Abstract
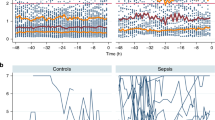
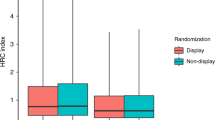
To test the hypothesis that heart rate characteristic (HRC) monitoring adds information to clinical signs of illness in diagnosing neonatal sepsis, we prospectively recorded clinical data and the HRC index in 76 episodes of proven sepsis and 80 episodes of clinical sepsis in 337 infants in the University of Virginia NICU more than 7 d old. We devised an illness severity score based on clinical findings and tests relevant to sepsis. Point scores were derived from coefficients of multivariable regression models, and we internally validated a total score. We determined relationships of the HRC index with individual clinical signs, laboratory tests, and the total score. We found highly significant correlations of the clinical score and individual clinical signs with the HRC index. The clinical score and HRC index added independent information in predicting sepsis, and were similar in clinical and proven sepsis. The clinical score and the HRC index rose before sepsis, and the HRC index rose first. We conclude that clinical signs of illness and HRC monitoring add independent information to one another in the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- HRC:
-
heart rate characteristics
- I:T ratio:
-
ratio of immature to total neutrophils
- VLBW:
-
very low birth weight
- WBC:
-
white blood cell count
References
Stoll BJ, Hansen N, Fanaroff AA, Wright LL, Carlo WA, Ehrenkranz RA, Lemons JA, Donovan EF, Stark AR, Tyson JE, Oh W, Bauer CR, Korones SB, Shankaran S, Laptook AR, Stevenson DK, Papile LA, Poole WK 2002 Late-onset sepsis in very low birth weight neonates: the experience of the NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Pediatrics 110: 285–291
Fanaroff AA, Korones SB, Wright LL, Verter J, Poland RL, Bauer CR, Tyson JE, Philips JB, Edwards W, Lucey JF, Catz CS, Shankaran S, Oh W 1998 Incidence, presenting features, risk factors and significance of late onset septicemia in very low birth weight infants. The National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. Pediatr Infect Dis J 17: 593–598
Kellogg JA, Ferrentino FL, Goodstein MH, Liss J, Shapiro SL, Bankert DA 1997 Frequency of low level bacteremia in infants from birth to two months of age. Pediatr Infect Dis J 16: 381–385
Schelonka RL, Chai MK, Yoder BA, Hensley D, Brockett RM, Ascher DP 1996 Volume of blood required to detect common neonatal pathogens. J Pediatr 129: 275–278
Neal PR, Kleiman MB, Reynolds JK, Allen SD, Lemons JA, Yu PL 1986 Volume of blood submitted for culture from neonates. J Clin Microbiol 24: 353–356
Pierce JR, Merenstein GB, Stocker JT 1984 Immediate postmortem cultures in an intensive care nursery. Pediatr Infect Dis 3: 510–513
Squire E, Favara B, Todd J 1979 Diagnosis of neonatal bacterial infection: hematologic and pathologic findings in fatal and nonfatal cases. Pediatrics 64: 60–64
Garner JS, Jarvis WR, Emori TG, Horan TC, Hughes JM 1988 CDC definitions for nosocomial infections, 1988. Am J Infect Control 16: 128–140
Stoll BJ, Hansen NI, Adams-Chapman I, Fanaroff AA, Hintz SR, Vohr B, Higgins RD 2004 Neurodevelopmental and growth impairment among extremely low-birth-weight infants with neonatal infection. JAMA 292: 2357–2365
American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine Consensus Conference Committee (ACCP/SCCM) 1992 American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine Consensus Conference: Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. Crit Care Med 20: 864–874
Griffin MP, Moorman JR 2001 Toward the early diagnosis of neonatal sepsis and sepsis-like illness using novel heart rate analysis. Pediatrics 107: 97–104
Moorman JR, Lake DE, Griffin MP 2006 5 Heart rate characteristics monitoring in neonatal sepsis. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 53: 126–132
Kovatchev BP, Farhy LS, Cao H, Griffin MP, Lake DE, Moorman JR 2003 Sample asymmetry analysis of heart rate characteristics with application to neonatal sepsis and systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Pediatr Res 54: 892–898
Lake DE, Richman JS, Griffin MP, Moorman JR 2002 Sample entropy analysis of neonatal heart rate variability. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol.Am J Physiol 283: R789–R797
