Abstract
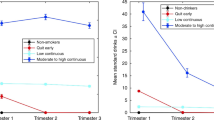
We investigated the effects of prenatal cocaine exposure (PCE) on heart rate (HR) and heart rate variability (HRV) in the presence of orthostatic stress among near- and full-term neonates. PCE infants (n = 21) and controls (n = 23) were enrolled within 120 h of birth. ECG was recorded for an hour during quiet sleep, 30 min in supine position and then 30 min in an inclined position. Linear mixed models were used to analyze HR and HRV in the time domain and wavelet and power spectrum analyses in the frequency domain. PCE infants had tachycardia both before (p = 0.091) and after tilting (p = 0.015), but with a clear interaction between PCE and orthostatic stress (p = 0.049). Compared with controls, PCE infants had a delayed and prolonged reaction to orthostatic stress. There was also a pronounced interaction with regard to log-transformed SDDRR, a measure of HRV (p = 0.049). Controls experienced an instantaneous increase in log (SDDRR) followed by a prompt return to normal levels, while PCE infants had a gradual increase that did not dissipate quickly. Frequency-domain analyses also distinguished between the cocaine-exposed infants and the controls. Results suggest that the effects of PCE on the development of sympathetic and parasympathetic systems could lead to altered cardiovascular function.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- ANS:
-
autonomic nervous system
- BP:
-
blood pressure
- corSDRR:
-
corrected SDRR
- HR:
-
heart rate
- HRV:
-
heart rate variability
- LMM:
-
linear mixed model
- PCE:
-
prenatal cocaine exposure
- PSA:
-
power spectrum analysis
- SDRR:
-
standard deviation of the R-R intervals
- SDDRR:
-
standard deviation of differences between successive R-R intervals
References
Sahni R, Schulze KF, Kashyap S, Ohira-Kist K, Fifer WP, Myers MM 2000 Maturational changes in heart rate and heart rate variability in low birth weight infants. Dev Psychobiol 37: 73–81
Schechtman VL, Raetz SL, Harper RK, Garfinkel A, Wilson AJ, Southall DP, Harper RM 1992 Dynamic analysis of cardiac R-R intervals in normal infants and in infants who subsequently succumbed to the sudden infant death syndrome. Pediatr Res 31: 606–612
Hermida RC, Ayala DE, Fernandez JR, Fraga JM 1994 Hardware-software approach for neonatal cardiovascular risk estimation. Biomed Instrum Technol 28: 43–51
Karin J, Hirsch M, Akselrod S 1993 An estimate of fetal autonomic state by spectral analysis of fetal heart rate fluctuations. Pediatr Res 34: 134–138
Sibony O, Fouillot JP, Benaoudia M, Benhalla A, Oury JF, Sureau C, Blot P 1994 Quantification of the fetal heart rate variability by spectral analysis of fetal well-being and fetal distress. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 54: 103–108
Hadeed AJ, Siegel SR 1989 Maternal cocaine use during pregnancy: effect on the newborn infant. Pediatrics 84: 205–210
Bauer CR, Shankaran S, Bada HS, Lester B, Wright LL, Krause-Steinrauf H, Smeriglio VL, Finnegan LP, Maza PL, Verter J 2002 The Maternal Lifestyle Study: drug exposure during pregnancy and short-term maternal outcomes. Am J Obstet Gynecol 186: 487–495
Bauer CR, Langer JC, Shankaran S, Bada HS, Lester B, Wright LL, Krause-Steinrauf H, Smeriglio VL, Finnegan LP, Maza PL, Verter J 2005 Acute neonatal effects of cocaine exposure during pregnancy. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 159: 824–834
Oriol NE, Bennett FM, Rigney DR, Goldberger AL 1993 Cocaine effects on neonatal heart rate dynamics: preliminary findings and methodological problems. Yale J Biol Med 66: 75–84
Mehta SK, Super DM, Salvator A, Singer L, Connuck D, Fradley LG, Harcar-Sevcik RA, Kaufman ES 2001 Heart rate variability in cocaine-exposed newborn infants. Am Heart J 142: 828–832
Mehta SK, Super DM, Connuck D, Kirchner HL, Salvator A, Singer L, Fradley LG, Kaufman ES 2002 Autonomic alterations in cocaine-exposed infants. Am Heart J 144: 1109–1115
Regalado MG, Schechtman VL, Del Angel AP, Bean XD 1996 Cardiac and respiratory patterns during sleep in cocaine-exposed neonates. Early Hum Dev 44: 187–200
