Abstract
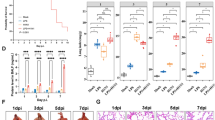
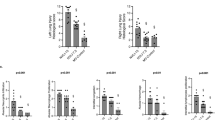
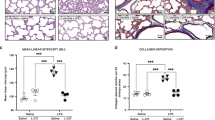
Infection/inflammation and mechanical ventilation have both independently been shown to increase cytokine/chemokine levels in lung tissue and blood samples of premature patients. Little is known about the combined effect of systemic inflammation and mechanical ventilation on cytokine expression in the lung. We tested whether pre-existing inflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) exposure would modify cytokine/chemokine response in newborn rat lungs to high tidal volume ventilation (HTVV). Newborn rats were randomly assigned to four groups: groups I and II (saline); groups III and IV: 3 mg/kg LPS. Groups II and IV were 24h later subjected to 3h of ventilation with a tidal volume of 25 mL/kg. HTVV alone increased IL-1β, IL-6 and the chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 2 (CXCL2) mRNA expression. Although the cytokine response to LPS alone had disappeared after 24 h, the combination of LPS pretreatment and HTVV significantly increased the expression of IL-6 and IL-1β mRNA when compared with HTVV alone. TNF-α expression was increased neither by HTVV alone nor in combination with LPS. IL-6 protein content in bronchoalveolar lavage increased due to the combined treatment. Thus, a subtle pre-existing inflammation combined with HTVV amplifies the proinflammatory cytokine/chemokine expression in the newborn rat lung compared with HTVV alone.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- BALF:
-
bronchoalveolar lavage fluid
- BPD:
-
bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- CXCL-:
-
chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand
- HTVV:
-
High tidal volume ventilation
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
References
Smith VC, Zupancic JA, McCormick MC, Croen LA, Greene J, Escobar GJ, Richardson DK 2005 Trends in severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia rates between 1994 and 2002. J Pediatr 146: 469–473
Watterberg KL, Demers LM, Scott SM, Murphy S 1996 Chorioamnionitis and early lung inflammation in infants in whom bronchopulmonary dysplasia develops. Pediatrics 97: 210–215
Van Marter LJ, Dammann O, Allred EN, Leviton A, Pagano M, Moore M, Martin C 2002 Chorioamnionitis, mechanical ventilation, and postnatal sepsis as modulators of chronic lung disease in preterm infants. J Pediatr 140: 171–176
Proost P, De Wolf-Peeters C, Conings R, Opdenakker G, Billiau A, Van DJ 1993 Identification of a novel granulocyte chemotactic protein (GCP-2) from human tumor cells. In vitro and in vivo comparison with natural forms of GRO, IP-10, and IL-8. J Immunol 150: 1000–1010
McColm JR, McIntosh N 1994 Interleukin-8 in bronchoalveolar lavage samples as predictor of chronic lung disease in premature infants. Lancet 343: 729
Ghezzi F, Gomez R, Romero R, Yoon BH, Edwin SS, David C, Janisse J, Mazor M 1998 Elevated interleukin-8 concentrations in amniotic fluid of mothers whose neonates subsequently develop bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 78: 5–10
Bagchi A, Viscardi RM, Taciak V, Ensor JE, McCrea KA, Hasday JD 1994 Increased activity of interleukin-6 but not tumor necrosis factor-alpha in lung lavage of premature infants is associated with the development of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr Res 36: 244–252
Hoffmann E, Dittrich-Breiholz O, Holtmann H, Kracht M 2002 Multiple control of interleukin-8 gene expression. J Leukoc Biol 72: 847–855
Shapiro L, Dinarello CA 1997 Hyperosmotic stress as a stimulant for proinflammatory cytokine production. Exp Cell Res 231: 354–362
DeForge LE, Preston AM, Takeuchi E, Kenney J, Boxer LA, Remick DG 1993 Regulation of interleukin 8 gene expression by oxidant stress. J Biol Chem 268: 25568–25576
Tremblay L, Valenza F, Ribeiro SP, Li J, Slutsky AS 1997 Injurious ventilatory strategies increase cytokines and c-fos m-RNA expression in an isolated rat lung model. J Clin Invest 99: 944–952
Gurkan OU, O'Donnell C, Brower R, Ruckdeschel E, Becker PM 2003 Differential effects of mechanical ventilatory strategy on lung injury and systemic organ inflammation in mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 285: L710–L718
Altemeier WA, Matute-Bello G, Frevert CW, Kawata Y, Kajikawa O, Martin TR, Glenny RW 2004 Mechanical ventilation with moderate tidal volumes synergistically increases lung cytokine response to systemic endotoxin. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 287: L533–L542
Burri PH 1997 Structural aspects of prenatal and postnatal development and growth of the lung. In: McDonald JA (ed) Lung growth and development. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 1–35.
