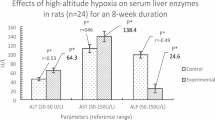
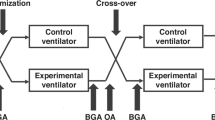
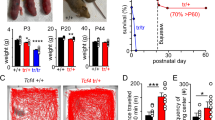
Abstract
We sought to examine the role of the basomedial hypothalamus in the regulation of breathing in neonatal rats. Small basomedial hypothalamic lesions were produced by a lesioning agent, goldthioglucose, in 5-d-old male rat pups, and 2 d later, baseline ventilation and the ventilatory responses to hypoxia and hypercapnia were examined. When compared with vehicle-injected controls, goldthioglucose-lesioned rat pups had a significantly slower respiratory rate and longer expiratory time at baseline. Lesioned rats displayed an impaired increase in breathing frequency in response to hypoxia, and augmented increases in tidal volume and respiratory drive (the ratio of tidal volume to inspiratory time) during hypoxia relative to controls. Hypercapnic responses were not affected. These data demonstrate that cells in a restricted area of the hypothalamus specifically influence the respiratory response to hypoxia.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- GTG:
-
goldthioglucose
- NPY:
-
neuropeptide Y
- PVN:
-
paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus
- TE:
-
expiratory duration
- TI:
-
inspiratory duration
- TTOT:
-
length of respiratory cycle
- Vt:
-
tidal volume
REFERENCES
Horn EM, Waldrop TG 1994 Modulation of the respiratory responses to hypoxia and hypercapnia by synaptic input onto caudal hypothalamic neurons. Brain Res 664: 25–33
Horn EM, Dillon GH, Fan Y-P, Waldrop TG 1999 Developmental aspects and mechanisms of rat caudal hypothalamic neuronal responses to hypoxia. J Neurophysiol 81: 1949–1959
Dillon GH, Waldrop TG 1993 Responses of feline caudal hypothalamic cardiorespiratory neurons in hypoxia and hypercapnia. Exp Brain Res 96: 260–272
Berquin P, Bodineau L, Gros F, Larnicol N 2000 Brainstem and hypothalamic areas involved in respiratory chemoreflexes: a Fos study in adult rats. Brain Res 857: 30–40
Haxhiu MA, Yung K, Erokwu B, Cherniack NS 1996 CO2-induced c-fos expression in the CNS catecholaminergic neurons. Respir Physiol 105: 35–45
Nitsos I, Walker DW 1999 The distribution of FOS-immunoreactive neurons in the brainstem, midbrain and diencephalon of fetal sheep in response to acute hypoxia in mid and late gestation. Dev Brain Res 114: 9–26
Baskin DG, Hahn TM, Schwartz MW 1999 Leptin sensitive neurons in the hypothalamus. Horm Metab Res 31: 345–350
Mercer JG, Moar KM, Hoggard N 1998 Localization of leptin receptor (Ob-R) messenger ribonucleic acid in the rodent hindbrain. Endocrinology 139: 29–34
O'Donnell CP, Tankersley CG, Polotsky VP, Schwartz AR, Smith PL 2000 Leptin, obesity, and respiratory function. Respir Physiol 119: 163–170
Hinrichsen CFL, Maskrey M, Mortola JP 1998 Ventilatory and metabolic responses to cold and hypoxia in conscious rats with discrete hypothalamic lesions. Respir Physiol 111: 247–256
Young JK 1989 The glial drug methionine sulfoximine reduces goldthioglucose lesions in mice. Brain Res Bull 24: 929–936
Yeh ER, Erokwu B, LaManna JC, Haxhiu MA 1997 The paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus influences respiratory timing and activity in the rat. Neurosci Lett 232: 63–66
Smith JC, Ellenberger HH, Ballanyi K, Richter DW, Feldman JL 1991 Pre-Botzinger complex: a brainstem region that may generate respiratory rhythm in mammals. Science 254: 726–729
Schwanzel-Fukuda M, Morrell JI, Pfaff DW 1984 Localization of forebrain neurons which project directly to the medulla and spinal cord of the rat by retrograde tracing with wheat germ agglutinin. J Comp Neurol 226: 1–20
Martin RJ, DiFiore JM, Jana L, Davis RL, Miller MJ, Coles SK, Dick TE 1998 Persistence of the biphasic ventilatory response to hypoxia in preterm infants. J Pediatr 132: 960–964
