Abstract
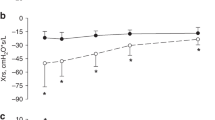
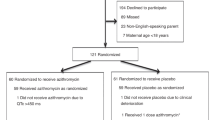
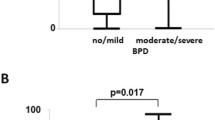
Animal studies have shown that induction of cytochrome P450 (CYP) in the lung by oxygen exposure may result in the release of free radical oxidants and arachidonic acid metabolites, which can cause lung injury that is reduced by treatment with cimetidine, a CYP inhibitor. To determine whether cimetidine would reduce lung injury in human infants at risk for chronic lung disease, we conducted a randomized clinical trial in which we administered either cimetidine or a placebo for 10 d beginning <24 h after birth to 84 newborn infants weighing ≤1250 g who were receiving O2 and mechanical ventilation. Cimetidine had no significant effect on severity of respiratory insufficiency assessed at 10 d postnatal age. F2-isoprostane levels (a marker of oxidant injury) in tracheal aspirates were significantly higher in the cimetidine group at 4 d and at 10 d. There were no significant differences between the groups in tracheal aspirate levels of inflammatory markers (leukotriene B4, IL-8, and nucleated cell count) or arachidonic acid metabolites. We conclude that cimetidine does not reduce lung injury in newborn premature infants receiving O2 and mechanical ventilation. It is possible that cimetidine was not an adequate CYP inhibitor in this context.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- AA:
-
arachidonic acid
- CLD:
-
chronic lung disease
- CYP:
-
cytochrome P450
- EET:
-
epoxyeicosatrienoic acid
- IVH:
-
intraventricular hemorrhage
- LTB4:
-
leukotriene B4
- PDA:
-
symptomatic patent ductus arteriosus
- PMA:
-
postmenstrual age
- RII:
-
respiratory insufficiency index
- TA:
-
tracheal aspirate
References
Hazinski TA, France M, Kennedy KA, Hansen TN 1989 Cimetidine reduces hyperoxic lung injury in lambs. J Appl Physiol 67: 2586–2592
Hazinski TA, Noisin E, Hamon I, DeMatteo A 1995 Sheep lung cytochrome P450IA1 (Cyp1A1): cDNA cloning and transcriptional regulation by oxygen tension. J Clin Invest 96: 2083–2089
Thibeault DW, Downing G, Reddy N, Sonderfan AJ, Parkinson A 1991 Oxygen-induced lung damage in newborn rats, potentiated by 3-methylcholanthrene, a P-450 inducer, and lack of protection by cimetidine, a P-450 inhibitor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 259: 444–451
Sakai H, Okamoto T, Yamamoto R, Sindhu RK, Kikkawa Y 1992 Suppressive effect of interleukin-1 on pulmonary cytochrome P450 and superoxide anion production. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 185: 1083–1090
Bysani GK, Kennedy TP, Ky N, Rao NV, Blaze CA, Hoidal JR 1990 Role of cytochrome P-450 in reperfusion injury of the rabbit lung. J Clin Invest 86: 1434–1441
Granville DJ, Tashakkor B, Takeuchi C, Gustafsson AB, Huang C, Sayen MR, Wentworth P Jr, Yeager M, Gottlieb RA 2004 Reduction of ischemia and reperfusion-induced myocardial damage by cytochrome P450 inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101: 1321–1326
Morrow JD, Awad JA, Kato T, Takahashi K, Badr KF, Roberts LJ 2nd, Burk RF 1992 Formation of novel non-cyclooxygenase-derived prostanoids (F2-isoprostanes) in carbon tetrachloride hepatotoxicity. An animal model of lipid peroxidation. J Clin Invest 90: 2502–2507
Gonder JC, Proctor RA, Will JA 1985 Genetic differences in oxygen toxicity are correlated with cytochrome P-450 inducibility. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 82: 6315–6319
Todd NW, Hunt CM, Kennedy TP, Piantadosi CA, Whorton AR 1992 Effects of inhibition and induction of cytochrome P-450 isozymes on hyperoxic lung injury in rats. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 7: 222–229
Omiecinski CJ, Aicher L, Swenson L 1994 Developmental expression of human microsomal epoxide hydrolase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 269: 417–423
Nebert DW, Russell DW 2002 Clinical importance of the cytochromes P450. Lancet 360: 1155–1162
Nelson DR, Zeldin DC, Hoffman SM, Maltais LJ, Wain HM, Nebert DW 2004 Comparison of cytochrome P450 (CYP) genes from the mouse and human genomes, including nomenclature recommendations for genes, pseudogenes and alternative-splice variants. Pharmacogenetics 14: 1–18
Zeldin DC 2001 Epoxygenase pathways of arachidonic acid metabolism. J Biol Chem 276: 36059–36062
Capdevila JH, Falck JR 2001 The CYP P450 arachidonic acid monooxygenases: from cell signaling to blood pressure regulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 285: 571–576
Kroetz DL, Zeldin DC 2002 Cytochrome P450 pathways of arachidonic acid metabolism. Curr Opin Lipidol 13: 273–283
Shenai JP, Mellen BG, Chytil F 2000 Vitamin A status and postnatal dexamethasone treatment in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatrics 106: 547–553
