Abstract
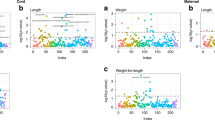
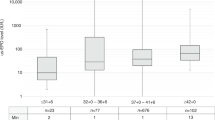
The leptin to fat ratio early in life could contribute to fixing the set point of leptin feedback at the hypothalamic level. Subjects from Asian and Caucasian ethnicities differ in body composition. We tested the hypothesis that anthropometric markers and their relationship to umbilical cord leptin, cortisol and cortisone, DHEAs and oestriol differed between Caucasians and Asians at birth. Birthweight, length, arm, calf and abdominal circumferences, scapular, triceps, quadriceps and abdominal skinfolds were measured in 180 healthy, full-term newborns of Asian and Caucasian ethnicities. Leptin and steroid hormone concentrations were determined in umbilical cord plasma. There was a significant difference in the slope of the regression between leptin and birthweight (p = 0.03) and calf circumference (p = 0.05) between male Caucasian and Asian neonates. In contrast, in female neonates, there was no significant difference (p = 0.099 and p = 0.07 for birthweight and calf circumference, respectively). In addition, while the slopes of the regression plots were not affected by gender in Asian newborns, there was a significant difference between male and female Caucasian newborns (p = 0.006 and p = 0.002 for birthweight and calf circumference, respectively). There was no significant correlation between cord leptin concentrations or anthropometric markers and steroid hormone concentrations. In conclusion, gender and ethnic differences in the relationship between leptin and anthropometric markers are detectable at birth between Asians and Caucasians, two ethnic groups that have been demonstrated to have different body compositions later in life. This may represent the first clinical evidence of a difference in leptin regulation between these two ethnic groups.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- BMI:
-
body mass index
- DHEAs:
-
dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate
REFERENCES
Wauters M, Considine RV, Van Gaal LF 2000 Human leptin: from an adipocyte hormone to an endocrine mediator. Eur J Endocrinol 143: 293–311
Schwartz MW, Woods SC, Porte D, Seeley RJ, Baskin DG 2000 Central nervous system control of food intake. Nature 404: 661–671
Considine RV, Sinha MK, Heiman ML, Kriauciunas A, Stephens TW, Nyce MR, Ohannesian JP, Marco CC, McKee LJ, Bauer TL 1996 Serum immunoreactive-leptin concentrations in normal-weight and obese humans. N Engl J Med 334: 292–295
Matsuda J, Yokota I, Iida M, Murakami T, Naito E, Ito M, Shima K, Kuroda Y 1997 Serum leptin concentration in cord blood: relationship to birth weight and gender. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82: 1642–1644
Schubring C, Kiess W, Englaro P, Rascher W, Dotsch J, Hanitsch S, Attanasio A, Blum WF 1997 Levels of leptin in maternal serum, amniotic fluid, and arterial and venous cord blood: relation to neonatal and placental weight. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82: 1480–1483
Sivan E, Lin WM, Homko CJ, Reece EA, Boden G 1997 Leptin is present in human cord blood. Diabetes 46: 917–919
Hartmann BW, Wagenbichler P, Soregi G 1997 Maternal and umbilical-cord serum leptin concentrations in normal, full-term pregnancies. N Engl J Med 337: 863
Shekhawat PS, Garland JS, Shivpuri C, Mick GJ, Sasidharan P, Pelz CJ, McCormick KL 1998 Neonatal cord blood leptin: its relationship to birth weight, body mass index, maternal diabetes, and steroids. Pediatr Res 43: 338–343
Maffeis C, Moghetti P, Vettor R, Lombardi AM, Vecchini S, Tato L 1999 Leptin concentration in newborn's cord blood: relationship to gender and growth-regulating hormones. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 23: 943–947
Christou H, Connors JM, Ziotopoulou M, Hatzidakis V, Papathanassoglou E, Ringer SA, Mantzoros CS 2001 Cord blood leptin and insulin-like growth factor levels are independent predictors of fetal growth. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86: 935–938
Proietto J, Thorburn AW 1994 Animal models of obesity–theories of aetiology. Baillieres Clin Endocrinol Metab 8: 509–525
