Abstract
Obesity is a complex disease that involves interactions between environmental and genetic factors. Obesity results from an imbalance between food intake and energy expenditure over several years. The genetic approach both in animal models and in humans has allowed immense progress in the understanding of body weight regulation. Monogenic forms of obesity in humans have been characterized and result from mutations in genes involved in the central pathways of food intake regulation. However, these cases are extremely rare and generally obesity must be considered as a complex polygenic disease involving interactions between multiple genes and the environment. Numerous studies, including studies in children, have tried to identify “susceptibility” genes. At present, the results are not conclusive inasmuch as they are highly variable between studies and because the relative risk associating a specific gene allele and obesity remains low. Thus, it seems highly premature to genotype obese patients on a large scale for predictive testing. When specific pharmacological treatments based on recent discoveries become available, however, genetic testing could help discriminate between the subtypes of obesity that may respond differentially to treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
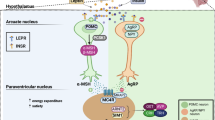
Abbreviations
- BMI:
-
body mass index
- MC4R:
-
melanocortin 4 receptor
- α-MSH:
-
α-melanocyte stimulating hormone
- PC-1:
-
pro-hormone convertase 1
- POMC:
-
pro-opiomelanocortin
- PPARγ:
-
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ
- UCP1:
-
uncoupling protein 1
References
Troiano RP, Flegal KM 1998 Overweight children and adolescents: description, epidemiology, and demographics. Pediatrics 101: 497–504
Spiegelman BM, Flier JS 2001 Obesity and the regulation of energy balance. Cell 104: 531–543
Franco C, Bengtsson BA, Johannsson G 2001 Visceral obesity and the role of the somatotropic axis in the development of metabolic complications. Growth Horm IGF Res 11: S97–S102
Trayhurn P, Beattie JH 2001 Physiological role of adipose tissue: white adipose tissue as an endocrine and secretory organ. Proc Nutr Soc 60: 329–339
Schwartz MW, Woods SC, Porte D, Seeley RJ, Baskin DG 2000 Central nervous system control of food intake. Nature 404: 661–671
Flegal KM, Wei R, Ogden C 2002 Weight-for-stature compared with body mass index-for-age growth charts for the United States from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Am J Clin Nutr 75: 761–766
Jequier E, Tappy L 1999 Regulation of body weight in humans. Physiol Rev 79: 451–480
Barsh GS, Farooqi IS, O'Rahilly S 2000 Genetics of body-weight regulation. Nature 404: 644–651
Foufelle F, Ferré P 2002 New perspectives in the regulation of hepatic glycolytic and lipogenic genes by insulin and glucose: a role for the transcription factor SREBP-1c. Biochem J 366: 377–391
Rankinen T, Perusse L, Weisnagel SJ, Snyder EE, Chagnon YC, Bouchard C 2002 The human obesity gene map: the 2001 update. Obes Res 10: 196–243
Clement K, Vaisse C, Lahlou N, Cabrol S, Pelloux V, Cassuto D, Gourmelen M, Dina C, Chambaz J, Lacorte JM, Basdevant A, Bougneres P, Lebouc Y, Froguel P, Guy-Grand B 1998 A mutation in the human leptin receptor gene causes obesity and pituitary dysfunction. Nature 392: 398–401
Krude H, Gruters A 2000 Implications of proopiomelanocortin (POMC) mutations in humans: the POMC deficiency syndrome. Trends Endocrinol Metab 11: 15–22
Vaisse C, Clement K, Durand E, Hercberg S, Guy-Grand B, Froguel P 2000 Melanocortin-4 receptor mutations are a frequent and heterogeneous cause of morbid obesity. J Clin Invest 106: 253–262
Dubern B, Clement K, Pelloux V, Froguel P, Girardet JP, Guy-Grand B, Tounian P 2001 Mutational analysis of melanocortin-4 receptor, agouti-related protein, and alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone genes in severely obese children. J Pediatr 139: 204–209
Le Stunff C, Le Bihan C, Schork NJ, Bougneres P 2000 A common promoter variant of the leptin gene is associated with changes in the relationship between serum leptin and fat mass in obese girls. Diabetes 49: 2196–2200
Heo M, Leibel RL, Fontaine KR, Boyer BB, Chung WK, Koulu M, Karvonen MK, Pesonen U, Rissanen A, Laakso M, Uusitupa MI, Chagnon Y, Bouchard C, Donohoue PA, Burns TL, Shuldiner AR, Silver K, Andersen RE, Pedersen O, Echwald S, Sorensen TI, Behn P, Permutt MA, Jacobs KB, Elston RC, Hoffman DJ, Gropp E, Allison DB 2002 A meta-analytic investigation of linkage and association of common leptin receptor (LEPR) polymorphisms with body mass index and waist circumference. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 26: 640–646
Miraglia del Giudice E, Cirillo G, Santoro N, D'Urso L, Carbone MT, Di Toro R, Perrone L 2001 Molecular screening of the proopiomelanocortin (POMC) gene in Italian obese children: report of three new mutations. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 25: 61–67
Le Stunff C, Fallin D, Schork NJ, Bougnères P 2000 The insulin gene VNTR is associated with fasting insulin levels and development of juvenile obesity. Nat Genet 26: 444–446
Witchel SF, White C, Siegel ME, Aston CE 2001 Inconsistent effects of the proline12 –> alanine variant of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma2 gene on body mass index in children and adolescent girls. Fertil Steril 76: 741–747
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Professor A. Basdevant for helpful discussions and Dr. B. Hegarty for kindly correcting the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clément, K., Ferré, P. Genetics and the Pathophysiology of Obesity. Pediatr Res 53, 721–725 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000059753.61905.58
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000059753.61905.58
This article is cited by
-
An exposome-wide association study on body mass index in adolescents using the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2003–2004 and 2013–2014 data
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Sodium intake assessed by 24-h urine excretion and its relationship with anthropometric measurements in Malaysian adults
Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition (2021)
-
Genetics of Obesity
Indian Journal of Clinical Biochemistry (2016)
-
Current review of genetics of human obesity: from molecular mechanisms to an evolutionary perspective
Molecular Genetics and Genomics (2015)
-
Determinants of overweight and obesity among Bangladeshi diabetic women of reproductive age
BMC Research Notes (2014)