecule Pages (2005)