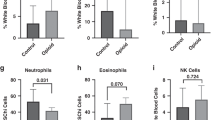
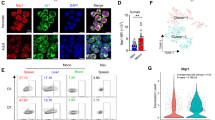
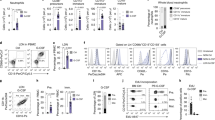
Abstract
Apoptosis, which leads to phagocytosis by mononuclear cells, represents the primary mechanism for removing neutrophils from inflamed tissues and minimizing injury. The present studies show that membrane phosphatidylserine turnover and permeability, as well as DNA fragmentation, were reduced in neutrophils from neonates when compared with adults. The activity of caspase 3 and expression of the proapoptotic proteins Bax, Bad, and Bak were also decreased in neonatal relative to adult neutrophils. These findings are consistent with impaired apoptosis in neonatal cells, which may contribute to prolonged inflammation in infants after oxidative stress or infection. Neutrophil apoptosis is induced by endogenous ligands such as Fas (FasL), which engage death receptors of the tumor necrosis factor/nerve growth factor superfamily, including Fas receptor (FasR). We found that expression of FasR was decreased in neonatal when compared with adult cells. Moreover, neonatal neutrophils did not undergo apoptosis in response to anti-FasR antibody and exhibited impaired chemotaxis to soluble FasL. However, in both adult and neonatal cells, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors blocked Fas-induced activity. These data suggest that prolonged survival of neonatal neutrophils at injured sites is due, in part, to reduced responsiveness to FasL. This may be related to decreased expression of both FasR and Bcl-2–family proteins that mediate neutrophil apoptosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Hill HR 1987 Biochemical, structural, and functional abnormalities of polymorphonuclear leukocytes in the neonate. Pediatr Res 22: 375–382
Qing G, Rajaraman K, Bortolussi R 1995 Diminished priming of neonatal polymorphonuclear leukocytes by lipopolysaccharide is associated with reduced CD14 expression. Infect Immun 63: 248–252
Bortolussi R, Howlett S, Rajaraman K, Halperin S 1993 Deficient priming activity of newborn cord blood-derived polymorphonuclear neutrophilic granulocytes with lipopolysaccharide and tumor necrosis factor-α-triggered with formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine. Pediatr Res 34: 243–248
Abughali N, Dubyak G, Tosi MF 1993 Impairment of chemoattractant-stimulated hexose uptake in neonatal neutrophils. Blood 82: 2182–2187
Savill J 1997 Apoptosis in resolution of inflammation. J Leukoc Biol 61: 375–380
Savill J, Haslett C 1995 Granulocyte clearance by apoptosis in the resolution of inflammation. Semin Cell Biol 6: 385–393
Akgul C, Moulding DA, Edwards SW 2001 Molecular control of neutrophil apoptosis. FEBS Lett 487: 318–322
Renshaw SA, Timmons SJ, Eaton V, Usher LR, Akil M, Bingle CD, Whyte MK 2000 Inflammatory neutrophils retain susceptibility to apoptosis mediated via the Fas death receptor. J Leukoc Biol 67: 662–668
Tortorella C, Piazzolla G, Spaccavento F, Antonaci S 1998 Effects of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and cyclic AMP interaction on human neutrophil apoptosis. Mediators Inflamm 7: 391–396
Simon HU 2003 Neutrophil apoptosis pathways and their modifications in inflammation. Immunol Rev 193: 101–110
Moulding DA, Akgul C, Derouet M, White MR, Edwards SW 2001 BCL-2 family expression in human neutrophils during delayed and accelerated apoptosis. J Leukoc Biol 70: 783–792
Santos-Beneit AM, Mollinedo F 2000 Expression of genes involved in initiation, regulation, and execution of apoptosis in human neutrophils and during neutrophil differentiation of HL-60 cells. J Leukoc Biol 67: 712–72413
Hengartner MO 2000 The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature 407: 770–776
Hsieh SC, Huang MH, Tsai CY, Tsai YY, Tsai ST, Sun KH, Yu HS, Han SH, Yu CL 1997 The expression of genes modulating programmed cell death in normal human polymorphonuclear neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 233: 700–706
Oei J, Lui K, Wang H, Henry R 2003 Decreased neutrophil apoptosis in tracheal fluids of preterm infants at risk of chronic lung disease. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 88: F245–F249
Allgaier B, Shi M, Luo D, Koenig JM 1998 Spontaneous and Fas-mediated apoptosis are diminished in umbilical cord blood neutrophils compared with adult neutrophils. J Leukoc Biol 64: 331–336
Ferrante A, Thong YH 1980 Optimal conditions for simultaneous purification of mononuclear and polymorphonuclear leucocytes from human blood by the Hypaque-Ficoll method. J Immunol Methods 36: 109–117
Watanabe M, Hitomi M, van der Wee K, Rothenberg F, Fisher SA, Zucker R, Svoboda KK, Goldsmith EC, Heiskanen KM, Nieminen AL 2002 The pros and cons of apoptosis assays for use in the study of cells, tissues, and organs. Microsc Microanal 8: 375–391
Boyden S 1962 The chemotactic effect of mixtures of antibody and antigen on polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Exp Med 115: 453–466
