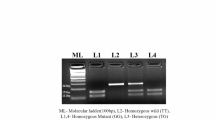
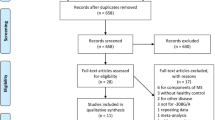
Abstract
Granulomas may be found in 30–70% of patients with Crohn's disease (CD). The etiology of granuloma formation in CD is presently unknown. Elevated levels of TNF-α are found within granuloma tissue, and are required to maintain granuloma formation in animal models. TNF-α production has been shown to influenced by TNF-α promoter polymorphisms. We hypothesized that heterogeneity for granulomas in CD might be influenced by the TNF-α promoter genotype. Patients with confirmed CD that had undergone full colonoscopy with multiple biopsies and/or surgical resection, served as the study group. One hundred healthy individuals served as a control population for genotyping. Patients and controls underwent genotyping for four TNF-α polymorphisms: 238G/A, 308 G/A,857 C/T, and 863 C/A. Inclusion and exclusion criteria were met in 155 patients (1–68 y). Polymorphisms in the TNF promoter were found in 16.6% (238G/A), 14.5% (308 G/A), 36.6% (857 C/T) and 30.7% (863G/A). No significant association was found for any of the individual polymorphisms with presence or absence of granulomas. In conclusion, we did not find an association between individual polymorphisms in the TNF-α promoter and presence of granulomas in CD. The reason for heterogeneity in granuloma formation in patients with CD remains elusive.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- CD:
-
Crohn's disease
- SNPs:
-
single nucleotide polymorphisms
- TLR:
-
toll-like receptors
References
Shepherd NA 2002 Granulomas in the diagnosis of intestinal Crohn's disease: a myth exploded?. Histopathology 41: 166–168
Kleer CG, Appelman HD 2001 Surgical pathology of Crohn's disease. Surg Clin North Am 81: 13–30
Abbas AK, Lichtman AH, Pober JS 2000 Cellular and molecular immunology. WB Saunders Co, Philadelphia, pp 291–308
Co DO, Hogan LH, Kim SI, Sandor M 2004 Mycobacterial granulomas: keys to a long-lasting host-pathogen relationship. Clin Immunol 113: 130–136
Co DO, Hogan LH, Il-Kim S, Sandor M 2004 T-cell contributions to the different phases of granuloma formation. Immunol Lett 92: 135–142
Heimann TM, Miller F, Martinelli G, Szporn A, Greenstein AJ, Aufses AH 1988 Correlation of presence of granulomas with clinical and immunologic variables in Crohn's disease. Arch Surg 123: 46–48
Pulimood AB, Ramakrishna BS, Kurian G, Peter S, Patra S, Mathan VI, Mathan MM 1999 Endoscopic mucosal biopsies are useful in distinguishing granulomatous colitis due to Crohn's disease from tuberculosis. Gut 45: 537–541
Schmitz-Moormann P, Schag M 1990 Histology of the lower intestinal tract in Crohn's disease of children and adolescents. Multicentric Paediatric Crohn's Disease Study. Pathol Res Pract 186: 479–484
Fenhalls G, Stevens L, Bezuidenhout J, Amphlett GE, Duncan K, Bardin P, Lukey PT 2002 Distribution of IFN-gamma, IL-4 and TNF-α protein and CD8 T-cells producing IL-12p40 mRNA in human lung tuberculous granulomas. Immunology 105: 325–335
Haseeb MA, Shirazian DJ, Preis J 2001 Elevated serum levels of TNF-α, sTNF-RI and sTNF-RII in murine schistosomiasis correlate with schistosome oviposition and circumoval granuloma formation. Cytokine 15: 266–269
Naser SA, Ghobrial G, Romero C, Valentine JF 2004 Culture of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis from the blood of patients with Crohn's disease. Lancet 364: 1039–1044
Bernstein CN, Blanchard JF, Rawsthorne P, Collins MT 2004 Population-based case control study of seroprevalence of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis in patients with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. J Clin Microbiol 42: 1129–1135
Baksh FK, Finkelstein SD, Ariyanayagam-Baksh SM, Swalsky PA, Klein EC, Dunn JC 2004 Absence of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in the microdissected granulomas of Crohn's disease. Mod Pathol 17: 1289–1294
