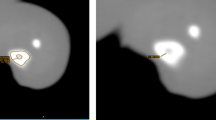
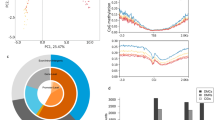
Abstract
There is evidence that intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) is associated with altered dopaminergic function in the immature brain. Compelling evidence exists that in the newborn brain, specific structures are especially vulnerable to O2 deprivation. The dopaminergic system is shown to be sensitive to O2 deprivation in the immature brain. However, the respective enzyme activities have not been measured in the living neonatal brain after IUGR under hypercapnic hypoxia (H/H). Therefore, 18F-labeled 6-fluoro-L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (FDOPA) together with positron emission tomography was used to estimate the aromatic amino acid decarboxylase activity of the brain of seven normal weight (body weight 2078 ± 434 g) and seven IUGR newborn piglets (body weight 893 ± 109 g). Two positron emission tomography scans were performed in each piglet. All animals underwent a period of normoxia and moderate H/H. Simultaneously, cerebral blood flow was measured with colored microspheres and cerebral metabolic rate of O2 was determined. In newborn normal-weight piglets, the rate constant for FDOPA decarboxylation was markedly increased in mesostriatal regions during H/H, whereas brain oxidative metabolism remained unaltered. In contrast, moderate H/H induced in IUGR piglets a marked reduction of clearance rates for FDOPA metabolites (p < 0.05), which was accompanied by a tendency of lowering the rate constant for FDOPA conversion. Furthermore, IUGR piglets maintained cerebral O2 uptake in the early period of H/H, but during the late period of H/H, a significantly reduced cerebral metabolic rate of O2 occurred (p < 0.05). Thus, IUGR is accompanied by a missing activation of dopaminergic activity and attenuated brain oxidative metabolism during moderate H/H. This may indicate endogenous brain protection against O2 deprivation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- AADC:
-
aromatic amino acid decarboxylase
- ADHD:
-
attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder
- CBF:
-
cerebral blood flow
- CMRO2:
-
cerebral metabolic rate of O2
- CVR:
-
cerebrovascular resistance
- DA:
-
dopamine
- FDA:
-
fluorodopamine
- FDOPA:
-
18F-labeled 6-fluoro-L-3, 4-dihydroxyphenylalanine
- H/H:
-
hypercapnic hypoxia
- IUGR:
-
intrauterine growth restriction
- K 1 FDOPA :
-
unidirectional clearance of FDOPA
- k 2 FDOPA :
-
regional rate constant for FDOPA backflux from the brain
- k 3 FDOPA :
-
apparent AADC activity
- k cl FDA+acids :
-
clearance rate constant for FDOPA metabolites
- MAP:
-
mean arterial blood pressure
- PET:
-
positron emission tomography
- PS FDOPA :
-
permeability-surface area product of FDOPA
References
Ashworth A 1998 Effects of intrauterine growth retardation on mortality and morbidity in infants and young children. Eur J Clin Nutr 52( suppl 1) S34–S41 S41–S42
Künzel W, Misselwitz B 2001 [Epidemiology of fetal growth retardation]. Gynäkologe 34: 784–792
Levene ML, Kornberg J, Williams TH 1985 The incidence and severity of post-asphyxial encephalopathy in full-term infants. Early Hum Dev 11: 21–26
Volpe JJ, Herscovitch P, Perlman JM, Kreusser KL, Raichle ME 1985 Positron emission tomography in the asphyxiated term newborn: parasagittal impairment of cerebral blood flow. Ann Neurol 17: 287–296
Vannucci RC 1997 Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: clinical aspects. In: Fanaroff AA, Martin RJ (eds) Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine. IV. Mosby-Year Book, Philadelphia pp 877–891