Miller MJ, Haxhiu MA, Haxhiu-Poskurica B, Dreshaj IA, DiFiore JM, Martin RJ 2000 Recurrent hypoxic exposure and reflex responses during development in the piglet. Respir Physiol 123: 51–61
Suguihara C, Bancalari E, Hehre D, Duara S, Gerhardt T 1994 Changes in ventilation and oxygen consumption during acute hypoxia in sedated newborn piglets. Pediatr Res 35: 536–540
Dawes GS, Gardner WN, Johnston BM, Walker DW 1983 Breathing in fetal lambs: the effect of brain stem section. J Physiol 335: 535–553
Gluckman PD, Johnston BM 1987 Lesions in the upper lateral pons abolish the hypoxic depression of breathing in unanaesthetized fetal lambs in utero. J Physiol 382: 373–383
Leloup C, Arluison M, Lepetit N, Cartier N, Marfaing-Jallat P, Ferre P, Penicaud L 1994 Glucose transporter 2 (Glut 2): expression in specific brain nuclei. Brain Res 638: 221–236
Haxhiu MA, Cherniack NS, van Lunteren E 1990 Central action of tachykinins on activity of expiratory pumping muscles. J Appl Physiol 69: 1981–1986
Young JK, McKenzie JC, Brady LS, Herkenham M 1994 Hypothalamic lesions increase levels of neuropeptide Y mRNA in the arcuate nucleus of mice. Neuroscience Lett 165: 13–17
Bergen HT, Mizuno TM, Taylor J, Mobbs CV 1998 Hyperphagia and weight gain after gold-thioglucose: relation to hypothalamic neuropeptide Y and proopiomelanocortin. Endocrinology 139: 4483–4488
Marks JL, Waite K, Cameron-Smith D, Blair SC, Cooney GJ 1996 Effects of goldthioglucose on neuropeptide Y messenger RNA levels in the mouse hypothalamus. Am J Physiol 270: R1208–R1214
Desjardins CG, Brawer JR, Beaudet A 1993 Estradiol is selectively neurotoxic to hypothalamic β-endorphin neurons. Endocrinology 132: 86–93
Harrison TA, Chen CT, Dun NJ, Chang JK 1999 Hypothalamic orexin A-immunoreactive neurons project to the rat dorsal medulla. Neurosci Lett 273: 17–20
Horvath TL, Diano S, van den Pol AN 1999 Synaptic interaction between hypocretin (orexin) and neuropeptide Y cells in the rodent and primate hypothalamus: a novel circuit implicated in metabolic and endocrine regulation. J Neurosci 19: 1072–1087
Abu-Shaweesh JM, Dreshaj IA, Thomas AJ, Haxhiu MA, Strohl KP, Martin RJ 1999 Changes in respiratory timing induced by hypercapnia in maturing rats. J Appl Physiol 87: 484–490
Jansson JO, Ishikawa K, Katakami H, Frohman LA 1987 Pre- and postnatal developmental changes in hypothalamic content of rat growth hormone-releasing factor. Endocrinology 120: 525–530
Makarenko IG, Ugrumov MV, Calas A 2001 Axonal projections from the hypothalamus to the median eminence in rats during ontogenesis: DiI tracing study. Anat Embryol (Berl) 204: 239–252
Lavie P, Klein E, Gadoth N, Bental E, Zomer J, Bechar M, Wajsbort J 1981 Further observations on sleep abnormalities in Kleine-Levin syndrome: abnormal breathing pattern during sleep. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 52: 98–101
Lindgren AC, Hellstrom LG, Ritzen Em, Milerad J 1999 Growth hormone treatment increases CO(2) response, ventilation and central inspiratory drive in children with Prader-Willi syndrome. Eur J Pediatr 158: 936–940
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by National Institutes of Health grants 1 U54 NS39407 (M.A.H.), HL 50527 (M.A.H.), and HL 62527 (R.J.M.).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dreshaj, I., Haxhiu, M., Martin, R. et al. The Basomedial Hypothalamus Modulates the Ventilatory Response to Hypoxia in Neonatal Rats. Pediatr Res 53, 945–949 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000064584.67771.82
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000064584.67771.82
This article is cited by
-
Suprapontine Structures Modulate Brainstem and Spinal Networks
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2023)