Sgonc R, Gruber J 1998 Apoptosis detection: an overview. Exp Gerontol 33: 525–533
Nagata S 2000 Apoptotic DNA fragmentation. Exp Cell Res 256: 12–18
Orlofsky A, Weiss LM, Kawachi N, Prystowsky MB 2002 Deficiency in the anti-apoptotic protein A1-alpha results in a diminished acute inflammatory response. J Immunol 168: 1840–1846
Weinmann P, Gaehtgens P, Walzog B 1999 Bcl-Xl and Bax-α-mediated regulation of apoptosis of human neutrophils via caspase-3. Blood 93: 3106–3115
McDonnell MA, Wang D, Khan SM, Vander Heiden MG, Kelekar A 2003 Caspase-9 is activated in a cytochrome c-independent manner early during TNF-α-induced apoptosis in murine cells. Cell Death Differ 10: 1005–1015
Dibbert B, Weber M, Nikolaizik WH, Vogt P, Schoni MH, Blaser K, Simon HU 1999 Cytokine-mediated Bax deficiency and consequent delayed neutrophil apoptosis: a general mechanism to accumulate effector cells in inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 13330–13335
Liles WC, Klebanoff SJ 1995 Regulation of apoptosis in neutrophils—Fas track to death?. J Immunol 155: 3289–3291
Mannick JB, Hausladen A, Liu L, Hess DT, Zeng M, Miao QX, Kane LS, Gow AJ, Stamler JS 1999 Fas-induced caspase denitrosylation. Science 284: 651–654
Lile WC, Kiener PA, Ledbetter JA, Aruffo A, Klebanoff SJ 1996 Differential expression of Fas (CD95) and Fas ligand on normal human phagocytes: implications for the regulation of apoptosis in neutrophils. J Exp Med 184: 429–440
Alvarado-Kristensson M, Porn-Ares MI, Grethe S, Smith D, Zheng L, Andersson T 2001 p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activities have opposite effects on human neutrophil apoptosis. FASEB J 16: 129–131
Webb PR, Wang KQ, Scheel-Toellner D, Pongracz J, Salmon M, Lord JM 2000 Regulation of neutrophil apoptosis: a role for protein kinase C and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase. Apoptosis 5: 451–458
Tsujimoto Y 2003 Cell death regulation by the Bcl-2 protein family in the mitochondria. J Cell Physiol 195: 158–167
Brown SB, Savill J 1999 Phagocytosis triggers macrophage release of Fas ligand and induces apoptosis of bystander leukocytes. J Immunol 162: 480–485
Ottonello L, Tortolina G, Amellotti M, Dallegri F 1999 Soluble Fas ligand is chemotactic for human neutrophilic polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol 162: 3601–3606
Seino K, Iwabuchi K, Kayagaki N, Miyata R, Nagaoka I, Matsuzawa A, Fukao K, Yagita H, Okumura K 1998 Chemotactic activity of soluble Fas ligand against phagocytes. J Immunol 161: 4484–4488
Leuenroth S, Lee C, Grutkoski P, Keeping H, Simms HH 1998 Interleukin-8-induced suppression of polymorphonuclear leukocyte apoptosis is mediated by suppressing CD95 (Fas/Apo-1)-Fas-1 interactions. Surgery 124: 409–417
Le'Negrate G, Rostagno P, Auberger P, Rossi B, Hofman P 2003 Downregulation of caspases and Fas ligand expression, and increased lifespan of neutrophils after transmigration across intestinal epithelium. Cell Death Differ 10: 153–162
Colotta F, Re F, Polentarutti N, Sozzani S, Mantovani A 1992 Modulation of granulocyte survival and programmed cell death by cytokines and bacterial products. Blood 80: 2012–2020
Burg ND, Pillinger MH 2001 The neutrophil: function and regulation in innate and humoral immunity. Clin Immunol 99: 7–17
O'Brien D, O'Connor T, Shanahan F, O'Connell J 2002 Activation of the p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 pathways is required for Fas-induced IL-8 production in colonic epithelial cells. Ann NY Acad Sci 973: 161–165
Coulter KR, Doseff A, Sweeney P, Wang Y, Marsh CB, Wewers MD, Knoell DL 2002 Opposing effect by cytokines on Fas-mediated apoptosis in A549 lung epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 26: 58–66
Ivanov VN, Krasilnikov M, Ronai Z 2002 Regulation of Fas expression by STAT3 and c-Jun is mediated by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-AKT signaling. J Biol Chem 277: 4932–4944
Matute-Bello G, Liles WC, Radella F 2nd Steinberg KP, Ruzinski JT, Jonas M, Chi EY, Hudson LD, Martin TR 1997 Neutrophil apoptosis in the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 156: 1969–1977
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported by National Institutes of Health Grants HD42036, ES04738, ES05022, GM34310, and CA100994 and by a grant from the New Jersey Thoracic Society.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hanna, N., Vasquez, P., Pham, P. et al. Mechanisms Underlying Reduced Apoptosis in Neonatal Neutrophils. Pediatr Res 57, 56–62 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000147568.14392.F0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000147568.14392.F0
This article is cited by
-
Intermittent or sustained systemic inflammation and the preterm brain
Pediatric Research (2014)
-
Inflammatory Mediators in the Immunobiology of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology (2008)
-
Pulmonary inflammation and bronchopulmonary dysplasia
Journal of Perinatology (2006)