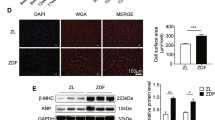
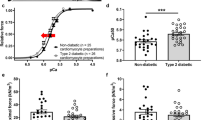
Abstract
Infants develop hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in ≈30% of diabetic pregnancies. We have characterized the effects of glucose on voltage-gated T-type Ca2+ channels and intracellular free calcium concentration, [Ca2+]i in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. We found that T-type Ca2+ channel current density increased significantly in primary culture neonatal cardiac myocytes that were treated with 25 mM glucose for 48 h when compared with those that were treated with 5 mM glucose. High-glucose treatment also caused a higher Ca2+ influx elicited by 50 mM KCl in the myocytes. KCl-induced Ca2+ influx was attenuated when nickel was present. Real-time PCR studies demonstrated that mRNA levels of both α1G (Cav3.1) and α1H (Cav3.2) T-type Ca2+ channels were elevated after high-glucose treatment. High-glucose also significantly increased ventricular cell proliferation as well as the proportion of cells in the S-phase of the cell cycle; both effects were reversed by nickel or mibefradil. These results indicate that high glucose causes a rise in [Ca2+]i in neonatal cardiac myocytes by a mechanism that is associated with the regulation of the T-type Ca2+ channel activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- [Ca2+]i:
-
cytoplasmic free Ca2+ concentration
- FBS:
-
fetal bovine serum
- IDM:
-
infants of diabetic mothers
- RT-PCR:
-
reverse transcriptase–PCR
References
Moore TR 1999 Maternal-Fetal Medicine, 4th Ed. W.B. Saunders Co, Philadelphia, pp 964–995
Ayres NA 1998 Fetal Cardiology, 2nd Ed. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 2281–2300
Haase H, Kresse A, Hohaus A, Schulte HD, Maier M, Osterziel KJ, Lange PE, Morano I 1996 Expression of calcium channel subunits in the normal and diseased human myocardium. J Mol Med 74: 99–104
Nuss HB, Houser SR 1993 T-type Ca2+ current is expressed in hypertrophied adult feline left ventricular myocytes. Circ Res 73: 777–782
Schaffer SW, Mozaffari MS, Artman M, Wilson GL 1989 Basis for myocardial mechanical defects associated with non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Am J Physiol 256: E25–E30
Gomez JP, Potreau D, Branka JE, Raymond G 1994 Developmental changes in Ca2+ currents from newborn rat cardiomyocytes in primary culture. Pflugers Arch 428: 241–249
Nalivaiko E, Pronchuk N, Sagach V 1992 Changes in T-type and L-type calcium current densities in newborn rat cardiomyocytes in culture. J Physiol 446: 145P
Wang R, Karpinski E, Pang PK 1991 Two types of voltage-dependent calcium channel currents and their modulation by parathyroid hormone in neonatal rat ventricular cells. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 17: 990–998
Kazazoglou T, Schmid A, Renaud JF, Lazdunski M 1983 Ontogenic appearance of Ca2+ channels characterized as binding sites for nitrendipine during development of nervous, skeletal and cardiac muscle systems in the rat. FEBS Lett 164: 75–79
Wibo M, Bravo G, Godfraind T 1991 Postnatal maturation of excitation-contraction coupling in rat ventricle in relation to the subcellular localization and surface density of 1,4-dihdropyridine and ryanodine receptors. Circ Res 68: 662–673
Beam KG, Knudson CM 1988 Effect of postnatal development on calcium currents and slow charge movement in mammalian skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol 91: 799–815
Bkaily G, Sculptoreanu A, Jacques D, Economos D, Menard D 1992 Apamin, a highly potent fetal L-type Ca2+ current blocker in single heart cells. Am J Physiol 262: H463–H471
Richard S, Neveu D, Carnac G, Bodin P, Travo P, Nargeot J 1992 Differential expression of voltage-gated Ca2+-currents in cultivated aortic myocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1160: 95–104
Sen L, Smith TW 1994 T-type Ca2+ channels are abnormal in genetically determined cardiomyopathic hamster hearts. Circ Res 75: 149–155
Bean BP 1989 Classes of calcium channels in vertebrate cells. Annu Rev Physiol 51: 367–384
Katz AM 1996 Calcium channel diversity in the cardiovascular system. J Am Coll Cardiol 28: 522–529
Guo W, Kamiya K, Kodmam I, Toyama J 1998 Cell cycle-related changes in the voltage-gated Ca2+ currents in cultured newborn rat ventricular myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 30: 1095–1103
Simpson P, Savion S 1982 Differentiation of rat myocytes in single cell cultures with and without proliferating nonmyocardial cells. Cross-striations, ultrastructure, and chronotropic response to isoproterenol. Circ Res 50: 101–116
Long CS, Henrich CJ, Simpson PC 1991 A growth factor for cardiac myocytes is produced by cardiac nonmyocytes. Cell Regul 2: 1081–1095