Glasser AL, Boudeau J, Barnich N, Perruchot MH, Colombel JF, Darfeuille-Michaud A 2001 Adherent invasive Escherichia coli strains from patients with Crohn's disease survive and replicate within macrophages without inducing host-cell death. Infect Immun 69: 5529–5537
Martin HM, Campbell BJ, Hart CA, Mpofu C, Nayar M, Singh R, Englyst H, Williams HF, Rhodes JM 2004 Enhanced. Escherichia coli adherence and invasion in Crohn's disease and colon cancer. Gastroenterology 127: 80–93
Darfeuille-Michaud A, Neut C, Barnich N, Lederman E, Di Martino P, Desreumaux P, Gambiez L, Joly B, Cortot A, Colombel JF 1998 Presence of adherent Escherichia coli strains in ileal mucosa of patients with Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology 115: 1405–1413
Swidsinski A, Ladhoff A, Pernthaler A, Swidsinski S, Loening-Baucke V, Ortner M, Weber J, Hoffmann U, Schreiber S, Dietel M, Lochs H 2002 Mucosal flora in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 122: 44–54
Hugot JP, Chamaillard M, Zouali H, Lesage S, Cezard JP, Belaiche J, Almer S, Tysk C, O'Morain CA, Gassull M, Binder V, Finkel Y, Cortot A, Modigliani R, Laurent-Puig P, Gower-Rousseau C, Macry J, Colombel JF, Sahbatou M, Thomas G 2001 Association of NOD2 leucine-rich repeat variants with susceptibility to Crohn's disease. Nature 2001 411: 599–603
Ogura Y, Bonen DK, Inohara N, Nicolae DL, Chen FF, Ramos R, Britton H, Moran T, Karaliuskas R, Duerr RH, Achkar JP, Brant SR, Bayless TM, Kirschner BS, Hanauer SB, Nunez G, Cho JH 2001 A frameshift mutation in NOD2 associated with susceptibility to Crohn's disease. Nature 411: 603–606
Hampe J, Cuthbert A, Croucher PJ, Mirza MM, Mascheretti S, Fisher S, Frenzel H, King K, Hasselmeyer A, MacPherson AJ, Bridger S, van Deventer S, Forbes A, Nikolaus S, Lennard-Jones JE, Foelsch UR, Krawczak M, Lewis C, Schreiber S, Mathew CG 2001 Association between insertion mutation in NOD2 gene and Crohn's disease in German and British populations. Lancet 357: 1925–1928
Bonen DK, Ogura Y, Nicolae DL, Inohara N, Saab L, Tanabe T, Chen FF, Foster SJ, Duerr RH, Brant SR, Cho JH, Nunez G 2003 Crohn's disease-associated NOD2 variants share a signaling defect in response to lipopolysaccharide and peptidoglycan. Gastroenterology 124: 140–146
Pierik M, De Hertogh G, Vermeire S, Van Assche G, Van Eyken P, Joossens S, Claessens G, Vlietinck R, Rutgeerts P, Geboes K 2005 Epithelioid granulomas, pattern recognition receptors, and phenotypes of Crohn's disease. Gut 54: 223–227
Shaoul R, Karban A, Weiss B, Reif S, Wasserman D, Pacht A, Eliakim R, Wardi J, Shirin H, Wine E, Leshinsky-Silver E, Levine A 2004 NOD2/CARD15 mutations and presence of granulomas in pediatric and adult Crohn's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 10: 709–714
Franchimont D, Vermeire S, El Housni H, Pierik M, Van Steen K, Gustot T, Quertinmont E, Abramowicz M, Van Gossum A, Deviere J, Rutgeerts P 2004 Deficient host-bacteria interactions in inflammatory bowel disease? The toll-like receptor(TLR)-4 Asp299gly polymorphism is associated with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Gut 53: 987–992
Roach DR, Bean AG, Demangel C, France MP, Briscoe H, Britton WJ 2002 TNF regulates chemokine induction essential for cell recruitment, granuloma formation, and clearance of mycobacterial infection. J Immunol 168: 4620–4627
Kindler V, Sappino AP, Grau GE, Piguet PF, Vassalli P 1989 The inducing role of tumor necrosis factor in the development of bactericidal granulomas during BCG infection. Cell 56: 731–740
Louis E, Peeters M, Franchimont D, Seidel L, Fontaine F, Demolin G, Croes F, Dupont P, Davin L, Omri S, Rutgeerts P, Belaiche J 2000 Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) gene polymorphism in Crohn's disease (CD): influence on disease behavior?. Clin Exp Immunol 119: 64–68
Gonzalez S, Rodrigo L, Martinez-Borra J, Lopez-Vazquez A, Fuentes D, Nino P, Cadahia V, Saro C, Dieguez MA, Lopez-Larrea C 2003 TNF-α-308A promoter polymorphism is associated with enhanced TNF-α production and inflammatory activity in Crohn's patients with fistulizing disease. Am J Gastroenterol 98: 1101–1106