Volgyesi GA, Tremblay LN, Webster P, Zamel N, Slutsky AS 2000 A new ventilator for monitoring lung mechanics in small animals. J Appl Physiol 89: 413–421
Copland IB, Martinez F, Kavanagh BP, Engelberts D, McKerlie C, Belik J, Post M 2004 High tidal volume ventilation causes different inflammatory responses in newborn versus adult lung. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 169: 739–748
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD 2001 Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25: 402–408
Tsuchida S, Engelberts D, Roth M, McKerlie C, Post M, Kavanagh BP 2005 Continuous positive airway pressure causes lung injury in a model of sepsis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 289: L554–L564
Chan A, Jayasuriya K, Berry L, Roth-Kleiner M, Post M, Belik J 2005 Volutrauma Activates the Clotting Cascade in the Newborn but not Adult Rat. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 290: L754–L760
Kornecki A, Tsuchida S, Ondiveeran HK, Engelberts D, Frndova H, Tanswell AK, Post M, McKerlie C, Belik J, Fox-Robichaud A, Kavanagh BP 2005 Lung development and susceptibility to ventilator-induced lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 171: 743–752
Tsuchida S, Engelberts D, Peltekova V, Hopkins N, Frndova H, Babyn P, McKerlie C, Post M, McLoughlin P, Kavanagh BP 2006 Atelectasis causes Alveolar Injury in Non-Atelectatic Lung Regions. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 174: 279–289
Roth-Kleiner M, Post M 2005 Similarities and dissimilarities of branching and septation during lung development. Pediatr Pulmonol 40: 113–134
Jobe AH, Bancalari E 2001 Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 163: 1723–1729
Speer CP 2006 Inflammation and bronchopulmonary dysplasia: A continuing story. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 11: 354–362
Pugin J, Dunn I, Jolliet P, Tassaux D, Magnenat JL, Nicod LP, Chevrolet JC 1998 Activation of human macrophages by mechanical ventilation in vitro. Am J Physiol 275: L1040–L1050
Belperio JA, Keane MP, Burdick MD, Londhe V, Xue YY, Li K, Phillips RJ, Strieter RM 2002 Critical role for CXCR2 and CXCR2 ligands during the pathogenesis of ventilator-induced lung injury. J Clin Invest 110: 1703–1716
Wilson MR, Choudhury S, Goddard ME, O'Dea KP, Nicholson AG, Takata M 2003 High tidal volume upregulates intrapulmonary cytokines in an in vivo mouse model of ventilator-induced lung injury. J Appl Physiol 95: 1385–1393
Copland IB, Kavanagh BP, Engelberts D, McKerlie C, Belik J, Post M 2003 Early changes in lung gene expression due to high tidal volume. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 168: 1051–1059
Chu EK, Whitehead T, Slutsky AS 2004 Effects of cyclic opening and closing at low- and high-volume ventilation on bronchoalveolar lavage cytokines. Crit Care Med 32: 168–174
Schultz C, Tautz J, Reiss I, Moller JC 2003 Prolonged mechanical ventilation induces pulmonary inflammation in preterm infants. Biol Neonate 84: 64–66
Cao L, Liu C, Cai B, Jia X, Kang L, Speer CP, Sun B 2004 Nuclear factor-kappa B expression in alveolar macrophages of mechanically ventilated neonates with respiratory distress syndrome. Biol Neonate 86: 116–123
