Abstract
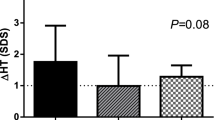
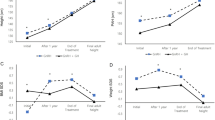
Little is known about factors determining height outcome during GH treatment in Turner syndrome (TS). We investigated 987 TS children within the Kabi International Growth Study (KIGS) who had reached near adult height (NAH) after >4 y GH treatment (including >1 y before puberty). Through multiple regression analysis we developed a model for NAH and total gain. Our results were as follows (median): 1) At start, age 9.7 yrs, height (HT) 118.0 cm (0.0 TS SDS), projected adult height 146.1 cm, GH dose 0.27 mg/kg wk; 2) NAH HT 151.0 cm (1.5 TS SDS); 3) Prepubertal gain 21.2 cm (1.6 TS SDS); 4) Pubertal gain 9.4 cm (0.0 TS SDS). NAH correlated (r2 = 0.67) with (ranked) HT at GH start (+), 1st year responsiveness to GH (+), MPH (+), age at puberty onset (+), age at GH start (−), and dose (+). The same factors explained (R2 = 0.90) the total HT gain. However, HT at GH start correlated negatively. Karyotype had no influence on outcome. Evidently, height at GH start (the taller, the better), age at GH start (the younger, the better), the responsiveness to GH (the higher, the better) and age at puberty (the later, the better) determine NAH.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- KIGS:
-
Kabi International Growth Study
- MPH:
-
mid-parental height
- NAH:
-
near adult height
- rhGH:
-
recombinant human GH
- TS:
-
Turner syndrome
References
Ranke MB, Saenger P 2001 Turner's syndrome. Lancet 358: 309–314
Ranke MB, Grauer ML 1994 Adult height in Turner syndrome: results of a multinational survey 1993. Horm Res 42: 90–94
Rao E, Weiss B, Fukami M, Rump A, Niesler B, Mertz A, Muroya K, Binder G, Kirsch S, Winkelmann M, Nordsiek G, Heinrich U, Breuning MH, Ranke MB, Rosenthal A, Ogata T, Rappold GA 1997 Pseudoautosomal deletions encompassing a novel homeobox gene cause growth failure in idiopathic short stature and Turner syndrome. Nat Genet 16: 54–63
Saenger P, Wikland KA, Conway GS, Davenport M, Gravholt CH, Hintz R, Hovatta O, Hultcrantz M, Landin-Wilhelmsen K, Lin A, Lippe B, Pasquino AM, Ranke MB, Rosenfeld R, Silberbach M 2001 Recommendations for the diagnosis and management of Turner syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86: 3061–3069
van Pareren YK, de Muinck Keizer-Schrama SM, Stijnen T, Sas TC, Jansen M, Otten BJ, Hoorweg-Nijman JJ, Vulsma T, Stokvis-Brantsma WH, Rouwe CW, Reeser HM, Gerver WJ, Gosen JJ, Rongen-Westerlaken C, Drop S 2003 Final height in girls with Turner syndrome after long-term growth hormone treatment in three dosages and low dose estrogens. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88: 1119–1125
Growth Hormone Research Society 2001 Critical evaluation of the safety of recombinant human growth hormone administration: Statement from the Growth Hormone Research Society. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86: 1868–1870
Quigley CA, Gill AM, Crowe BJ, Robling K, Chipman JJ, Rose SR, Ross JL, Cassorla FG, Wolka AM, Wit JM, Rekers-Mombarg LT, Cutler GB Jr 2005 Safety of growth hormone treatment in pediatric patients with idiopathic short stature. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90: 5188–5196
Jenkins PJ, Mukherjee A, Shalet SM 2006 Does growth hormone cause cancer?. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 64: 115–121
Cave CB, Bryant J, Milne R 2003 Recombinant growth hormone in children and adolescents with Turner syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 3: CD003887
Ranke MB, Lindberg A, Chatelain P, Wilton P, Cutfield W, Albertsson-Wikland K, Price DA 2000 Prediction of long-term response to recombinant human growth hormone in Turner syndrome: development and validation of mathematical models. KIGS International Board. Kabi International Growth Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85: 4212–4218
Tanner JM, Whitehouse RH, Takaishi M 1966 Standards from birth to maturity for height, weight, height velocity, and weight velocity: British children, 1965. II. Arch Dis Child 41: 613–635
Ranke MB, Price DA, Albertsson-Wikland KA, Maes M, Lindberg A 1997 Factors determining pubertal growth and final height in growth hormone treatment of idiopathic growth hormone deficiency - Analysis of 195 patients of the Kabi Pharmacia International Growth Study. Horm Res 48: 62–71
Freeman JV, Cole TJ, Chinn S, Jones PR, White EM, Preece MA 1995 Cross sectional stature and weight reference curves for the UK, 1990. Arch Dis Child 73: 17–24
Ranke MB, Stubbe P, Majewski F, Bierich JR 1988 Spontaneous growth in Turner's syndrome. Acta Paediatr Scand Suppl 343: 22–30
