Abstract
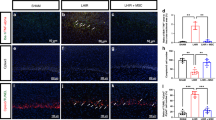
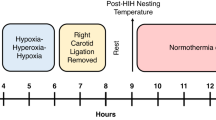
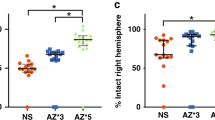
Perinatal brain damage is associated not only with hypoxic-ischemic insults but also with intrauterine inflammation. A combination of antenatal inflammation and asphyxia increases the risk of cerebral palsy >70 times. The aim of the present study was to determine the effect of intracisternal (i.c.) administration of endotoxin [lipopolysaccharides (LPS)] on subsequent hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in neonatal rats. Seven-day-old Wistar rats were subjected to i.c. application of NaCl or LPS (5 μg/pup). One hour later, the left common carotid artery was exposed through a midline neck incision and ligated with 6-0 surgical silk. After another hour of recovery, the pups were subjected to a hypoxic gas mixture (8% oxygen/92% nitrogen) for 60 min. The animals were randomized to four experimental groups:1) sham control group, left common carotid artery exposed but not ligated (n = 5);2) LPS group, subjected to i.c. application of LPS (n = 7);3) hypoxic-ischemic study group, i.c. injection of NaCl and exposure to hypoxia after ligation of the left carotid artery (n = 17); or 4) hypoxic-ischemic/LPS study group, i.c. injection of LPS and exposure to hypoxia after ligation of the left carotid artery (n = 19). Seven days later, neonatal brains were assessed for neuronal cell damage. In a second set of experiments, rat pups received an i.c. injection of LPS (5 μg/pup) and were evaluated for tumor necrosis factor-α expression by immunohistochemistry. Neuronal cell damage could not be observed in the sham control or in the LPS group. In the hypoxic-ischemic/LPS group, neuronal injury in the cerebral cortex was significantly higher than in animals that were subjected to hypoxia/ischemia after i.c. application of NaCl. Injecting LPS intracisternally caused a marked expression of tumor necrosis factor-α in the leptomeninges. Applying LPS intracisternally sensitizes the immature rat brain to a subsequent hypoxic-ischemic insult.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- LPS:
-
lipopolysaccharides
- TNF-α:
-
tumor necrosis factor-α
- i.c.:
-
intracisternal
- TLR:
-
toll-like receptor
References
Berger R, Garnier Y 1999 Pathophysiology of perinatal brain damage. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 30: 107–134
Volpe JJ 1995 Neurology of the Newborn. Saunders, Philadelphia
Dammann O, Leviton A 1997 Maternal intrauterine infection, cytokines, and brain damage in the preterm infant. Pediatr Res 42: 1–8
Nisswander KR, Gordon M 1972 The Women and Their Pregnancies. The Collaborative Perinatal Study of the National Institute of Neurological Diseases and Stroke. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 252–256.
Berger R, Bender S, Sefkow S, Klingmüller V, Künzel W, Jensen A 1997 Peri/intraventricular haemorrhage: a cranial ultrasound study on 5286 neonates. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 75: 191–203
Paneth N, Pinto-Martin J, Gardiner J, Wallenstein S, Katsikiotis V, Hegyi T, Hiatt IM, Susser M 1993 Incidence and timing of germinal matrix/ventricular hemorrhage in low birth weight infants. Am J Epidemiol 137: 1167–1176
Gatti S, Bartfai T 1993 Induction of tumor necrosis factor-alpha mRNA in the brain after peripheral endotoxin treatment: comparison with interleukin-1 family and interleukin-6. Brain Res 624: 291–294
Hillhouse EW, Mosley K 1993 Peripheral endotoxin induces hypothalamic immunoreactive interleukin-1 beta in the rat. Br J Pharmacol 109: 289–290
Van Dam AM, Bauer J, Tilders FJ, Berkenbosch F 1995 Endotoxin-induced appearance of immunoreactive interleukin-1 beta in ramified microglia in rat brain: a light and electron microscopic study. Neuroscience 65: 815–826
Barone FC, Arvin B, White RF, Miller A, Webb CL, Willette RN, Lysko PG, Feuerstein GZ 1997 Tumor necrosis factor-alpha. A mediator of focal ischemic brain injury. Stroke 28: 1233–1244
Cai Z, Pan Z, Pang Y, Evans OB, Rhodes PG 2000 Cytokine induction in fetal rat brains and brain injury in neonatal rats after maternal lipopolysaccharide administration. Pediatr Res 47: 64–72
Yoon BH, Kom CJ, Romero R, Jun JK, Park KH, Choi ST, Chi JG 1997 Experimentally induced intrauterine infection causes fetal brain white matter lesions in rabbits. Am J Obstet Gynecol 177: 797–802
Gilles FH, Averill DR, Kerr CS 1977 Neonatal endotoxin encephalopathy. Ann Neurol 2: 49–56
Eklind S, Mallard C, Leverin A, Gilland E, Blomgren K, Mattsby-Baltzer I, Hagberg H 2001 Bacterial endotoxin sensitizes the immature brain to hypoxic-ischaemic injury. Eur J Neurosci 13: 1101–1106
Garnier Y, Coumans ABC, Berger R, Jensen A, Hasaart THM 2001 Endotoxemia severely affects circulation during normoxia and asphyxia in immature fetal sheep. J Soc Gynecol Investig 8: 134–142
Nelson KB, Grether JK 1998 Potentially asphyxiating conditions and spastic cerebral palsy in infants of normal birth weight. Am J Obstet Gynecol 179: 507–513
Leib SL, Clements JM, Lindberg RL, Heimgartner C, Loeffler JM, Pfister LA, Tauber MG, Leppert D 2001 Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases and tumour necrosis factor alpha converting enzyme as adjuvant therapy in pneumococcal meningitis. Brain 124: 1734–1742
Rice JED, Vannucci RC, Brierley JB 1981 The influence of immaturity on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the rat. Ann Neurol 9: 131–141
Okamoto H, Ito O, Roman RJ, Hudetz AG 1998 Role of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 in endotoxin-induced cerebral hyperemia. Stroke 29: 1209–1218
Brian JE, Heistad DD, Faraci FM 1995 Dilatation of cerebral arterioles in response to lipopolysaccharide in vivo. Stroke 26: 277–281
Bona E, Johansson BB, Hagberg H 1997 Sensorimotor function and neuropathology five to six weeks after hypoxia-ischemia in seven-day-old rats. Pediatr Res 42: 678–683
Sherwood NM, Timiras PS 1970 A Stereotaxic Atlas of the Developing Rat Brain. University of California Press, Berkeley, pp 15–75.
