Abstract
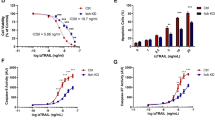
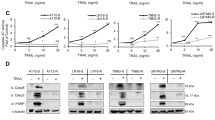
Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL/Apo2L) is a potent inducer of apoptosis in various cancer cells, whereas normal cells are not sensitive to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis. Four TRAIL/Apo2L receptors (DR4, DR5, DcR1, and DcR2) have been identified. DR4 and DR5 have a death domain, whereas DcR1 and DcR2 are called decoy receptors because of their incomplete or lack of a death domain. Malignant rhabdoid tumor (MRT) is an aggressive neoplasm showing a poor prognosis because of its resistance to chemotherapeutic agents. In this study, we examined whether TRAIL could induce apoptotic cell death in MRT cell lines. We found that although half of the MRT cell lines examined were sensitive to TRAIL/Apo2L, Western blot analysis revealed that the expression of DcR2 was low in TRAIL-sensitive MRT cells. We examined the effect of doxorubicin on the expression levels of TRAIL receptors and its enhancement on the susceptibility of MRT cell lines to TRAIL. Western blot and flow cytometric analyses revealed that doxorubicin significantly increased the expression of DR5, and somewhat up-regulated the expression of DR4 and DcR2. Moreover, doxorubicin, NF-κB inhibitor (SN50), and PI3-kinase/Akt inhibitor (wortmannin, LY294002) enhanced the susceptibility of MRT cell lines to TRAIL/Apo2L-induced apoptosis. These results suggest that TRAIL/Apo2L may provide the basis for clinical trials of TRAIL-based treatment to improve the outcome of MRT patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- MRT:
-
malignant rhabdoid tumor
- TNF:
-
tumor necrosis factor
- TRAIL/Apo2L:
-
tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand or Apo2 ligand
- NF-κB:
-
nuclear factor-κB
- PI3-kinase:
-
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- PI:
-
propidium iodide
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide
REFERENCES
Beckwith JB, Palmer NF 1978 Histopathology and prognosis of Wilms' tumor: Results from the first National Wilms' Tumor study. Cancer 41: 1937–1948
Biggs PJ, Garen PD, Powers JM, Garvin AJ 1987 Malignant rhabdoid tumor of the central nervous system. Hum Pathol 18: 332–337
Jakate SM, Marsden HB, Ingram L 1988 Primary rhabdoid tumor of brain. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol 412: 393–397
Blatt J, Russo P, Taylor S 1986 Extrarenal rhabdoid sarcoma. Med Pediatr Oncol 14: 221–226
Frierson HF, Mills SE, Inners DJ 1985 Malignant rhabdoid tumor of the pelvis. Cancer 55: 1963–1967
Schmidt D, Leuschner I, Harms D, Sprenger E, Schafer HJ 1989 Malignant rhabdoid tumor: a morphological and flow cytometric study. Pathol Res Pract 184: 202–210
Lynch HT, Shurin SB, Dahms BB, Izant RJ, Lynch J, Danes BS 1983 Paravertebral malignant rhabdoid tumor in infancy: in vitro studies of a familial tumor. Cancer 52: 290–296
Haas JE, Palmer NF, Weinberg AG, Beckwith JB 1981 Ultrastructure of malignant rhabdoid tumor of the kidney: a distinctive renal tumor of children. Hum Pathol 12: 646–657
Yoshida S, Narita T, Taga T, Ohta S, Takeuchi Y 2002 Malignant rhabdoid tumor shows incomplete neural characteristics as revealed by expression of SNARE complex. J Neurosci Res 69: 642–652
Rorke LB, Packer RJ, Biegel JA 1996 Central nervous system atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors of infancy and childhood: definition of an entity. J Neurosurg 85: 56–65
Packer RJ, Biegel JA, Blaney S, Finlay J, Geyer JR, Heideman R, Hilden J, Janss AJ, Kun L, Vezina G, Rorke LB, Smith M 2002 Atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor of the central nervous system: report on workshop. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 24: 337–342
Biegel JA, Tan L, Zhang F, Wainwright L, Russo P, Rorke LB 2002 Alterations of theh hSNF5/INI1 gene in central nervous system atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors and renal and extrarenal rhabdoid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 8: 3461–3467