Ravelli AC, van Der Meulen JH, Osmond C, Barker DJ, Bleker OP 1999 Obesity at the age of 50 y in men and women exposed to famine prenatally. Am J Clin Nutr 70: 811–816
Singhal A, Farooqi IS, O'Rahilly S, Cole TJ, Fewtrell M, Lucas A 2002 Early nutrition and leptin concentrations in later life. Am J Clin Nutr 75: 993–999
Masuzaki H, Ogawa Y, Isse N, Satoh N, Okazaki T, Shigemoto M, Mori K, Tamura N, Hosoda K, Yoshimasa Y 1995 Human obese gene expression. Adipocyte-specific expression and regional differences in the adipose tissue. Diabetes 44: 855–858
Montague CT, Prins JB, Sanders L, Zhang J, Sewter CP, Digby J, Byrne CD, O'Rahilly S 1998 Depot-related gene expression in human subcutaneous and omental adipocytes. Diabetes 47: 1384–1391
Deurenberg-Yap M, Schmidt G, van Staveren WA, Deurenberg P 2000 The paradox of low body mass index and high body fat percentage among Chinese, Malays and Indians in Singapore. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 24: 1011–1017
Wang J, Thornton JC, Russell M, Burastero S, Heymsfield S, Pierson RN 1994 Asians have lower body mass index (BMI) but higher percent body fat than do whites: comparisons of anthropometric measurements. Am J Clin Nutr 60: 23–28
Malina RM, Huang YC, Brown KH 1995 Subcutaneous adipose tissue distribution in adolescent girls of four ethnic groups. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 19: 793–797
He Q, Horlick M, Thornton J, Wang J, Pierson RN, Heshka S, Gallagher D 2002 Sex and race differences in fat distribution among Asian, African-American, and Caucasian prepubertal children. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87: 2164–2170
McConway MG, Johnson D, Kelly A, Griffin D, Smith J, Wallace AM 2000 Differences in circulating concentrations of total, free and bound leptin related to gender and body composition in humans. Ann Clin Biochem 37: 717–723
Considine RV 2001 Regulation of leptin production. Rev Endocr Metab Dis 2: 357–363
Wabitsh M, Jensen PB, Blum WF, Christoffersen CT, Englaro P, Heinze E, Rascher W, Teller W, Tornqvist H, Hauner H 1996 Insulin and cortisol promote leptin production in cultured human fat cells. Diabetes 45: 1435–1438
Askari H, Liu J, Dagogo-Jack S 2000 Hormonal regulation of human leptin in vivo: effects of hydrocortisone and insulin. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 24: 1254–1259
Duncan GJ, Daly MC, McDonough P, Williams DR 2002 Optimal indicators of socioeconomic status for health research. Am J Public Health 92: 1151–1157
Weber B, Lewicka S, Deuschle M, Colla M, Vecsei P, Heuser I 2000 Increased diurnal plasma concentrations of cortisone in depressed patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85: 1133–1136
Lepercq J, Challier JC, Guerre-Millo M, Cauzac M, Vidal H, Hauguel-de Mouzon S 2001 Prenatal leptin production: evidence that fetal adipose tissue produces leptin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86: 2409–2413
Jaquet D, Leger J, Levy-Marchal C, Oury JF, Czernichow P 1998 Ontogeny of leptin in human fetuses and newborns: effect of intrauterine growth retardation on serum leptin concentrations. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83: 1243–1246
Ashworth CJ, Hoggard N, Thomas L, Mercer JG, Wallace JM, Lea RG 2000 Placental leptin. Rev Reprod 5: 18–24
Hoggard N, Crabtree J, Allstaff S, Abramovich DR, Haggarty P 2001 Leptin secretion to both the maternal and fetal circulation in the ex vivo perfused human term placenta. Placenta 22: 347–352
de Bruin NC, van Velthoven KAM, Stijnen T, Juttmann RE, Degenhart HJ, Visser HKA 1995 Body fat and fat-free mass in infants: new and classic anthropometric indexes and prediction equations compared with total-body electrical conductivity. Am J Clin Nutr 61: 1195–1205
Tam SYM, Karlberg JPE, Kwan EYW, Tsang AMC, Sheng THP, He Q, Low LCK 1999 Body mass index is different in normal Chinese and Caucasian infants. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 12: 507–517
Hamill PVV, Drizd TA, Johnson CL, Reed RB, Roche AF 1977 NCHS growth curves for children, birth-18 years, United States. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics, DHEW Publication Number(PHS) 78–1650.