Vatay A, Bene L, Kovacs A, Prohaszka Z, Szalai C, Romics L, Fekete B, Karadi I, Fust G 2003 Relationship between the tumor necrosis factor alpha polymorphism and the serum C-reactive protein levels in inflammatory bowel disease. Immunogenetics 55: 247–252
Brinkman BM, Huizinga TW, Kurban SS, van der Velde EA, Schreuder GM, Hazes JM, Breedveld FC, Verweij CL 1997 Tumor necrosis factor alpha gene polymorphisms in rheumatoid arthritis: association with susceptibility to, or severity of disease?. Br J Rheumatol 36: 516–521
Louis E, Franchimont D, Piron A, Gevaert Y, Schaaf-Lafontaine N, Roland S, Mahieu P, Malaise M, De Groote D, Louis R, Belaiche J 1998 Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) gene polymorphism influences TNF-α production in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated whole blood cell culture in healthy humans. Clin Exp Immunol 113: 401–406
Skoog T, van't Hooft FM, Kallin B, Jovinge S, Boquist S, Nilsson J, Eriksson P, Hamsten A 1999 A common functional polymorphism (C→A substitution at position -863) in the promoter region of the tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF α) gene associated with reduced circulating levels of TNF-α. Hum Mol Genet 8: 1443–1449
Kaluza W, Reuss E, Grossmann S, Hug R, Schopf RE, Galle PR, Maerker-Hermann E, Hoehler T 2000 Different transcriptional activity and in vitro TNF-α production in psoriasis patients carrying the TNF-α 238A promoter polymorphism. J Invest Dermatol 114: 1180–1183
van Heel DA, Udalova IA, De Silva AP, McGovern DP, Kinouchi Y, Hull J, Lench NJ, Cardon LR, Carey AH, Jewell DP, Kwiatkowski D 2002 Inflammatory bowel disease is associated with a TNF polymorphism that affects an interaction between the OCT1 and NF-kB transcription factors. Hum Mol Genet 11: 1281–1289
Levine A, Karban A, Eliakim R, Shaoul R, Reif S, Pacht A, Wardi J, Yakir B, Silver EL 2005 A polymorphism in the TNF-α promoter gene is associated with pediatric onset and colonic location of Crohn's disease. Am J Gastroenterol 100: 407–413
Rezende CM, Goes TS, Goes VS, Azevedo V, Leite MF, Goes AM 2004 GM-CSF and TNF-α synergize to increase in vitro granuloma size of PBMC from humans induced by Schistosoma mansoni recombinant 28-kDa GST. Immunol Lett 95: 221–228
Price NM, Gilman RH, Uddin J, Recavarren S, Friedland JS 2003 Unopposed matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in human tuberculosis granuloma and the role of TNF-α-dependent monocyte networks. J Immunol 171: 5579–5586
Zganiacz A, Santosuosso M, Wang J, Yang T, Chen L, Anzulovic M, Alexander S, Gicquel B, Wan Y, Bramson J, Inman M, Xing Z 2004 TNF-α is a critical regulator of type 1 immune activation during intracellular bacterial infection. J Clin Invest 113: 401–413
Heresbach D, Alexandre JL, Branger B, Bretagne JF, Cruchant E, Dabadie A, Dartois-Hoguin M, Girardot PM, Jouanolle H, Kerneis J, Le Verger JC, Louvain V, Politis J, Richecoeur M, Robaszkiewicz M, Seyrig JA ABERMAD (Association Bretonne d'Etude et de Recherche sur les Maladies de l'Appareil Digestif) 2005 Frequency and significance of granulomas in a cohort of incident cases of Crohn's disease. Gut 54: 215–222
Morpurgo E, Petras R, Kimberling J, Ziegler C, Galandiuk S 2003 Characterization and clinical behavior of Crohn's disease initially presenting predominantly as colitis. Dis Colon Rectum 46: 918–924
Moller DR 2003 Treatment of sarcoidosis-from a basic sciences point of view. J Intern Med 253: 31–40
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dalal, I., Karban, A., Wine, E. et al. Polymorphisms in the TNF-α Promoter and Variability in the Granulomatous Response in Patients with Crohn's Disease. Pediatr Res 59, 825–828 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1203/01.pdr.0000215028.19269.94
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/01.pdr.0000215028.19269.94