Menkes JH, Curran J 1994 Clinical and MR correlates in children with extrapyramidal cerebral palsy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 15: 451–457
Hoon AH Jr Reinhardt EM, Kelley RI, Breiter SN, Morton DH, Naidu SB, Johnston MV 1997 Brain magnetic resonance imaging in suspected extrapyramidal cerebral palsy: observations in distinguishing genetic-metabolic from acquired causes. J Pediatr 131: 240–245
Roland EH, Poskitt K, Rodriguez E, Lupton BA, Hill A 1998 Perinatal hypoxic-ischemic thalamic injury: clinical features and neuroimaging. Ann Neurol 44: 161–166
Johnston MV, Trescher WH, Ishida A, Nakajima W 2001 Neurobiology of hypoxic-ischemic injury in the developing brain. Pediatr Res 49: 735–741
Gordon K, Statman D, Johnston MV, Robinson TE, Becker JB, Silverstein FS 1990 Transient hypoxia alters striatal catecholamine metabolism in immature brain: an in vivo microdialysis study. J Neurochem 54: 605–611
Pastuszko A, Saadat Lajevardi N, Chen J, Tammela O, Wilson DF, Delivoria-Papadopoulos M 1993 Effects of graded levels of tissue oxygen pressure on dopamine metabolism in the striatum of newborn piglets. J Neurochem 60: 161–166
Nakajima W, Ishida A, Takada G 1996 Effect of anoxia on striatal monoamine metabolism in immature rat brain compared with that of hypoxia: an in vivo microdialysis study. Brain Res 740: 316–322
Huang CC, Lajevardi NS, Tammela O, Pastuszko A, Delivoria-Papadopoulos M, Wilson DF 1994 Relationship of extracellular dopamine in striatum of newborn piglets to cortical oxygen pressure. Neurochem Res 19: 649–655
Bauer R, Brust P, Walter B, Vorwieger G, Bergmann R, Elhalag E, Fritz A, Steinbach J, Fuchtner F, Hinz R, Zwiener U, Johannsen B 2002 Effect of hypoxia/hypercapnia on metabolism of 6-[(18)F]fluoro-L-DOPA in newborn piglets. Brain Res 934: 23–33
Globus MY, Ginsberg MD, Dietrich WD, Busto R, Scheinberg P 1987 Substantia nigra lesion protects against ischemic damage in the striatum. Neurosci Lett 80: 251–256
Ren Y, Li X, Xu ZC 1997 Asymmetrical protection of neostriatal neurons against transient forebrain ischemia by unilateral dopamine depletion. Exp Neurol 146: 250–257
Bauer R, Walter B, Vorwieger G, Bergmann R, Füchtner F, Brust P 2001 Intrauterine growth restriction induces up-regulation of cerebral aromatic amino acid decarboxylase activity in newborn piglets: [18F]fluorodopa positron emission tomographic study. Pediatr Res 49: 474–480
Bauer R, Walter B, Hoppe A, Gaser E, Lampe V, Kauf E, Zwiener U 1998 Body weight distribution and organ size in newborn swine (sus scrofa domestica)—a study describing an animal model for asymmetrical intrauterine growth retardation. Exp Toxicol Pathol 50: 59–65
De Roth L, Downie HG 1976 Evaluation of viability of neonatal swine. Can Vet J 17: 275–279
Walter B, Bauer R, Gaser E, Zwiener U 1997 Validation of the multiple colored microsphere technique for regional blood flow measurements in newborn piglets. Basic Res Cardiol 92: 191–200
Bauer R, Walter B, Wurker E, Kluge H, Zwiener U 1996 Colored microsphere technique as a new method for quantitative-multiple estimation of regional hepatic and portal blood flow. Exp Toxicol Pathol 48: 415–420
Makowski EL, Meschia G, Droegemueller W, Battaglia FC 1968 Measurement of umbilical arterial blood flow to the sheep placenta and fetus in utero. Distribution to cotyledons and the intercotyledonary chorion. Circ Res 23: 623–631
Coyle MG, Oh W, Stonestreet BS 1993 Effects of indomethacin on brain blood flow and cerebral metabolism in hypoxic newborn piglets. Am J Physiol 264: H141–H149
Namavari M, Bishop A, Satyamurthy N, Bida G, Barrio JR 1992 Regioselective radiofluorodestannylation with [18F]F2 and [18F]CH3COOF: a high yield synthesis of 6-[18F]fluoro-L-dopa. Int J Rad Appl Instrum [A] 43: 989–996
