Abstract
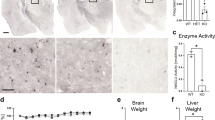
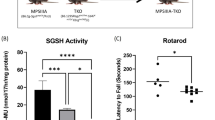
Mucopolysaccharidosis type IIIA (MPS IIIA; Sanfilippo syndrome) is a lysosomal storage disorder characterized by severe CNS degeneration, resulting in behavioral abnormalities and loss of learned abilities. Early treatment is vital to prevent long-term clinical pathology in lysosomal storage disorders. We have used naturally occurring MPS IIIA mice to assess the effects of long-term enzyme-replacement therapy initiated either at birth or at 6 wk of age. MPS IIIA and normal control mice received weekly i.v. injections of 1 mg/kg recombinant human sulfamidase until 20 wk of age. Sulfamidase is able to enter the brain until the blood-brain barrier completely closes at 10–14 d of age. MPS IIIA mice that were treated from birth demonstrated normal weight, behavioral characteristics, and ability to learn. MPS IIIA mice that were treated from birth performed significantly better in the Morris water maze than MPS IIIA mice that were treated from 6 wk of age or left untreated. A reduction in storage vacuoles in cells of the CNS in MPS IIIA mice that were treated from birth is consistent with the improvements observed. These data suggest that enzyme that enters the brain in the first few weeks of life, before the blood-brain barrier matures, is able to delay the development of behavior and learning difficulties in MPS IIIA mice.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- BBB:
-
blood-brain barrier
- ERT:
-
enzyme-replacement therapy
- LSD:
-
lysosomal storage disorder
- MPS:
-
mucopolysaccharidosis
- rhNS:
-
recombinant human sulfamidase
References
Neufeld EF, Muenzer J 2001 The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 3421–3452.
Meikle PJ, Hopwood JJ, Clague AE, Carey WF 1999 Prevalence of lysosomal storage disorders. JAMA 281: 249–254.
Cleary MA, Wraith JE 1993 Management of mucopolysaccharidosis type III. Arch Dis Child 69: 403–406.
Yogalingam G, Hopwood JJ 2001 Molecular genetics of mucopolysaccharidosis type IIIA and IIIB: diagnostic, clinical and biological implications. Hum Mutat 18: 264–281.
Bhaumik M, Muller VJ, Rozaklis T, Johnson L, Dobrenis K, Bhattacharyya R, Wurzelmann S, Finamore P, Hopwood JJ, Walkley SU, Stanley P 1999 A mouse model for mucopolysaccharidosis type IIIA (Sanfilippo syndrome). Glycobiology 9: 1389–1396.
Bhattacharyya R, Gliddon B, Beccari T, Hopwood JJ, Stanley P 2001 A novel missense mutation in lysosomal sulfamidase is the basis of MPS IIIA in a spontaneous mouse mutant. Glycobiology 11: 99–103.
Bond CS, Clements PR, Ashby SJ, Collyer CA, Harrop SJ, Hopwood JJ, Guss JM 1997 Structure of a human lysosomal sulfatase. Structure 5: 277–289.
Waldow A, Schmidt B, Dierks T, von Bulow R, von Figura K 1999 Amino acid residues forming the active site of arylsulfatase A. Role in catalytic activity and substrate binding. J Biol Chem 274: 12284–12288.
Hopwood JJ, Ballabio A 2001 The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Diseases. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 3725–3774.
Fischer A, Carmichael KP, Munnel JF, Jhabvala P, Thompson JN, Matalon R, Jezyk PF, Wang P, Giger U 1998 Sulfamidase deficiency in a family of Dachshunds: a canine model of mucopolysaccharidosis IIIA (Sanfilippo A). Pediatr Res 44: 74–82.
Jolly RD, Allan FJ, Collett MG, Rozaklis T, Muller VJ, Hopwood JJ 2000 Mucopolysaccharidosis IIIA (Sanfilippo syndrome) in a New Zealand Huntaway dog with ataxia. N Z Vet J 48: 144–148.
Li HH, Yu W-H, Rozengurt N, Zhao H-Z, Lyons KM, Anagnostaras S, Fanselow MS, Suzuki K, Vanier MT, Neufeld EF 1999 Mouse model of Sanfilippo syndrome type B produced by targeted disruption of the gene encoding α-N-acetylglucosaminidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96: 14505–14510.