Versteege I, Sevenet N, Lange J, Rousseau-Merk MF, Ambros P, Handgretinger R, Aurias A, Delattre O 1998 Truncating mutations of hSNF5/INI1 in aggressive paediatric cancer. Nature 394: 203–206
Walczak H, Miller RE, Ariail K, Gliniak B, Griffith TS, Kubin M, Chin W, Jones J, Woodward A, Le T, Smith C, Smolak P, Goodwin RG, Rauch CT, Schuh JC, Lynch DH 1999 Tumoricidal activity of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in vivo. Nat Med 5: 157–163
Ashkenazi A, Dixit VM 1999 Apoptosis control by death and decoy receptors. Curr Opin Cell Biol 11: 225–260
Walczak H, Degli-Esposti MA, Johnson RS, Smolak PJ, Waugh JY, Boiani N, Timour MS, Gerhart MJ, Schooley KA, Smith CA, Goodwin RG, Rauch CT 1997 TRAIL-R2: a novel apoptosis-mediating receptor for TRAIL. EMBO J 16: 5386–5397
Griffith TS, Chin WA, Jackson GC, Lynch DH, Kubin MZ 1998 Intracellular regulation of TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human melanoma cells. J Immunol 161: 2833–2840
Bodmer JL, Holler N, Reynard S, Vinciguerra P, Schneider P, Juo P, Blenis J, Tschopp J 2000 TRAIL receptor-2 signals apoptosis through FADD and caspase-8. Nat Cell Biol 2: 241–243
Kim EJ, Suliman A, Lam A, Srivastava RK 2001 Failure of Bcl-2 to block mitochondrial dysfunction during TRAIL-induced apoptosis: tumor necrosis-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. Int J Oncol 18: 187–194
Suliman A, Lam A, Datta R, Srivastava RK 2001 Intracellular mechanism of TRAIL: apoptosis through mitochondrial-dependent and -independent pathways. Oncogene 20: 2122–2133
Pitti RM, Marsters SA, Ruppert S, Donahue CJ, Moore A, Ashkenazi A 1996 Induction of apoptosis by Apo-2 ligand, a new member of the tumor necrosis factor cytokine family. J Biol Chem 271: 12687–12690
Wiley SR, Schooley K, Smolak PJ, Din WS, Huang CP, Nicholl JK, Sutherland GR, Smith TD, Rauch C, Smith CA 1995 Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity 3: 673–682
French LE, Tschopp J 1999 The TRAIL to selective tumor death. Nat Med 5: 146–147
Gura T 1997 How TRAIL kills cancer cells, but not normal cells. Science 277: 768
Rieger J, Naumann U, Glaser T, Ashkenazi A, Weller M 1998 APO2 ligand: a novel lethal weapon against malignant glioma?. FEBS Lett 427: 124–128
Pan G, Ni J, Wei Y-F, Yu G-L, Goodwin R, Dixit V M 1997 An antagonist decoy receptor and a death domain-containing receptor for TRAIL. Science 277: 815–818
Sheridan JP, Masters SA, Pitti RM, Gurney A, Skubatch M, Baldwin D, Ramakrishnan L, Gray CL, Baker K, Wood WI, Goddard AD, Godowski P, Askenazi A 1997 Control of TRAIL-induced apoptosis by a family of signaling and decoy receptors. Science 277: 818–821
Pan G, Ni J, Yu G-L, Wei Y-F, Dixit V M 1998 TRUNDD, a new member of the TRAIL receptor family that antagonizes TRAIL signaling. FEBS Lett 424: 41–45
van Noesel MM, van Bezouw S, Salomons GS, Voute PA, Pieters R, Baylin SB, Herman JG, Versteeg R 2002 Tumor-specific down-regulation of the tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand decoy receptors DcR1 and DcR2 is associated with dense promoter hypermethylation. Cancer Res 62: 2157–2161
Keane MM, Ettenberg SA, Nau MM, Russell EK, Lipkowitz S 1999 Chemotherapy augments TRAIL-induced apoptosis in breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 59: 734–741
Mitsiades CS, Treon SP, Mitsiades N, Shima Y, Richardson P, Schlossman R, Hideshima T, Anderson KC 2001 TRAIL/Apo2L ligands selectivity induces apoptosis and overcomes drug resistance in multiple myeloma: therapeutic applications. Blood 98: 795–804
Orban Z, Mitsiades N, Burke TR, Tsokos M, Chrousos GP 2000 Caffeic acid leukocyte phenethyl ester induces apoptosis, modulates nuclear factor-kappa B and suppresses acute inflammation. Neuroimmunomodulation 7: 99–105
Barkett M, Gilmore TD 1999 Control of apoptosis by Rel/NF-κB transcription factors. Oncogene 18: 6910–6924