Brust P, Bauer R, Walter B, Bergmann R, Fuchtner F, Vorwieger G, Steinbach J, Johannsen B, Zwiener U 1998 Simultaneous measurement of [18F]FDOPA metabolism and cerebral blood flow in newborn piglets. Int J Dev Neurosci 16: 353–364
Vorwieger G, Brust P, Bergmann R, Bauer R, Walter B, Fuchtner F, Steinbach J, Johannsen B 1998 HPLC analysis of the metabolism of 6-[F-18]fluoro-L-DOPA in the brain of neonatal pigs. In: Carson RE, Daube Witherspoon ME, Herscovitch P (eds) Quantitative Functional Brain Imaging with Positron Emission Tomography. Academic Press, San Diego pp 285–292
Brix G, Zaers J, Adam LE, Bellemann ME, Ostertag H, Trojan H, Haberkorn U, Doll J, Oberdorfer F, Lorenz WJ 1997 Performance evaluation of a whole-body PET scanner using the NEMA protocol. National Electrical Manufacturers Association. J Nucl Med 38: 1614–1623
Brust P, Zessin J, Kuwabara H, Pawelke B, Kretzschmar M, Hinz R, Bergman J, Eskola O, Solin O, Steinbach J, Johannsen B 2003 Positron emission tomography imaging of the serotonin transporter in the pig brain using [11C](+)-McN5652 and S-([18F]fluoromethyl)-(+)-McN5652. Synapse 47: 143–151
Huang SC, Yu DC, Barrio JR, Grafton S, Melega WP, Hoffman JM, Satyamurthy N, Mazziotta JC, Phelps ME 1991 Kinetics and modeling of L-6-[18F]fluoro-dopa in human positron emission tomographic studies. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 11: 898–913
Cumming P, Gjedde A 1998 Compartmental analysis of dopa decarboxylation in living brain from dynamic positron emission tomograms. Synapse 29: 37–61
Eisenhauer CL, Matsuda LS, Uyehara CF 1994 Normal physiologic values of neonatal pigs and the effects of isoflurane and pentobarbital anesthesia. Lab Anim Sci 44: 245–252
Cumming P, Kuwabara H, Ase A, Gjedde A 1995 Regulation of DOPA decarboxylase activity in brain of living rat. J Neurochem 65: 1381–1390
Cho S, Neff NH, Hadjiconstantinou M 1997 Regulation of tyrosine hydroxylase and aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase by dopaminergic drugs. Eur J Pharmacol 323: 149–157
Zhu MY, Juorio AV, Paterson IA, Boulton AA 1992 Regulation of aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase by dopamine receptors in the rat brain. J Neurochem 58: 636–641
Zhu MY, Juorio AV, Paterson IA, Boulton AA 1994 Regulation of aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase in rat striatal synaptosomes: effects of dopamine receptor agonists and antagonists. Br J Pharmacol 112: 23–30
Tammela O, Pastuszko A, Lajevardi NS, Delivoria-Papadopoulos M, Wilson DF 1993 Activity of tyrosine hydroxylase in the striatum of newborn piglets in response to hypocapnic hypoxia. J Neurochem 60: 1399–1406
Hedner T, Lundborg P, Engel J 1978 Effect of hypoxia on monoamine synthesis in brains of developing rats. III. Various O2 levels. Biol Neonate 34: 55–60
Olano M, Song D, Murphy S, Wilson DF, Pastuszko A 1995 Relationships of dopamine, cortical oxygen pressure, and hydroxyl radicals in brain of newborn piglets during hypoxia and posthypoxic recovery. J Neurochem 65: 1205–1212
Globus MY, Busto R, Dietrich WD, Martinez E, Valdes I, Ginsberg MD 1988 Effect of ischemia on the in vivo release of striatal dopamine, glutamate, and gamma-aminobutyric acid studied by intracerebral microdialysis. J Neurochem 51: 1455–1464
Boksa P, El-Khodor BF 2003 Birth insult interacts with stress at adulthood to alter dopaminergic function in animal models: possible implications for schizophrenia and other disorders. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 27: 91–101
Decker MJ, Hue GE, Caudle WM, Miller GW, Keating GL, Rye DB 2003 Episodic neonatal hypoxia evokes executive dysfunction and regionally specific alterations in markers of dopamine signaling. Neuroscience 117: 417–425