Brown AW, Brierley JB 1972 Anoxic-ischaemic cell change in rat brain light microscopic and fine structural observations. J Neurol Sci 16: 59–84
Berger R, Lehmann T, Karcher J, Garnier Y, Jensen A 1998 Low dose flunarizine protects the fetal brain from ischemic injury in sheep. Pediatr Res 44: 277–282
Berger R, Lehmann T, Karcher J, Schachenmayr W, Jensen A 1996 Relation between cerebral oxygen delivery and neuronal cell damage in fetal sheep near term. Reprod Fertil Dev 8: 317–321
Mallard EC, Williams CE, Gunn AJ, Gunning MI, Gluckman PD 1993 Frequent episodes of brief ischemia sensitize the fetal sheep brain to neuronal loss and induce striatal injury. Pediatr Res 33: 61–65
Leib SL, Leppert D, Clements J, Täuber MG 2000 Matrix metalloproteinases contribute to brain damage in experimental pneumococcal meningitis. Infect Immun 68: 615–620
Dawson DA, Furuya K, Gotoh J, Nakao Y, Hallenbeck JM 1999 Cerebrovascular hemodynamics and ischemic tolerance: lipopolysaccharide-induced resistance to focal cerebral ischemia is not due to changes in severity of the initial ischemic insult, but is associated with preservation of microvascular perfusion. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 19: 616–623
Ulevitch RJ, Tobias PS 1995 Receptor-dependent mechanisms of cell stimulation by bacterial endotoxin. Annu Rev Immunol 13: 437–457
Kopp EB, Medzhitov R 1999 The Toll-receptor family and control of innate immunity. Curr Opin Immunol 11: 13–18
Ulevitch RJ, Tobias PS 1999 Recognition of gram-negative bacteria and endotoxin by the innate immune system. Curr Opin Immunol 11: 19–22
Allan SM, Rothwell NJ 2001 Cytokines and acute neurodegeneration. Nat Rev Neurosci 2: 734–744
Serou MJ, DeCoster MA, Bazan NG 1999 Interleukin-1 beta activates expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase in primary hippocampal neuronal culture: platelet-activating factor as a preferential mediator of cyclooxygenase-2 expression. J Neurosci Res 58: 593–598
Rosenberg GA, Estrada EY, Dencoff JE, Stetler-Stevenson WG 1995 Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced gelatinase B causes delayed opening of the blood-brain barrier: an expanded therapeutic window. Brain Res 703: 151–155
Leviton A, Paneth N, Reuss ML, Susser M, Allred EN, Dammann O, Kuban K, Van Marter LJ, Pagano M, Hegyi T, Hiatt M, Sanocka U, Shahrivar F, Abiri M, Disalvo D, Doubilet P, Kairam R, Kazam E, Kirpekar M, Rosenfeld D, Schonfeld S, Share J, Collins M, Genest D, Shen-Schwarz S 1999 Maternal infection, fetal inflammatory response, and brain damage in very low birth weight infants. Developmental Epidemiology Network Investigators. Pediatr Res 46: 566–575
Wu YW, Colford JM 2000 Chorioamnionitis as a risk factor for cerebral palsy: a meta-analysis. JAMA 284: 1417–1424
Faggioni R, Fantuzzi G, Villa P, Buurman W, van Tits LJ, Ghezzi P 1995 Independent down-regulation of central and peripheral tumor necrosis factor production as a result of lipopolysaccharide tolerance in mice. Infect Immun 63: 1473–1477
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Be 1688/4-3), The Dutch Foundations “De Drie Lichten,” and “De Oranjekliniek” as well as the Swiss National Science Foundation (32-61654.00).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coumans, A., Middelanis, J., Garnier, Y. et al. Intracisternal Application of Endotoxin Enhances the Susceptibility to Subsequent Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Damage in Neonatal Rats. Pediatr Res 53, 770–775 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000059221.40073.82
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000059221.40073.82
This article is cited by
-
Frühe Hirnschäden verhindern
Pädiatrie (2016)
-
Neuronal self-injury mediated by IL-1β and MMP-9 in a cerebral palsy model of severe neonatal encephalopathy induced by immune activation plus hypoxia-ischemia
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2015)
-
Complex pattern of interaction between in uterohypoxia-ischemia and intra-amniotic inflammation disrupts brain development and motor function
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2014)
-
Neuroprotektion bei Frühgeborenen
Der Gynäkologe (2014)
-
Involvement of neuronal IL-1β in acquired brain lesions in a rat model of neonatal encephalopathy
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2013)