Abstract
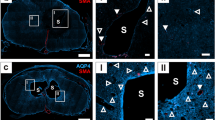
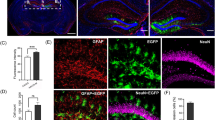
Edema formation can be observed using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in patients with stroke. Recent studies have shown that aquaporin-4 (AQP4), a water channel, is induced early after stroke and potentially participates in the development of brain edema. We studied whether induction of AQP4 correlated with edema formation in a rat pup filament stroke model using high field (11.7-Tesla) MRI followed by immunohistochemical investigation of AQP4 protein expression. At 24 h, we observed increased T2 values and decreased apparent diffusion coefficients (ADC) within injured cortical and striatal regions that reflected the edema formation. Coincident with these MR changes were significant increases in AQP4 expression on astrocytic end-feet in the border regions of injured tissues. Striatal imaging findings were still present at 72 h with a slow normalization of AQP4 expression in the border regions. At 28 d, AQP4 expression normalized in the border while in this region ADC values increased. We show that induction of AQP4 is increased during the period of active edema formation in the border region without regional correlation with edema. Finally, induction of AQP4 on astrocyte end-feet could participate in tissue preservation after ischemia in the immature rat brain.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- ADC:
-
apparent diffusion coefficients
- AQP:
-
aquaporins
- AQP4-IR:
-
AQP4-immunoreactivity
- DWI:
-
diffusion-weighted imaging
- HII:
-
hypoxic-ischemic injury
- MCA:
-
middle cerebral artery
- T2WI:
-
T2-weighted imaging
- tfMCAO:
-
transient filament middle cerebral artery occlusion
References
Lynch JK, Hirtz DG, DeVeber G, Nelson KB 2002 Report of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke workshop on perinatal and childhood stroke. Pediatrics 109: 116–123
De Vries LS, Van der Grond J, Van Haastert IC, Groenendaal F 2005 Prediction of outcome in new-born infants with arterial ischaemic stroke using diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Neuropediatrics 36: 12–20
Kuker W, Mohrle S, Mader I, Schoning M, Nagele T 2004 MRI for the management of neonatal cerebral infarctions: importance of timing. Childs Nerv Syst 20: 742–748
Krishnamoorthy KS, Soman TB, Takeoka M, Schaefer PW 2000 Diffusion-weighted imaging in neonatal cerebral infarction: clinical utility and follow-up. J Child Neurol 15: 592–602
Rumpel H, Ferrini B, Martin E 1998 Lasting cytotoxic edema as an indicator of irreversible brain damage: a case of neonatal stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19: 1636–1638
Loubinoux I, Volk A, Borredon J, Guirimand S, Tiffon B, Seylaz J, Meric P, Rosenberg GA 1997 Spreading of vasogenic edema and cytotoxic edema assessed by quantitative diffusion and T2 magnetic resonance imaging. Stroke 28: 419–427
Meng S, Qiao M, Lin L, Del Bigio MR, Tomanek B, Tuor UI 2004 Correspondence of AQP4 expression and hypoxic-ischaemic brain oedema monitored by magnetic resonance imaging in the immature and juvenile rat. Eur J Neurosci 19: 2261–2269
Badaut J, Hirt L, Granziera C, Bogousslavsky J, Magistretti PJ, Regli L 2001 Astrocyte-specific expression of aquaporin-9 in mouse brain is increased after transient focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 21: 477–482
Ribeiro Mde C, Hirt L, Bogousslavsky J, Regli L, Badaut J 2006 Time course of aquaporin expression after transient focal cerebral ischemia in mice. J Neurosci Res 83: 1231–1240
Manley GT, Fujimura M, Ma T, Noshita N, Filiz F, Bollen AW, Chan P, Verkman AS 2000 Aquaporin-4 deletion in mice reduces brain edema after acute water intoxication and ischemic stroke. Nat Med 6: 159–163
Papadopoulos MC, Manley GT, Krishna S, Verkman AS 2004 Aquaporin-4 facilitates reabsorption of excess fluid in vasogenic brain edema. FASEB J 18: 1291–1293