Decker MJ, Rye DB 2002 Neonatal intermittent hypoxia impairs dopamine signaling and executive functioning. Sleep Breath 6: 205–210
Lou HC, Rosa P, Pryds O, Karrebaek H, Lunding J, Cumming P, Gjedde A 2004 ADHD: increased dopamine receptor availability linked to attention deficit and low neonatal cerebral blood flow. Dev Med Child Neurol 46: 179–183
Bauer R, Walter B, Vollandt R, Zwiener U 2004 Intrauterine growth restriction ameliorates the effects of gradual hemorrhagic hypotension on regional cerebral blood flow and brain oxygen uptake in newborn piglets. Pediatr Res 56: 639–646
Xi Q, Tcheranova D, Parfenova H, Horowitz B, Leffler CW, Jaggar JH 2004 Carbon monoxide activates KCa channels in newborn arteriole smooth muscle cells by increasing apparent Ca2+ sensitivity of alpha-subunits. Am J Physiol 286: H610–H618
Heinonen K, Fedinec A, Leffler CW 2003 Dexamethasone pretreatment attenuates cerebral vasodilative responses to hypercapnia and augments vasoconstrictive responses to hyperventilation in newborn pigs. Pediatr Res 53: 260–265
Langley-Evans SC, Phillips GJ, Benediktsson R, Gardner DS, Edwards CR, Jackson AA, Seckl JR 1996 Protein intake in pregnancy, placental glucocorticoid metabolism and the programming of hypertension in the rat. Placenta 17: 169–172
Klemcke HG 2000 Dehydrogenase and oxoreductase activities of porcine placental 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Life Sci 66: 1045–1052
Armstead WM 1995 Opioids and nitric oxide contribute to hypoxia-induced pial arterial vasodilation in newborn pigs. Am J Physiol 268: H226–H232
Armstead WM 1998 Role of opioids in hypoxic pial artery dilation is stimulus duration dependent. Am J Physiol 275: H861–H867
Jagolino AL, Armstead WM 2003 PTK, MAPK, and NOC/oFQ impair hypercapnic cerebrovasodilation after hypoxia/ischemia. Am J Physiol 284: H101–H107
Philip S, Armstead WM 2003 Newborn pig nociceptin/orphanin FQ activates protein tyrosine kinase and mitogen activated protein kinase to impair NMDA cerebrovasodilation after ischemia. Neuroreport 14: 201–203
Blood AB, Hunter CJ, Power GG 2003 Adenosine mediates decreased cerebral metabolic rate and increased cerebral blood flow during acute moderate hypoxia in the near-term fetal sheep. J Physiol 553: 935–945
Hunter CJ, Bennet L, Power GG, Roelfsema V, Blood AB, Quaedackers JS, George S, Guan J, Gunn AJ 2003 Key neuroprotective role for endogenous adenosine A1 receptor activation during asphyxia in the fetal sheep. Stroke 34: 2240–2245
Hochachka PW, Buck LT, Doll CJ, Land SC 1996 Unifying theory of hypoxia tolerance: molecular/metabolic defense and rescue mechanisms for surviving oxygen lack. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 9493–9498
Bickler PE, Donohoe PH 2002 Adaptive responses of vertebrate neurons to hypoxia. J Exp Biol 205: 3579–3586
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs. E. Will and H. Linemann for help during the PET studies and U. Jäger, I. Witte, R. Lücke, R. Herrlich, and L. Wunder for skillful technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Thuringian State Ministry of Science, Research, and Arts, Grant 3/95-13 (R.B.) and the Saxon Ministry of Science and Art, Grant 7541.82-FZR/309 (P.B.).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bauer, R., Walter, B., Vorwieger, G. et al. Effect of Moderate Hypercapnic Hypoxia on Cerebral Dopaminergic Activity and Brain O2 Uptake in Intrauterine Growth–Restricted Newborn Piglets. Pediatr Res 57, 363–370 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000150800.19956.F0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000150800.19956.F0