Abstract
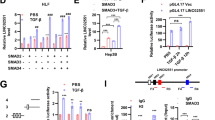
The Smad2/3 pathway plays a key role in mediating TGF-β1 inhibition of branching morphogenesis and induction of connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) expression in embryonic lungs. Because a number of cell-specific interactions have been described between TGF-β1-driven Smad signaling and the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway, we have investigated the effects of JNK inhibition on TGF-β1 activation of Smad2, inhibition of branching, induction of CTGF expression, and apoptosis in mouse embryonic lung explants. Mouse embryonic day 12.5 (E12.5) lung explants were treated with TGF-β1 in the presence or absence of a specific pharmacologic JNK inhibitor (SP600125) and a specific JNK peptide inhibitor (JNKI). We found that TGF-β1 activated the JNK pathway by stimulating c-Jun phosphorylation, which was blocked by JNK inhibitors. Treatment with SP600125 stimulated Smad2 phosphorylation and enhanced TGF-β1-induced Smad2 phosphorylation. Treatment with JNK inhibitors also decreased normal branching morphogenesis and induced CTGF expression as well as augmented TGF-β1 inhibition of branching and induction of CTGF expression. Furthermore, JNK inhibition-induced apoptosis. Our results demonstrate that inhibition of the JNK pathway promotes TGF-β1-driven Smad2 responses in lung branching morphogenesis. These data suggest that the JNK pathway may antagonize TGF-β1 dependent Smad2 signaling during mouse embryonic lung development.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- AP-1:
-
activating-protein-1
- CTGF:
-
connective tissue growth factor
- JNK:
-
c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase
- JNKI:
-
JNK peptide inhibitor
- JNKC:
-
JNK peptide control
- MAPK:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MKK:
-
MAPK kinase
- p-c-Jun:
-
phosphorylated c-Jun
- p-Smad2:
-
phosphorylated smad2
- TβRI:
-
TGF-β receptor I
- TβRII:
-
TGF-β receptor II
- t-c-Jun:
-
total c-Jun
- t-Smad2:
-
total Smad2
References
Moses HL 1990 Growth Factors from Genes to Clinical Application. Raven Press, New York. pp 141–155
Moses HL, Yang EY, Pietenpol JA 1990 TGF-beta stimulation and inhibition of cell proliferation: new mechanistic insights. Cell 63: 245–247
Zhou L, Dey CR, Wert SE, Whitsett JA 1996 Arrested lung morphogenesis in transgenic mice bearing a SP-C-TGF-beta 1 chimeric gene. Dev Biol 175: 227–238
Zeng X, Gray M, Stahlman MT, Whitsett JA 2001 TGF-beta1 perturbs vascular development and inhibits epithelial differentiation in fetal lung in vivo. Dev Dyn 221: 289–301
Serra R, Pelton RW, Moses HL 1994 TGF beta 1 inhibits branching morphogenesis and n-myc expression in lung bud organ cultures. Development 120: 2153–2161
Bragg AD, Moses HL, Serra R 2001 Signaling to the epithelium is not sufficient to mediate all of the effects of transforming growth factor beta and bone morphogenetic protein 4 on murine embryonic lung development. Mech Dev 109: 13–26
Zhao J, Bu D, Lee M, Slavkin HC, Hall FL, Warburton D 1996 Abrogation of transforming growth factor-beta type II receptor stimulates embryonic mouse lung branching morphogenesis in culture. Dev Biol 180: 242–257
Massague J, Cheifetz S, Boyd FT, Andres LJ 1990 TGF-beta receptors and TGF-beta binding proteoglycans: recent progress in identifying their functional properties. Ann NY Acad Sci 593: 59–72
Franzen P, ten Dijke P, Ichijo H, Yamashita H, Schulz P, Heldin CH, Miyazono K 1993 Cloning of a TGF beta type I receptor that forms a heteromeric complex with the TGF beta type II receptor. Cell 75: 681–692
Massague J 1998 TGF-beta signal transduction. Annu Rev Biochem 67: 753–791
Massague J, Chen YG 2000 Controlling TGF-beta signaling. Genes Dev 14: 627–644
Afrakhte M, Moren A, Jossan S, Itoh S, Sampath K, Westermark B, Heldin CH, Heldin NE, ten Dijke P 1998 Induction of inhibitory Smad6 and Smad7 mRNA by TGF-beta family members. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 249: 505–511
Derynck R, Zhang YE 2003 Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways in TGF-β signaling. Nature 425: 577–584
Moustakas A, Heldin CH 2005 Non-Smad TGF-β signals. J Cell Sci 118: 3573–3584
Watanabe H, de Caestecker MP, Yamada Y 2001 Transcriptional cross-talk between Smad, erk1/2, and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways regulates transforming growth factor-beta-induced aggrecan gene expression in chondrogenic atdc5 cells. J Biol Chem 276: 14466–14473
Kale VP 2004 Differential activation of MAPK signaling pathways by TGF-beta1 forms the molecular mechanism behind its dose-dependent bidirectional effects on hematopoiesis. Stem Cells Dev 13: 27–38
Davis RJ 2000 Signal transduction by the JNK group of MAP kinases. Cell 103: 239–252
Angel P, Hattori K, Smeal T, Karin M 1988 The jun proto-oncogene is positively autoregulated by its product, Jun/AP-1. Cell 55: 875–885
Derijard B, Hibi M, Wu IH, Barrett T, Su B, Deng T, Karin M, Davis RJ 1994 JNK1: a protein kinase stimulated by UV light and Ha-Ras that binds and phosphorylates the c-Jun activation domain. Cell 76: 1025–1037