Lin YZ, Yao SY, Veach RA, Torgerson TR, Hawiger J 1995 Inhibition of nuclear translocation of transcription factor NF-kappa B by a synthetic peptide containing a cell membrane-permeable motif and nuclear localization sequence. J Biol Chem 270: 14255–14258
Taylor CC 2000 Platelet-derived growth factor activates porcine thecal cell phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase-Akt/PKB and ras-extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1/2 kinase signaling pathways via the platelet-derived growth factor-beta receptor. Endocrinology 141: 1545–1553
Datta SR, Dudek H, Tao X, Masters S, Fu H, Gotoh Y, Greenberg ME 1997 Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples survival signals to the cell intrinsic death machinery. Cell 91: 231–241
Cardone MH, Roy N, Stennicke HR, Salvesen GS, Franke TF, Stanbridge E, Frisch S, Reed JC 1998 Regulation of cell death protease caspase-9 by phosphorylation. Science 282: 1318–1321
Romashkova JA, Makarov SS 1999 NF-kappaB is a target of AKT in anti-apoptotic PDGF signaling. Nature 401: 86–90
Ozes ON, Mayo LD, Gustin JA, Pfeffer SR, Pfeffer LM, Donner DB 1999 NF-kappaB activation by tumour necrosis factor requires the Akt serine-threonine kinase. Nature 401: 82–85
Uno K, Takita J, Yokomori K, Tanaka Y, Ohta S, Shimada H, Floyd H, Sugita K, Abe S, Sako M, Hashizume K, Hayashi Y 2002 Aberrations of the hSNF5/INI1 gene are restricted to malignant rhabdoid tumors or atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors in pediatric solid tumors. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 34: 33–41
Zhao S, Asgary Z, Wang Y, Goodwin R, Andereff M, Younes A 1999 Functional expression of TRAIL by lymphoid and myeloid tumor cells. Br J Haematol 106: 827–832
Gazitt Y, Shaughnessy P, Montgomery W 1999 Apoptosis-induced by TRAIL and TNF-alpha in human multiple myeloma cells is not blocked by BCL-2. Cytokine 11: 1010–1019
Gazitt Y 1999 TRAIL is a potent inducer of apoptosis in myeloma cells derived from multiple myeloma patients and is not cytotoxic to hematopoietic stem cells. Leukemia 13: 1817–1824
Bonavida B, Ng CP, Jazirehi A, Schiller G, Mizutani Y 1999 Selectivity of TRAIL-mediated apoptosis of cancer cells and synergy with drugs: the trail to non-toxic cancer therapeutics [review]. Int J Oncol 15: 793–802
Tschopp J, Irmler M, Thome M 1998 Inhibition of fas death signals by FLIPs. Curr Opin Immunol 10: 552–558
Higuchi H, Bronk SF, Taniai M, Canbay A, Gores GJ 2002 Cholestasis increases tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-R2/DR5 expression and sensitizes the liver to TRAIL-mediated cytotoxicity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 303: 461–467
Wen J, Ramadevi N, Nguyen D, Perkins C, Worthington E, Bhalla K 2000 Antileukemic drugs increase death receptor 5 levels and enhance Apo-2L-induced apoptosis of human acute leukemia cells. Blood 96: 3900–3906
Zhang X, Franco A, Myers K, Gray C, Nguyen T, Hersey P 1999 Relation of TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) receptor and FLICE-inhibitory protein expression to TRAIL-induced apoptosis of melanoma. Cancer Res 59: 2747–2753
Pai SI, Wu GS, Ozoren N, Wu L, Jen J, Sidransky D, El-Deiry WS 1998 Rare loss-of-function mutation of death receptor gene in head and neck cancer. Cancer Res 58: 3515–3518
Lee SH, Shin MS, Kim HS, Lee HK, Park WS, Kim SY, Lee JH, Han SY, Park JY, Oh RR, Jang JJ, Han JY, Lee JY, Yoo NJ 1999 Alterations of the DR5/TRAIL receptor 2 gene in non-small cell lung cancers. Cancer Res 59: 5683–5686
Wu M, Das A, Tan Y, Zhu C, Cui T, Wong MC 2000 Induction of apoptosis in glioma cell lines by TRAIL/Apo-2L. J Neurosci Res 61: 464–470
Zhang X, Franco AV, Nguyen T, Gray CP, Hersey P 2000 Differential localization and regulation of death and decoy receptors for TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) in human melanoma cells. J Immunol 164: 3961–3970