Lyon AJ, Preece MA, Grant DB 1985 Growth curve for girls with Turner syndrome. Arch Dis Child 60: 932–935
Niklasson A, Ericson A, Fryer JG, Karlberg J, Lawrence C, Karlberg P 1991 An update of the Swedish reference standards for weight, length and head circumference at birth for given gestational age (1977–1981). Acta Paediatr Scand 80: 756–762
Ranke MB 1996 Towards a consensus on the definition of idiopathic short stature. Horm Res 45: 64–66
Greulich WW, Pyle SI 1952 Radiographic atlas of the skeletal development of the hand and wrist. University Press, Stanford, CA,
Rosenfeld RG, Attie KM, Frane J, Brasel JA, Burstein S, Cara JF, Chernausek S, Gotlin RW, Kuntze J, Lippe BM, Mahoney CP, Moore WV, Saenger P, Johanson AJ 1998 Growth hormone therapy of Turner's syndrome: beneficial effect on adult height. J Pediatr 132: 319–324
Stephure DK 2005 Impact of growth hormone supplementation on adult height in Turner syndrome: results of the Canadian randomized controlled trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90: 3360–3366
Harris M, Hofman PL, Cutfield WS 2004 Growth hormone treatment in children: review of safety and efficacy. Paediatr Drugs 6: 93–106
Ranke MB, Partsch CJ, Lindberg A, Dorr HG, Bettendorf M, Hauffa BP, Schwarz HP, Mehls O, Sander S, Stahnke N, Steinkamp H, Said E, Sippell W 2002 Adult height after GH therapy in 188 Ullrich-Turner syndrome patients: results of the German IGLU Follow-up Study 2001. Eur J Endocrinol 147: 625–633
Quigley CA, Crowe BJ, Anglin DG, Chipman JJ 2002 Growth hormone and low dose estrogen in Turner syndrome: results of a United States multi-center trial to near-final height. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87: 2033–2041
Chernausek SD, Attie KM, Cara JF, Rosenfeld RG, Frane J 2000 Growth hormone therapy of Turner syndrome: the impact of age of estrogen replacement on final height. Genentech, Inc., Collaborative Study Group. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85: 2439–2445
Mauras N, Attie KM, Reiter EO, Saenger P, Baptista J 2000 High dose recombinant human growth hormone (GH) treatment of GH-deficient patients in puberty increases near-final height: a randomized, multicenter trial. Genentech, Inc., Cooperative Study Group. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85: 3653–3660
Ranke MB, Lindberg A, Martin DD, Bakker B, Wilton P, Albertsson-Wikland K, Cowell CT, Price DA, Reiter EO 2003 The mathematical model for total pubertal growth in idiopathic growth hormone (GH) deficiency suggests a moderate role of GH dose. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88: 4748–4753
Soriano-Guillen L, Coste J, Ecosse E, Léger J, Tauber M, Cabrol S, Nicolino M, Brauner R, Chaussain J-L, Carel J-C 2005 Adult height and pubertal growth in Turner syndrome after treatment with recombinant growth hormone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90: 5197–5204
Binder G, Baur F, Schweizer R, Ranke MB 2006 The d3 growth hormone receptor polymorphism is associated with increased responsiveness to GH in Turner syndrome and short SGA children. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91: 659–664
Dos Santos C, Essioux L, Teinturier C, Tauber M, Goffin V, Bougneres P 2004 A common polymorphism of the growth hormone receptor is associated with increased responsiveness to growth hormone. Nat Genet 36: 720–724
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Priscilla Herrmann for her assistance in the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ranke, M., Lindberg, A., Longás, A. et al. Major Determinants of Height Development in Turner Syndrome (TS) Patients Treated With GH: Analysis of 987 Patients From KIGS. Pediatr Res 61, 105–110 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1203/01.pdr.0000250039.42000.c9
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/01.pdr.0000250039.42000.c9
This article is cited by
-
Development and validation of a nomogram to predict poor short-term response to recombinant human growth hormone treatment in children with growth disorders
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation (2022)
-
Turner syndrome: French National Diagnosis and Care Protocol (NDCP; National Diagnosis and Care Protocol)
Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (2022)
-
Comparison of response to 2-years’ growth hormone treatment in children with isolated growth hormone deficiency, born small for gestational age, idiopathic short stature, or multiple pituitary hormone deficiency: combined results from two large observational studies
International Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology (2012)
-
Therapie mit Wachstumshormon bei Ullrich-Turner-Syndrom
Monatsschrift Kinderheilkunde (2010)