Richman JS, Moorman JR 2000 Physiological time series analysis using approximate entropy and sample entropy. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.Am J Physiol 278: H2039–H2049
Griffin MP, O'Shea TM, Bissonette EA, Harrell FE, Lake DE, Moorman JR 2003 Abnormal heart rate characteristics preceding neonatal sepsis and sepsis-like illness. Pediatr Res 53: 920–926
Griffin MP, O'Shea TM, Bissonette EA, Harrell FE Jr, Lake DE, Moorman JR 2004 Abnormal heart rate characteristics are associated with neonatal mortality. Pediatr Res 55: 782–788
Griffin MP, Lake DE, Bissonette EA, Harrell FE Jr, O'Shea TM, Moorman JR 2005 Heart rate characteristics: novel physiomarkers to predict neonatal infection and death. Pediatrics 116: 1070–1074
Griffin MP, Lake DE, Moorman JR 2005 Heart rate characteristics and laboratory tests in neonatal sepsis. Pediatrics 115: 937–941
Escobar GJ, Shaheen SM, Breed EM, Botas C, Greene JD, Yoshida CK, Zupancic J, Newman TB 2004 Richardson score predicts short-term adverse respiratory outcomes in newborns <= 34 weeks gestation. J Pediatr 145: 754–760
Richman JS, Lake DE, Moorman JR . Sample entropy. Methods Enzymol 2004 384: 172–184
Steyerberg EW, Harrell FE, Borsboom GJ, Eijkemans MJ, Vergouwe Y, Habbema JD 2001 Internal validation of predictive models: Efficiency of some procedures for logistic regression analysis. J Clin Epidemiol 54: 774–781
Moons KG, Harrell FE, Steyerberg EW 2002 Should scoring rules be based on odds ratios or regression coefficients?. J Clin Epidemiol 55: 1054–1055
Anderson MR, Blumer JL 1997 Advances in the therapy for sepsis in children. Pediatr Clin North Am 44: 179–205
Kuster H, Weiss M, Willeitner AE, Detlefsen S, Jeremias I, Zbojan J, Geiger R, Lipowsky G, Simbruner G 1998 Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist and interleukin-6 for early diagnosis of neonatal sepsis 2 days before clinical manifestation. Lancet 352: 1271–1277
Stoll BJ, Gordon T, Korones SB, Shankaran S, Tyson JE, Bauer CR, Fanaroff AA, Lemons JA, Donovan EF, Oh W, Stevenson DK, Ehrenkranz RA, Papile LA, Verter J, Wright LL 1996 Late-onset sepsis in very low birth weight neonates: a report from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. J Pediatr 129: 63–71
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Medical Predictive Science Corporation of Charlottesville, Virginia, has a license to market technology related to heart rate characteristics monitoring of newborn infants, supplied partial funding for this study, and aided in collection of data. The company played no role in the study design, analysis and interpretation of data, writing of the report, or the decision to submit the paper for publication. M.P.G., and J.R.M. have an equity share in this company.
Additional support was provided by the American Heart Association, Mid-Atlantic Research Affiliate; University of Virginia Children's Hospital Research Fund; Virginia's Center for Innovative Technology; and NIGMS-64640 from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences.
Presented in part at the Pediatric Academic Societies' Meeting, May 3–6, 2003, Seattle, WA.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Griffin, M., Lake, D., O'Shea, T. et al. Heart Rate Characteristics and Clinical Signs in Neonatal Sepsis. Pediatr Res 61, 222–227 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1203/01.pdr.0000252438.65759.af
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/01.pdr.0000252438.65759.af
This article is cited by
-
Sample entropy correlates with intraventricular hemorrhage and mortality in premature infants early in life
Pediatric Research (2024)
-
Cardiorespiratory signature of neonatal sepsis: development and validation of prediction models in 3 NICUs
Pediatric Research (2023)
-
Novel approaches to capturing and using continuous cardiorespiratory physiological data in hospitalized children
Pediatric Research (2023)
-
The principles of whole-hospital predictive analytics monitoring for clinical medicine originated in the neonatal ICU
npj Digital Medicine (2022)
-
Vital signs as physiomarkers of neonatal sepsis
Pediatric Research (2022)