Cotton RB, Haywood JL, FitzGerald GA 1991 Symptomatic patent ductus arteriosus following prophylactic indomethacin. A clinical and biochemical appraisal. Biol Neonate 60: 273–282
Papile LA, Burstein J, Burstein R, Koffler H 1978 Incidence and evolution of subependymal intraventricular hemorrhage: a study of infants with weights less than 1500 grams. J Pediatr 92: 529–534
Lloyd CW, Martin WJ, Taylor BD 1985 The pharmacokinetics of cimetidine and metabolites in a neonate. Drug Intell Clin Pharm 19: 203–205
Ziemniak JA, Wynn RJ, Aranda JV, Zarowitz BJ, Schentag JJ 1984 The pharmacokinetics and metabolism of cimetidine in neonates. Dev Pharmacol Ther 7: 30–38
Aranda JV, Outerbridge EW, Schentag JJ 1983 Pharmacodynamics and kinetics of cimetidine in a premature newborn. Am J Dis Child 137: 1207
Xu K, Arora VK, Chaudhary AK, Cotton RB, Blair IA 1999 Quantitative analysis of cimetidine in human plasma using LC/APCI/SRM/MS. Biomed Chromatogr 13: 455–461
Morrow JD, Roberts LJ 2nd 1994 Mass spectrometry of prostanoids: F2-isoprostanes produced by non-cyclooxygenase free radical-catalyzed mechanism. Methods Enzymol 233: 163–174
Zeldin DC, Plitman JD, Kobayashi J, Miller RF, Snapper JR, Falck JR, Szarek JL, Philpot RM, Capdevila JH 1995 The rabbit pulmonary cytochrome P450 arachidonic acid metabolic pathway: characterization and significance. J Clin Invest 95: 2150–2160
Levine M, Law EY, Bandiera SM, Chang TK, Bellward GD 1998 In vivo cimetidine inhibits hepatic CYP2C6 and CYP2C11 but not CYP1A1 in adult male rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 284: 493–499
Seubert J, Yang B, Bradbury JA, Graves J, Degraff LM, Gabel S, Gooch R, Foley J, Newman J, Mao L, Rockman HA, Hammock BD, Murphy E, Zeldin DC 2004 Enhanced postischemic functional recovery in CYP2J2 transgenic hearts involves mitochondrial ATP-sensitive K+ channels and p42/p44 MAPK pathway. Circ Res 95: 506–514
Node K, Huo Y, Ruan X, Yang B, Spiecker M, Ley K, Zeldin DC, Liao JK 1999 Anti-inflammatory properties of cytochrome P450 epoxygenase-derived eicosanoids. Science 285: 1276–1279
Moorthy B, Parker KM, Smith CV, Bend JR, Welty SE 2000 Potentiation of oxygen-induced lung injury in rats by the mechanism-based cytochrome P-450 inhibitor, 1-aminobenzotriazole. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 292: 553–560
Moorthy B, Nguyen UT, Gupta S, Stewart KD, Welty SE, Smith CV 1997 Induction and decline of hepatic cytochromes P4501A1 and 1A2 in rats exposed to hyperoxia are not paralleled by changes in glutathione S-transferase-alpha. Toxicol Lett 90: 67–75
Sinha A, Muthiah K, Jiang W, Couroucli X, Barrios R, Moorthy B 2005 Attenuation of hyperoxic lung injury by the CYP1A inducer {beta}-naphthoflavone. Toxicol Sci 87: 204–212
Lilly JR, Hitch DC, Javitt NB 1978 Cimetidine cholestatic jaundice in children. J Surg Res 24: 384–387
Spapen H, Diltoer M, Nguyen DN, Ingels G, Ramet J, Huyghens L 1995 One week treatment with cimetidine does not attenuate the cortisol response to a short corticotropin test in stable intensive care patients: a prospective, randomized, and controlled study. Acta Anaesthesiol Belg 46: 133–140
Rojas MA, Efird MM, Lozano JM, Bose CL, Rojas MX, Rondon MA, Ruiz G, Pineros JG, Rojas C, Robayo G, Hoyos A, Gosendi MH, Cruz H, O'Shea M, Leon A 2005 Risk factors for nosocomial infections in selected neonatal intensive care units in Colombia, South America. J Perinatol 25: 537–541
Coceani F, Kelsey L, Seidlitz E, Korzekwa K 1996 Inhibition of the contraction of the ductus arteriosus to oxygen by 1-aminobenzotriazole, a mechanism-based inactivator of cytochrome P450. Br J Pharmacol 117: 1586–1592
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Robert A. Parker and Dr. Beverly G. Mellen for the valuable advice regarding study design and data analysis. We also thank are Dr. William Walsh, Dr. H\akan Sundell, Dr. Daniel Lindstrom, and Dr. Beverly Mellen for their service on the oversight committee.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by HL56697, GM42056, GM15431, and DK26657 from the National Institutes of Health and by the Intramural Research Program of the National Environmental Health Services Division, National Institutes of Health.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cotton, R., Hazinski, T., Morrow, J. et al. Cimetidine Does Not Prevent Lung Injury in Newborn Premature Infants. Pediatr Res 59, 795–800 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1203/01.pdr.0000219397.35473.5f
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/01.pdr.0000219397.35473.5f
This article is cited by
-
Impact of Feeding and Medical Practices on the Development of Necrotizing Enterocolitis
Current Pediatrics Reports (2014)