Zhao J, Moore AN, Clifton GL, Dash PK 2005 Sulforaphane enhances aquaporin-4 expression and decreases cerebral edema following traumatic brain injury. J Neurosci Res 82: 499–506
Ashwal S, Tone B, Tian HR, Chong S, Obenaus A 2006 Serial magnetic resonance imaging in a rat pup filament stroke model. Exp Neurol 202: 294–301
Wong SK 2004 A 384-well cell-based phospho-ERK assay for dopamine D2 and D3 receptors. Anal Biochem 333: 265–272
Schaefer PW, Hunter GJ, He J, Hamberg LM, Sorensen AG, Schwamm LH, Koroshetz WJ, Gonzalez RG 2002 Predicting cerebral ischemic infarct volume with diffusion and perfusion MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23: 1785–1794
Klatzo I 1985 Brain oedema following brain ischaemia and the influence of therapy. Br J Anaesth 57: 18–22
Gartshore G, Patterson J, Macrae IM 1997 Influence of ischemia and reperfusion on the course of brain tissue swelling and blood-brain barrier permeability in a rodent model of transient focal cerebral ischemia. Exp Neurol 147: 353–360
Ashwal S, Tone B, Tian HR, Chong S, Obenaus A 2007 Comparison of two neonatal ischemic injury models using magnetic resonance imaging. Pediatr Res 61: 9–14
Amiry-Moghaddam M, Otsuka T, Hurn PD, Traystman RJ, Haug FM, Froehner SC, Adams ME, Neely JD, Agre P, Ottersen OP, Bhardwaj A 2003 An alpha-syntrophin-dependent pool of AQP4 in astroglial end-feet confers bidirectional water flow between blood and brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100: 2106–2111
Ringer TM, Neumann-Haefelin T, Sobel RA, Moseley ME, Yenari MA 2001 Reversal of early diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging abnormalities does not necessarily reflect tissue salvage in experimental cerebral ischemia. Stroke 32: 2362–2369
Saadoun S, Papadopoulos MC, Watanabe H, Yan D, Manley GT, Verkman AS 2005 Involvement of aquaporin-4 in astroglial cell migration and glial scar formation. J Cell Sci 118: 5691–5698
Hiroaki Y, Tani K, Kamegawa A, Gyobu N, Nishikawa K, Suzuki H, Walz T, Sasaki S, Mitsuoka K, Kimura K 2006 Implications of the aquaporin-4 structure on array formation and cell adhesion. J Mol Biol 355: 628–639
Sulyok E 2006 Physical water compartments: a revised concept of perinatal body water physiology. Physiol Res 55: 133–138
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Mr. S. Chong for assistance with the neuroimaging and Mrs. M. F. Hamou for assistance with immunohistochemistry.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported in part by the Pediatric Research Fund, Department of Pediatrics, and a NASA Cooperative Agreement NCC9-149 to the Radiobiology Program, Department of Radiation Medicine at Loma Linda University, the Swiss Science Foundation (FN 3100AO-108001); SwissHeart Foundation; Fondazione Per Lo Studio Delle Malattie Neurodegenerative Delle Persone Adulte e Dell' Anziano, from Lugano, Switzerland.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Badaut, J., Ashwal, S., Tone, B. et al. Temporal and Regional Evolution of Aquaporin-4 Expression and Magnetic Resonance Imaging in a Rat Pup Model of Neonatal Stroke. Pediatr Res 62, 248–254 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3180db291b
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3180db291b
This article is cited by
-
Brain Maturation as a Fundamental Factor in Immune-Neurovascular Interactions in Stroke
Translational Stroke Research (2024)
-
AQP4 is an Emerging Regulator of Pathological Pain: A Narrative Review
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
-
Signaling pathways involved in ischemic stroke: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2022)
-
Neurovascular Unit as a Source of Ischemic Stroke Biomarkers—Limitations of Experimental Studies and Perspectives for Clinical Application
Translational Stroke Research (2020)
-
Modulating the water channel AQP4 alters miRNA expression, astrocyte connectivity and water diffusion in the rodent brain
Scientific Reports (2018)