Jones MZ, Alroy J, Boyer PJ, Cavanagh KT, Johnson K, Gage D, Vorro J, Render JA, Common RS, Leedle RA, Lowrie C, Sharp P, Liour S-S, Levene B, Hoard H, Lucas R, Hopwood JJ 1998 Caprine mucopolysaccharidosis-IIID: clinical, biochemical, morphological and immunohistochemical characteristics. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 57: 148–157.
Altarescu G, Hill S, Wiggs E, Jeffries N, Kreps C, Parker CC, Brady RO, Barton NW, Schiffmann R 2001 The efficacy of enzyme replacement therapy in patients with chronic neuronopathic Gaucher's disease. J Pediatr 138: 539–547.
Altarescu G, Schiffmann R, Parker CC, Moore DF, Kreps C, Brady RO, Barton NW 2000 Comparative efficacy of dose regimens in enzyme replacement therapy of type I Gaucher disease. Blood Cells Mol Dis 26: 285–290.
Schiffmann R, Kopp JB, Austin HA 3rd, Sabnis S Morre DF Weibel T Balow JE Brady RO 2001 Enzyme replacement therapy in Fabry disease: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 285: 2743–2749.
Eng CM, Guffon N, Wilcox WR, Germain DP, Lee P, Waldek S, Caplan L, Linthorst GE, Desnick RJ 2001 Safety and efficacy of recombinant human α-galactosidase A replacement therapy in Fabry's disease. N Engl J Med 345: 9–16.
Kakkis ED, Muenzer J, Tiller GE, Waber L, Belmont J, Passage M, Izykowski B, Phillips J, Doroshow R, Walot I, Hoft R, Neufeld EF 2001 Enzyme-replacement therapy in mucopolysaccharidosis I. N Engl J Med 344: 182–188.
Downs-Kelly E, Jones MZ, Alroy J, Cavanagh KT, King B, Lucas RE, Baker JC, Kraemer SA, Hopwood JJ 2000 Caprine mucopolysaccharidosis IIID: a preliminary trial of enzyme replacement therapy. J Mol Neurosci 15: 251–262.
Yu W-H, Zhao K-W, Ryazantsev S, Rozengurt N, Neufeld EF 2000 Short-term enzyme replacement in the murine model of Sanfilippo syndrome type B. Mol Genet Metab 71: 573–580.
Stewart PA, Hayakawa EM 1987 Interendothelial junctional changes underlie the developmental ‘tightening’ of the blood-brain barrier. Dev Brain Res 32: 271–281.
Vogler C, Sands M, Higgins A, Levy B, Grubb J, Birkenmeier EH, Sly WS 1993 Enzyme replacement with recombinant beta-glucuronidase in the newborn mucopolysaccharidosis type VII mouse. Pediatr Res 34: 837–840.
Sands MS, Vogler C, Kyle JW, Grubb JH, Levy B, Galvin N, Sly WS, Birkenmeier EH 1994 Enzyme replacement therapy for murine mucopolysaccharidosis type VII. J Clin Invest 93: 2324–2331.
O'Connor LH, Erway LC, Vogler CA, Sly WS, Nicholes A, Grubb J, Holmberg SW, Levy B, Sands MS 1998 Enzyme replacement therapy for murine mucopolysaccharidosis type VII leads to improvements in behavior and auditory function. J Clin Invest 101: 1394–1400.
Freeman C, Hopwood JJ 1986 Human liver sulphamate sulphohydrolase. Determinations of native protein and subunit Mr values and influence of substrate aglycone structure on catalytic properties. Biochem J 234: 83–92.
Scott HS, Blanch L, Guo XH, Freeman C, Orsborn A, Barker E, Sutherland GR, Morris CP, Hopwood JJ 1995 Cloning of the sulphamidase gene and identification of mutations in Sanfilippo A syndrome. Nat Genet 11: 465–467.
Bielicki J, Hopwood JJ, Melville EL, Anson DS 1998 Recombinant human sulphamidase: expression, amplification, purification and characterisation. Biochem J 329: 145–150.
