Abstract
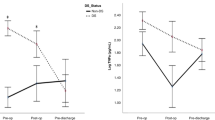
Posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus (PHHC) represents a major complication of preterm birth. The aim of this study was to determine whether cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-18, and interferon (IFN)-γ are altered in the CSF of preterm infants with PHHC and may serve as a marker of white matter damage (WMD). Twenty-seven preterm infants with PHHC were included in the study; 13 of them had signs of cystic WMD (cWMD) on ultrasound examinations. CSF sample 1 was obtained at first ventriculostomy, sample 2 at shunt implantation. Results were compared with a control group of 20 age-matched patients without neurologic diseases. IL-1β concentrations were elevated in CSF sample 1 of PHHC patients without WMD and in sample 1 of patients with cWMD. Concentrations of IL-18 were increased in both samples of patients without WMD and in sample 2 of patients with cWMD. CSF levels of IFN-γ were elevated in sample 1 of PHHC patients with cWMD. The pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-1β and IL-18 levels in the CSF are elevated in patients with PHHC. Higher IFN-γ levels are detected in a subgroup of patients developing cWMD, indicating its involvement in the pathogenesis of cWMD in the context of PHHC.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- CSF:
-
cerebrospinal fluid
- cWMD:
-
cystic white matter damage
- IVH:
-
intraventricular hemorrhage
- PHHC:
-
posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus
- WMD:
-
white matter damage
References
Cherian S, Whitelaw A, Thoresen M, Love S 2004 The pathogenesis of neonatal post-hemorrhagic hydrocephalus. Brain Pathol 14: 305–311
Del Bigio MR 2004 Cellular damage and prevention in childhood hydrocephalus. Brain Pathol 14: 317–324
Cai Z, Pan ZL, Pang Y, Evans OB, Rhodes PG 2000 Cytokine induction in fetal rat brains and brain injury in neonatal rats after maternal lipopolysaccharide administration. Pediatr Res 47: 64–72
Sharief MK, Hentges R 1991 Association between tumor necrosis factor-alpha and disease progression in patients with multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 325: 467–472
Barone FC, Hillegass LM, Price WJ, White RF, Lee EV, Feuerstein GZ, Sarau HM, Clark RK, Griswold DE 1991 Polymorphonuclear leukocyte infiltration into cerebral focal ischemic tissue: myeloperoxidase activity assay and histologic verification. J Neurosci Res 29: 336–345
Liu XH, Kwon D, Schielke GP, Yang GY, Silverstein FS, Barks JD 1999 Mice deficient in interleukin-1 converting enzyme are resistant to neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 19: 1099–1108
Allan SM, Tyrrell PJ, Rothwell NJ 2005 Interleukin-1 and neuronal injury. Nat Rev Immunol 5: 629–640 Review.
Lu KT, Wang YW, Yang JT, Yang YL, Chen HI 2005 Effect of interleukin-1 on traumatic brain injury-induced damage to hippocampal neurons. J Neurotrauma 22: 885–895
Hailer NP, Vogt C, Korf HW, Dehghani F 2005 Interleukin-1beta exacerbates and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist attenuates neuronal injury and microglial activation after excitotoxic damage in organotypic hippocampal slice cultures. Eur J Neurosci 21: 2347–2360
Szaflarski J, Burtrum D, Silverstein FS 1995 Cerebral hypoxia-ischemia stimulates cytokine gene expression in perinatal rats. Stroke 26: 1093–1100
Yoon BH, Jun JK, Romero R, Park KH, Gomez R, Choi JH, Kim IO 1997 Amniotic fluid inflammatory cytokines (interleukin-6, interleukin-1beta, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha), neonatal brain white matter lesions, and cerebral palsy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 177: 19–26
Hedtjarn M, Mallard C, Arvidsson P, Hagberg H 2005 White matter injury in the immature brain: role of interleukin-18. Neurosci Lett 373: 16–20
Nakamura K, Okamura H, Nagata K, Komatsu T, Tamura T 1993 Purification of a factor which provides a costimulatory signal for gamma interferon production. Infect Immun 61: 64–70
Okamura H, Tsutsui H, Komatsu T, Yutsudo M, Hakura K, Tanimoto T, Torigoe K, Okura T, Nukada Y, Hattori K 1995 Cloning of a new cytokine that induces IFN-gamma production by T cells. Nature 378: 88–91
Tsutsui H, Matsui K, Kawada N, Hyodo Y, Hayashi N, Okamura H, Higashino K, Nakanishi K 1997 IL-18 accounts for both TNF-alpha- and Fas ligand-mediated hepatotoxic pathways in endotoxin-induced liver injury in mice. J Immunol 159: 3961–3967
Degliantoni G, Murphy M, Kobayashi M, Francis MK, Perussia B, Trinchieri G 1985 Natural killer (NK) cell-derived hematopoietic colony-inhibiting activity and NK cytotoxic factor. Relationship with tumor necrosis factor and synergism with immune interferon. J Exp Med 162: 1512–1530
Schreiber GH, Schreiber RD 2003 Interferon-γ. In: Thomason AW, Lotze MT (eds.). The Cytokine Handbook, 4th Ed. Elsevier Science Ltd, London, pp 567–601
Hirsch RL, Panitch HS, Johnson KP 1985 Lymphocytes from multiple sclerosis patients produce elevated levels of gamma interferon in vitro. J Clin Immunol 5: 386–389
Panitch HS, Hirsch RL, Schindler J, Johnson KP 1987 Treatment of multiple sclerosis with gamma interferon: Exacerbations associated with activation of the immune system. Neurology 37: 1097–1102
Mana P, Linares D, Fordham S, Staykova M, Willenborg D 2006 Deleterious role of IFN gamma in a toxic model of central nervous system demyelination. Am J Pathol 168: 1464–1473