Le Stunff C, Le Bihan C, Schork NJ, Bougneres P 2000 A common promoter variant of the leptin gene is associated with changes in the relationship between serum leptin and fat mass in obese girls. Diabetes 49: 2196–2200
Speroff L, Glass RH, Kase NG 1999 Clinical Gynecologic Endocrinology and Infertility, 6th Ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 275–335.
Perry L, Hickson R, Obiekwe BC, Chard T 1986 Maternal oestriol levels reflect placental function rather than fetal function. Acta Endocrinol 111: 563–566
Parker CR, Leveno K, Carr BR, Hauth J, MacDonald PC 1982 Umbilical cord plasma levels of dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate during human gestation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 54: 1216–1220
Mesiano S, Katz SL, Lee JY, Jaffe RB 1999 Phytoestrogens alter adrenocortical function: genistein and daidzein suppress glucocorticoid and stimulate androgen production by cultured adrenal cortical cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84: 2443–2448
Kao YC, Zhou C, Sherman M, Laughton CA, Chen S 1998 Molecular basis of the inhibition of human aromatase (estrogen synthetase) by flavone and isoflavone phytoestrogens: A site-directed mutagenesis study. Environ Health Perspect 106: 85–92
O'Brien JE, Dvorin E, Drugan A, Johnson MP, Yaron Y, Evans MI 1997 Race-ethnicity-specific variation in multiple-marker biochemical screening: alpha-fetoprotein, hCG, and estriol. Obstet Gynecol 89: 355–358
Stewart PM, Rogerson FM, Mason JI 1995 Type 2 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase messenger ribonucleic acid and activity in human placenta and fetal membranes: its relationship to birth weight and putative role in fetal adrenal steroidogenesis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 80: 885–890
Rogerson FM, Kayes KM, White PC 1997 Variation in placental type 2 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity is not related to birth weight or placental weight. Mol Cell Endocrinol 128: 103–109
Shams M, Kilby MD, Somerset DA, Howie AJ, Gupta A, Wood PJ, Afnan M, Stewart PM 1998 11Beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 in human pregnancy and reduced expression in intrauterine growth restriction. Hum Reprod 13: 799–804
Seckl JR, Cleasby M, Nyirenda MJ 2000 Glucocorticoids, 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, and fetal programming. Kidney Int 57: 1412–1417
Kirel B, Tekin N, Tekin B, Kilic FS, Dogruel N, Aydogdu SD 2000 Cord blood leptin levels: relationship to body weight, body mass index, sex and insulin and cortisol levels of maternal-newborn pairs at delivery. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 13: 71–77
Acknowledgements
We thank the nurses of the delivery room at Children's and Women's Hospital for their assistance in the collection of the cord-blood samples and the technicians of the endocrine laboratory for processing the hormonal samples. The expert statistical help from Lee Shean Er, Statistician, British Columbia's Cardiac Registry at St-Paul's Hospital, Vancouver, is also gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeung, L., Wong, A., Wang, X. et al. Different Relationship Between Anthropometric Markers and Umbilical Cord Plasma Leptin in Asian and Caucasian Neonates. Pediatr Res 53, 1019–1024 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000067140.75177.ED
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000067140.75177.ED