Perkins KJ, Byers S, Yogalingam G, Weber B, Hopwood JJ 1999 Expression and characterisation of wild type and mutant recombinant human sulfamidase. Implications for Sanfilippo (mucopolysaccharidosis IIIA) syndrome. J Biol Chem 274: 37193–37199.
Whitfield PD, Nelson P, Sharp PC, Bindloss CA, Dean C, Ravenscroft EM, Fong BA, Fietz MJ, Hopwood JJ, Meikle PJ 2002 Correlation among genotype, phenotype, and biochemical markers in Gaucher disease: implications for the prediction of disease severity. Mol Genet Metab 45: 46–55.
Sands MS, Barker JE 1999 Percutaneous intravenous injection in neonatal mice. Lab Anim Sci 49: 328–330.
Turner CT, Hopwood JJ, Brooks DA 2000 Enzyme replacement therapy in mucopolysaccharidosis I: altered distribution and targeting of alpha-L-iduronidase in immunized rats. Mol Genet Metab 69: 277–285.
Morris R 1984 Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 11: 47–60.
Perkins KJ, Muller V, Weber B, Hopwood JJ 2001 Prediction of Sanfilippo phenotype severity from immunoquantification of heparan-N-sulfamidase in cultured fibroblasts from mucopolysaccharidosis type IIIA patients. Mol Genet Metab 73: 306–312.
Sands MS, Vogler C, Torrey A, Levy B, Gwynn B, Grubb J, Sly WS, Birkenmeier EH 1997 Murine mucopolysaccharidosis type VII: long term therapeutic effects of enzyme replacement followed by bone marrow transplantation. J Clin Invest 99: 1596–1605.
Baumkotter J, Cantz M 1983 Decreased ganglioside neuraminidase activity in fibroblasts from mucopolysaccharidosis patients: inhibition of the activity in vitro by sulfated glycosaminoglycans and other compounds. Biochim Biophys Acta 761: 163–170.
Avila JL, Convit J 1975 Inhibition of leucocytic lysosomal enzymes by glycosaminoglycans in vitro. Biochem J 152: 57–64.
Walkley SU 1998 Cellular pathology of lysosomal storage disorders. Brain Pathol 8: 175–193.
Platt FM, Jeyakumar M, Andersson U, Priestman DA, Dwek RA, Butters TD, Cox TM, Lachmann RH, Hollack C, Aerts JM, Van Weely S, Hrebicek M, Moyses C, Gow I, Elstein D, Zimran A 2001 Inhibition of substrate synthesis as a strategy for glycolipid lysosomal storage disease therapy. J Inherit Metab Dis 24: 275–290.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the animal care staff at the WCH for daily care of the mouse colony. We thank Peter Clements, Liz Melville, and Vivienne Muller for supplying rhNS and substrate. Allison Crawley is gratefully acknowledged for assistance with histologic analysis and Mark Sands for expert guidance regarding the Morris water maze and superficial temporal vein injections. Assistance from Elaine Ravenscroft is greatly appreciated, as is technical assistance from Lyn Waterhouse and Craig Hirte. The original MPS IIIA mice were given by Pamela Stanley from the Albert Einstein Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by a Sam Lister PhD scholarship to B.G. and the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gliddon, B., Hopwood, J. Enzyme-Replacement Therapy from Birth Delays the Development of Behavior and Learning Problems in Mucopolysaccharidosis Type IIIA Mice. Pediatr Res 56, 65–72 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000129661.40499.12
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000129661.40499.12
This article is cited by
-
Glycosaminoglycan levels and structure in a mucopolysaccharidosis IIIA mice and the effect of a highly secreted sulfamidase engineered to cross the blood-brain barrier
Metabolic Brain Disease (2017)
-
Mucopolysaccharidosis IIIB confers enhanced neonatal intracranial transduction by AAV8 but not by 5, 9 or rh10
Gene Therapy (2016)
-
Liver Production of Sulfamidase Reverses Peripheral and Ameliorates CNS Pathology in Mucopolysaccharidosis IIIA Mice
Molecular Therapy (2012)
-
Lessons learnt from animal models: pathophysiology of neuropathic lysosomal storage disorders
Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease (2010)
-
Mannitol-facilitated CNS entry of rAAV2 vector significantly delayed the neurological disease progression in MPS IIIB mice
Gene Therapy (2009)