Lafleur RL, Abrahamsen MS, Maheswaran SK 1998 The biphasic mRNA expression pattern of bovine interleukin-8 in Pasteurella haemolytica lipopolysaccharide-stimulated alveolar macrophages is primarily due to tumor necrosis factor alpha. Infect Immun 66: 4087–4092
Ulich TR, Guo K, Yin S, del Castillo J, Yi ES, Thompson RC, Eisenberg SP 1992 Endotoxin-induced cytokine gene expression in vivo. IV. Expression of interleukin-1 alpha/beta and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist mRNA during endotoxemia and during endotoxin-initiated local acute inflammation. Am J Pathol 141: 61–68
Johnston CJ, Finkelstein JN, Gelein R, Oberdorster G 1998 Pulmonary cytokine and chemokine mRNA levels after inhalation of lipopolysaccharide in C57BL/6 mice. Toxicol Sci 46: 300–307
Coalson JJ 2003 Pathology of new bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Semin Neonatol 8: 73–81
Willet KE, Kramer BW, Kallapur SG, Ikegami M, Newnham JP, Moss TJ, Sly PD, Jobe AH 2002 Intra-amniotic injection of IL-1 induces inflammation and maturation in fetal sheep lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 282: L411–L420
Willet KE, Jobe AH, Ikegami M, Newnham J, Brennan S, Sly PD 2000 Antenatal endotoxin and glucocorticoid effects on lung morphometry in preterm lambs. Pediatr Res 48: 782–788
He T, Peterson TE, Katusic ZS 2005 Paracrine mitogenic effect of human endothelial progenitor cells: role of interleukin-8. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 289: H968–H972
Keshamouni VG, Arenberg DA, Reddy RC, Newstead MJ, Anthwal S, Standiford TJ 2005 PPAR-gamma activation inhibits angiogenesis by blocking ELR + CXC chemokine production in non-small cell lung cancer. Neoplasia 7: 294–301
Kallapur SG, Bachurski CJ, Le Cras TD, Joshi SN, Ikegami M, Jobe AH 2004 Vascular changes after intra-amniotic endotoxin in preterm lamb lungs. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 287: L1178–L1185
Lundblad LK, Thompson-Figueroa J, Leclair T, Sullivan MJ, Poynter ME, Irvin CG, Bates JH 2005 Tumor necrosis factor-alpha overexpression in lung disease: a single cause behind a complex phenotype. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 171: 1363–1370
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by: Operating grant (MOP-15272) from the Canadian Institute of Health Research and infrastructure grant (CCURE) from the Canadian Foundation for Innovation. M. Roth-Kleiner is recipient of a Swiss Neonatology Research Award and is supported by the Fonds de perfectionnement et de pediatrie du CHUV, Lausanne, Switzerland, the Foundation Eugenio Litta, Switzerland and the Foundation Pittet, Lausanne, Switzerland and the Swiss Life Foundation, Switzerland.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roth-Kleiner, M., Ridsdale, R., Cao, L. et al. Lipopolysaccharide Exposure Modifies High Tidal Volume Ventilation-Induced Proinflammatory Mediator Expression in Newborn Rat Lungs. Pediatr Res 61, 191–196 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1203/01.pdr.0000252437.51779.21
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/01.pdr.0000252437.51779.21
This article is cited by
-
Gene expression profile in newborn rat lungs after two days of recovery of mechanical ventilation
Pediatric Research (2015)