Corbin JG, Kelly D, Rath EM, Baerwald KD, Suzuki K, Popko B 1996 Targeted CNS expression of interferon-gamma in transgenic mice leads to hypomyelination, reactive gliosis, and abnormal cerebellar development. Mol Cell Neurosci 7: 354–370
Baerwald KD, Popko B 1998 Developing and mature oligodendrocytes respond differently to the immune cytokine interferon-gamma. J Neurosci Res 52: 230–239
Folkerth RD, Keefe RJ, Haynes RL, Trachtenberg FL, Volpe JJ, Kinney HC 2004 Interferon-γ expression in periventricular leukomalacia in the human brain. Brain Pathol 14: 265–274
Papile LA, Burstein J, Burstein R, Koffler H 1978 Incidence and evaluation of subependymal haemorrhage: a study of children with a birth weights less than 1,500 gM. J Pediatr 92: 529–534
Paneth N 1999 Classifying brain damage in preterm infants. J Pediatr 134: 527–529
Levene MI 1981 Measurement of the growth of the lateral ventricles in preterm infants with real-time ultrasound. Arch Dis Child 56: 900–904
Roelants-van Rijn AM, Groenendaal F, Beek FJ, Eken P, van Haastert IC, de Vries LS 2001 Parenchymal brain injury in the preterm infant: comparison of cranial ultrasound, MRI and neurodevelopmental outcome. Neuropediatrics 32: 80–89
Heep A, Stoffel-Wagner B, Bartmann P, Benseler S, Schaller C, Groneck P, Obladen M, Felderhoff-Mueser U 2004 Vascular endothelial growth factor and transforming growth factor-beta1 are highly expressed in the cerebrospinal fluid of premature infants with posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus. Pediatr Res 56: 768–774
Allan SM, Rothwell NJ. 2003 Inflammation in central nervous system injury. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 358: 1669–1677 Review.
Yoon BH, Jun J, Romero R, Park K, Gomez R, Choi JH, Kim IO 1997 Amniotic fluid inflammatory cytokines (interleukin-6, interleukin-1β, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha), neonatal brain white matter lesions, and cerebral palsy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 177: 19–26
Savman K, Blennow M, Hagberg H, Tarkowski E, Thoresen M, Whitelaw A 2002 Cytokine response in cerebrospinal fluid from preterm infants with posthaemorrhagic ventricular dilatation. Acta Paediatr 91: 1357–1363
Hedtjarn M, Leverin AL, Eriksson K, Blomgren K, Mallard C, Hagberg H 2002 Interleukin-18 involvement in hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. J Neurosci 22: 5910–5919
Felderhoff-Mueser U, Sifringer M, Polley O, Dzietko M, Leineweber B, Mahler L, Baier M, Bittigau P, Obladen M, Ikonomidou C, Buhrer C 2005 Caspase-1 processed interleukins in hyperoxia-induced cell death in the developing brain. Ann Neurol 57: 50–59
Jander S, Stoll G 1998 Differential induction of interleukin-12, interleukin-18, and interleukin-1beta converting enzyme mRNA in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis of the Lewis rat. J Neuroimmunol 91: 93–99
Losy J, Niezgoda A 2001 IL-18 in patients with multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol Scand 104: 171–173
Minagawa K, Tsuji Y, Ueda K, Koyama K, Tanizawa H, Okamura T, Hashimoto-Tamaoki T 2002 Possible correlation between high levels of IL-18 in the cord blood of preterm infants and neonatal development of periventricular leukomalacia and cerebral palsy. Cytokine 17: 164–170
Hansen-Pupp I, Harling S, Berg AC, Cilio C, Hellstrom-Westas L, Ley D 2005 Circulating interferon-gamma and white matter brain damage in preterm infants. Pediatr Res 58: 946–952
Ellison VJ, Mocatta TJ, Winterbourn CC, Darlow BA, Volpe JJ, Inder TE 2005 The relationship of CSF and plasma cytokine levels to cerebral white matter injury in the premature newborn. Pediatr Res 57: 282–286
Mirmiran M, Barnes PD, Keller K, Constantinou JC, Fleisher BE, Hintz SR, Ariagno RL 2004 Neonatal brain magnetic resonance imaging before discharge is better than serial cranial ultrasound in predicting cerebral palsy in very low birth weight preterm infants. Pediatrics 114: 992–998
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Evelyn Strauss for skilled technical assistance and Boris Metze for statistical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was supported by BMBF grant Z01ZZ0101.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmitz, T., Heep, A., Groenendaal, F. et al. Interleukin-1β, Interleukin-18, and Interferon-γ Expression in the Cerebrospinal Fluid of Premature Infants with Posthemorrhagic Hydrocephalus—Markers of White Matter Damage?. Pediatr Res 61, 722–726 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1203/pdr.0b013e31805341f1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/pdr.0b013e31805341f1
This article is cited by
-
Pro-inflammatory cerebrospinal fluid profile of neonates with intraventricular hemorrhage: clinical relevance and contrast with CNS infection
Fluids and Barriers of the CNS (2024)
-
Posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus associates with elevated inflammation and CSF hypersecretion via activation of choroidal transporters
Fluids and Barriers of the CNS (2022)
-
Pathophysiologic mechanisms and strategies for the treatment of post-hemorrhagic hydrocephalus of prematurity
Child's Nervous System (2022)
-
Elevated CSF inflammatory markers in patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus do not promote NKCC1 hyperactivity in rat choroid plexus
Fluids and Barriers of the CNS (2021)
-
Opportunities in posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus research: outcomes of the Hydrocephalus Association Posthemorrhagic Hydrocephalus Workshop
Fluids and Barriers of the CNS (2018)