Kim K, Fisher MJ, Xu SQ, el-Deiry WS 2000 Molecular determinants of response to TRAIL in killing of normal and cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 6: 335–346
Wu GS, Burns TF, McDonald ER, Jiang W, Meng R, Krantz ID, Kao G, Gan DD, Zhou JY, Muschel R, Hamilton SR, Spinner NB, Markowitz S, Wu G, el-Deiry WS 1997 KILLER/DR5 is a DNA damage-inducible p53-regulated receptor gene. Nat Genet 17: 141–143
Sheikh MS, Burns TF, Huang Y, Wu GS, Amundson S, Brooks KS, Fornace AJ, el-Deiry WS 1998 p53-dependent and -independent regulation of the death receptor KILLER/DR5 gene expression in response to genotoxic stress and tumor necrosis factor alpha. Cancer Res 58: 1593–1598
Nagane M, Pan G, Weddle JJ, Dixit VM, Cavenee WK, Huang HJ 2000 Increased death receptor 5 expression by chemotherapeutic agents in human gliomas causes synergistic cytotoxicity with tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res 60: 847–856
Gibson SB, Oyer R, Spalding AC, Anderson SM, Johnson GL 2000 Increased expression of death receptor 4 and 5 synergized the apoptosis response to combined treatment with etoposide and TRAIL. Mol Cell Biol 20: 205–212
Degli-Esposti MA, Dougall WC, Smolak PJ, Waugh JY, Smith CA, Goodwin RG 1997 The novel receptor TRAIL-R4 induces NF-kappa B and protects against TRAIL-mediated apoptosis, yet retains an incomplete death domain. Immunity 7: 818–820
Schneider P, Thome M, Burns K, Bodmer JL, Hofmann K, Kataoka T, Holler N, Tschopp J 1997 TRAIL receptors 1 (DR4) and 2 (DR5) signal FADD-dependent apoptosis and activate NF-kappa B. Immunity 7: 831–836
Lin Y, Devin A, Cook A, Keane MM, Kelliher M, Lipkowitz S, Liu ZG 2000 The death domain kinase RIP is essential for TRAIL (Apo2L)-induced activation of Ikappa B kinase and c-Jun N-terminal kinase. Mol Cell Biol 20: 6638–6645
Oya M, Ohtsubo M, Takayanagi A, Tachibana M, Shimizu N, Murai M 2001 Constitutive activation of nuclear factor-kappaB prevents TRAIL-induced apoptosis in renal cancer cells. Oncogene 20: 3888–3896
Keane MM, Rubinstein Y, Cuello M, Ettenberg SA, Banerjee P, Nau MM, Lipkowitz S 2000 Inhibition of NF-kappaB activity enhances TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in breast cancer cell lines. Breast Cancer Res Treat 64: 211–219
Chen X, Thakkar H, Tyan F, Gim S, Robinson H, Lee C, Pandey SK, Nwokorie C, Onwudiwe N, Srivastava RK 2001 Constitutively active Akt is an important regulator of TRAIL sensitivity in prostate cancer. Oncogene 42: 6073–6083
Nesterov A, Lu X, Johnson M, Miller GJ, Ivashchenko Y, Kraft AS 2001 Elevated AKT activity protects the prostate cancer cell line LNCaP from TRAIL-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 276: 10767–10774
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Timothy J Triche, Dr. Hiroyuki Shimada (Children's Hospital, Los Angeles, CA), and Dr. Kanji Sugita (Yamanashi Medical University. Kofu). We also thank Masaki Suzaki (Central Research Laboratory, Shiga University of Medical Science).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported in part by the Grant of Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japanese Government Grant-in-aid(C) No.14570741 and (A) No. 14207071.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshida, S., Narita, T., Koshida, S. et al. TRAIL/Apo2L Ligands Induce Apoptosis in Malignant Rhabdoid Tumor Cell Lines. Pediatr Res 54, 709–717 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000085038.53151.D0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000085038.53151.D0
This article is cited by
-
Fenretinide-dependent upregulation of death receptors through ASK1 and p38α enhances death receptor ligand-induced cell death in Ewing's sarcoma family of tumours
British Journal of Cancer (2010)
-
Dependence on PI3K/Akt signaling for malignant rhabdoid tumor cell survival
Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology (2009)