Lambert RC, McKenna F, Maulet Y, Talley EM, Bayliss DA, Cribbs LL, Lee JH, Perez-Reyes E, Feltz A 1998 Low-voltage-activated Ca2+ currents are generated by members of the CavT subunit family (α1G/H) in rat primary sensory neurons. J Neurosci 18: 8605–8613
Zhuang H, Bhattacharjee A, Hu F, Zhang M, Goswami T, Wang L, Wu S, Berggren PO, Li M 2000 Cloning of a T-type Ca2+ channel isoform in insulin-secreting cells. Diabetes 49: 59–64
Cribbs LL, Lee JH, Yang J, Satin J, Zhang Y, Daud A, Barclay J, Williamson MP, Fox M, Rees M, Perez-Reyes E 1998 Cloning and characterization of α1H from human heart, a member of the T-type Ca2+ channel gene family. Circ Res 83: 103–109
Mishra SK, Hermsmeyer K 1994 Selective inhibition of T-type Ca2+ channels by Ro 40–5967. Circ Res 75: 144–148
Clozel JP, Ertel EA, Ertel SI 1999 Voltage-gated T-type Ca2+ channels and heart failure. Proc Assoc Am Physicians 111: 429–437
Ferron L, Capuano V, Ruchon Y, Deroubaix E, Coulombe A, Renaud JF 2003 Angiotensin II signaling pathways mediate expression of cardiac T-type calcium channels. Circ Res 93: 1241–1248
Izumi T, Kihara Y, Sarai N, Yoneda T, Iwanaga Y, Inagaki K, Onozawa Y, Takenaka H, Kita T, Noma A 2003 Reinduction of T-type calcium channels by endothelin-1 in failing hearts in vivo and in adult rat ventricular myocytes in vitro. Circulation 108: 2530–2535
Kuga T, Kobayashi S, Hirakawa Y, Kanaide H, Takeshita A 1996 Cell cycle-dependent expression of L- and T-type Ca2+ currents in rat aortic smooth muscle cells in primary culture. Circ Res 79: 14–19
Richard S, Tiaho F, Charnet P, Nargeot J, Nerbonne JM 1990 Two pathways for Ca2+ channel gating differentially modulated by physiological stimuli. Am J Physiol 258: H1872–H1881
Ciapa B, Pesando D, Wilding M, Whitaker M 1994 Cell-cycle calcium transients driven by cyclic changes in inositol trisphosphate levels. Nature 368: 875–878
Ariyoshi H, Okahara K, Sakon M, Kambayashi J, Kawashima S, Kawasaki T, Monden M 1998 Possible involvement of m-calpain in vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 18: 493–498
Akagi K, Nagao T, Urushidani T 1999 Correlation between Ca2+ oscillation and cell proliferation via CCK(B)/gastrin receptor. Biochim Biophys Acta 1452: 243–253
Chen YJ, Lin JK, Lin-Shiau SY 1999 Proliferation arrest and induction of CDK inhibitors p21 and p27 by depleting the calcium store in cultured C6 glioma cells. Eur J Cell Biol 78: 824–831
Baral E, Nagy E, Kwok S, NcNicol A, Gerrard J, Berczi I 2000 Suppression of lymphocyte mitogenesis by tamoxifen: studies on protein kinase C, calmodulin and calcium. Neuroimmunomodulation 7: 68–76
Wonderlin WF, Strobl JS 1996 Potassium channels, proliferation and G1 progression. J Membr Biol 154: 91–107
Tyrala EE 1996 The infant of the diabetic mother. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am 23: 221–241
Mehta S, Nuamah I, Kalhan S 1991 Altered diastolic function in asymptotic infants of mothers with gestational diabetes. Diabetes 40( suppl 2): 56–60
Repetto G, del Peso A, Sanz P, Repetto M 2001 In vitro effects of lithium and nickel at different levels on Neuro-2a mouse Neuroblastoma cells. Toxicol In Vitro 15: 363–368
Bhattacharjee A, Whitehurst RM Jr, Zhang M, Wang L, Li M 1997 T-type Calcium channels facilitate insulin secretion by enhancing general excitability in the insulin-secreting β-cell line, INS-1. Endocrinology 183: 3735–3740
Nair RR, Nair P 2001 Age-dependent variation in contractility of adult myocytes. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 33: 119–125
Pascarel C, Brette F, Le Guennec JY 2001 Enhancement of the T-type calcium current by hyposmotic shock in isolated guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 33: 1363–1369
Lee JH, Gomora J, Cribbs LL, Perez-Reyes E 1999 Nickel block of three cloned T-type calcium channels: low concentrations selectively block α1H. Biophys J 77: 3034–3042
Cribbs LL, Martin BL, Schroder EA, Keller BB, Delisle BP, Satin J 2001 Identification of the T-type calcium channel (Ca(v)3.1d) in developing mouse heart. Circ Res 88: 403–407
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was supported by a research-in-aid award of the American Heart Association to M.L.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Zhang, M., Huang, L. et al. T-Type Ca2+ Channels Are Involved in High Glucose–Induced Rat Neonatal Cardiomyocyte Proliferation. Pediatr Res 57, 550–556 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000155756.89681.3C
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000155756.89681.3C
This article is cited by
-
High glucose initiates calpain-induced necrosis before apoptosis in LLC-PK1 cells
Kidney International (2007)