Zhang Y, Feng XH, Derynck R 1998 Smad3 and Smad4 cooperate with c-jun/c-fos to mediateTGF-beta-induced transcription. Nature 394: 909–913
Engel ME, McDonnell MA, Law BK, Moses HL 1999 Interdependent Smad and JNK signaling in transforming growth factor-beta-mediated transcription. J Biol Chem 274: 37413–37420
Wu S, Peng J, Duncan MR, Kasisomayajula K, Grotendorst G, Bancalari E 2007 Alk-5 mediates endogenous and tgf-beta1-induced expression of connective tissue growth factor in embryonic lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 36: 552–561
Zhao J, Lee M, Smith S, Warburton D 1998 Abrogation of Smad3 and Smad2 or of Smad4 gene expression positively regulates murine embryonic lung branching morphogenesis in culture. Dev Biol 194: 182–195
Bork P 1993 The modular architecture of a new family of growth regulators related to connective tissue growth factor. FEBS Lett 327: 125–130
Leask A, Abraham DJ 2003 The role of connective tissue growth factor, a multifunctional matricellular protein, in fibroblast biology. Biochem Cell Biol 81: 355–363
Grotendorst GR 1997 Connective tissue growth factor: a mediator of TGF-beta action on fibroblasts. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 8: 171–179
Kothapalli D, Hayashi N, Grotendorst GR 1998 Inhibition of TGF-beta-stimulated CTGF gene expression and anchorage-independent growth by cAMP identifies a CTGF-dependent restriction point in the cell cycle. FASEB J 12: 1151–1161
Duncan MR, Frazier KS, Abramson S, Williams S, Klapper H, Huang X, Grotendorst GR 1999 Connective tissue growth factor mediates transforming growth factor beta-induced collagen synthesis: down-regulation by cAMP. FASEB J 13: 1774–1786
Grotendorst GR, Rahmanie H, Duncan MR 2004 Combinatorial signaling pathways determine fibroblast proliferation and myofibroblast differentiation. FASEB J 18: 469–479
Bennett BL, Sasaki DT, Murray BW, O'Leary EC, Sakata ST, Xu W, Leisten JC, Motiwala A, Pierce S, Satoh Y 2001 SP600125, an anthrapyrazolone inhibitor of jun n-terminal kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 13681–13686
Bonny C, Oberson A, Negri S, Sauser C, Schorderet DF 2001 Cell-permeable peptide inhibitors of JNK: novel blockers of beta-cell death. Diabetes 50: 77–82
Hamada M, Sumi T, Iwai S, Nakazawa M, Yura Y 2006 Induction of endonuclease G-medictaed apoptosis in human oral sequamous cell carcinoma cells by protein kinase C inhibitor satingol. Apoptosis 11: 47–56
Tran TH, Andreka P, Rodrigues CO, Webster KA, Bishopric NH 2007 Jun kinase delay caspase-9 activation by interaction with apoptosome. J Biol Chem 282: 20340–20350
Pessah M, Prunier C, Marais J, Ferrand N, Mazars A, Lallemand F, Gauthier JM, Atfi A 2001 C-jun interacts with the corepressor TG-interacting factor (TGIF) to suppress Smad2 transcriptional activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 6198–6203
Pessah M, Marais J, Prunier C, Ferrand N, Lallemand F, Mauviel A, Atfi A 2002 C-jun associates with the oncoprotein ski and suppresses Smad2 transcriptional activity. J Biol Chem 277: 29094–29100
Wendling J, Marchand A, Mauviel A, Verrecchia F 2003 5-fluorouracil blocks transforming growth factor-beta-induced alpha 2 type I collagen gene (COL1A2) expression in human fibroblasts via c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase/activator protein-1 activation. Mol Pharmacol 64: 707–713
Ventura JJ, Kennedy NJ, Flavell RA, Davis RJ 2004 JNK regulates autocrine expression of TGF-beta1. Mol Cell 15: 269–278
Holmes A, Abraham DJ, Sa S, Shiwen X, Black CM, Leask A 2001 CTGF and SMADs, maintenance of scleroderma phenotype is independent of SMAD signaling. J Biol Chem 276: 10594–10601
Leask A, Holmes A, Black CM, Abraham DJ 2003 Connective tissue growth factor gene expression: requirments for its induction by transforming growth factor-β2 in fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 278: 13008–13015
Utsugi M, Dobashi K, Ishizuka T, Masubuchic K, Shimizu Y, Nakazawa T, Mori M 2003 C-Jun-NH2-terminal kinase mediates expression of connective tissue growth factor induced by transforming growth factor-beta1 in human lung fibroblasts. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 28: 754–761
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported, in part, by grant K08 HD046582 from NIH, by Project NewBorn University of Miami, and by a grant from the Bank of American Charitable Foundation, Inc.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, S., Kasisomayajula, K., Peng, J. et al. Inhibition of JNK Enhances TGF-β1-Activated Smad2 Signaling in Mouse Embryonic Lung. Pediatr Res 65, 381–386 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181991c67
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181991c67
This article is cited by
-
Multifunctional, JNK-inhibiting nanotherapeutics for augmented elastic matrix regenerative repair in aortic aneurysms
Drug Delivery and Translational Research (2018)
-
A potential role of the JNK pathway in hyperoxia-induced cell death, myofibroblast transdifferentiation and TGF-β1-mediated injury in the developing murine lung
BMC Cell Biology (2011)