Garde S, Regalado MG, Schechtman VL, Khoo MC 2001 Nonlinear dynamics of heart rate variability in cocaine-exposed neonates during sleep. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 280: H2920–H2928
Regalado MG, Schechtman VL, Khoo MC, Shin J, Bean XD 1998 Sources of heart rate variation during sleep in cocaine-exposed neonates. Ann N Y Acad Sci 846: 415–418
Mansier P, Clairambault J, Charlotte N, Medigue C, Vermeiren C, LePape G, Carre F, Gounaropoulou A, Swynghedauw B 1996 Linear and non-linear analyses of heart rate variability: a minireview. Cardiovasc Res 31: 371–379
Coumel P, Hermida JS, Wennerblom B, Leenhardt A, Maison-Blanche P, Cauchemez B 1991 Heart rate variability in left ventricular hypertrophy and heart failure, and the effects of beta-blockade. A non-spectral analysis of heart rate variability in the frequency domain and in the time domain. Eur Heart J 12: 412–422
Neuman MR, Watson H, Mendenhall RS, Zoldak JT, Di Fiore JM, Peucker M, Baird TM, Crowell DH, Hoppenbrouwers TT, Hufford D, Hunt CE, Corwin MJ, Tinsley LR, Weese-Mayer DE, Sackner MA 2001 Cardiopulmonary monitoring at home: the CHIME monitor. Physiol Meas 22: 267–286
McDonald R, Jenkins J, Arzbaecher R, Thorne R 1989 A software trigger for intracardiac waveform detection with automatic threshold adjustment. IEEE Computers in Cardiology Proceedings, IEEE Computer Society Press, Washington, DC, pp 167–170
Regalado MG, Schechtman VL, Khoo MC, Bean XD 2001 Spectral analysis of heart rate variability and respiration during sleep in cocaine-exposed neonates. Clin Physiol 21: 428–436
Van Ravenswaaij-Arts C, Hopman J, Kollee L, Stoelinga G, Van Geijn H 1994 Spectral analysis of heart rate variability in spontaneously breathing very preterm infants. Acta Paediatr 83: 473–480
Dykes FD, Ahmann PA, Baldzer K, Carrigan TA, Kitney R, Giddens DP 1986 Breath amplitude modulation of heart rate variability in normal full term neonates. Pediatr Res 20: 301–308
Jimenez RF, Gunther B, Salazar A 1997 Continuous wavelet transform of aortic pressure oscillations in anesthetized dogs: effects of 45 degrees tilting. Biol Res 30: 53–64
Borst C, Wieling W, van Brederode JF, Hond A, de Rijk LG, Dunning AJ 1982 Mechanisms of initial heart rate response to postural change. Am J Physiol 243: H676–H681
Andriessen P, Oetomo SB, Peters C, Vermeulen B, Wijn PF, Blanco CE 2005 Baroreceptor reflex sensitivity in human neonates: the effect of postmenstrual age. J Physiol 568: 333–341
DiPietro JA, Suess PE, Wheeler JS, Smouse PH, Newlin DB 1995 Reactivity and regulation in cocaine-exposed neonates. Infant Behav Dev 18: 407–414
O'Connor SJ, Gardner DS, Ousey JC, Holdstock N, Rossdale P, Edwards CM, Fowden AL, Giussani DA 2005 Development of baroreflex and endocrine responses to hypotensive stress in newborn foals and lambs. Pflugers Arch 450: 298–306
Segar JL, Van Natta T, Smith OJ 2002 Effects of fetal ovine adrenalectomy on sympathetic and baroreflex responses at birth. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 283: R460–R467
Magnano CL, Gardner JM, Karmel BZ 1992 Differences in salivary cortisol levels in cocaine-exposed and noncocaine-exposed NICU infants. Dev Psychobiol 25: 93–103
Levine S 1962 Plasma-free corticosteroid response to electric shock in rats stimulated in infancy. Science 135: 795–796
Goto M, Nagashima M, Baba R, Nagano Y, Yokota M, Nishibata K, Tsuji A 1997 Analysis of heart rate variability demonstrates effects of development on vagal modulation of heart rate in healthy children. J Pediatr 130: 725–729
Finley JP, Nugent ST 1995 Heart rate variability in infants, children and young adults. J Auton Nerv Syst 51: 103–108
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The study was funded in part by a grant from the Children's Miracle Network, KY Children's Hospital.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
John, V., Dai, H., Talati, A. et al. Autonomic Alterations in Cocaine-Exposed Neonates Following Orthostatic Stress. Pediatr Res 61, 251–256 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1203/01.pdr.0000252436.62151.67
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/01.pdr.0000252436.62151.67