Abstract
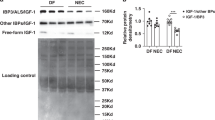
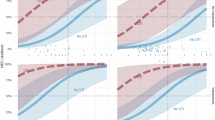
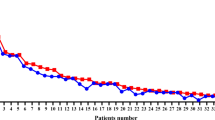
We have previously demonstrated that enterally administered heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF) produced in Escherichia coli decreases the incidence and severity of intestinal injury in a neonatal rat model of necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC). In preparation for upcoming human clinical trials, large-scale production of HB-EGF according to Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) has been successfully accomplished using a Pichia pastoris yeast system. The current studies used a neonatal rat model of NEC to elucidate several important preclinical characteristics of HB-EGF therapy. We found that enteral administration of HB-EGF (800 μg/kg/dose) four times a day effectively reduced the incidence and severity of NEC, that Pichia-derived HB-EGF was not significantly different from E. coli-derived HB-EGF in preventing NEC, that EGF was not superior to HB-EGF in preventing NEC, and that prophylactic administration of HB-EGF added to formula starting with the first feed or 12 h later significantly reduced the incidence of NEC, with no change in the incidence of NEC noted if HB-EGF was added to the formula starting 24, 48, or 72 h after birth. Thus, large-scale production of GMP-grade HB-EGF in Pichia pastoris yeast produces a biologically active molecule suitable for human clinical trials.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- EGFR:
-
epidermal growth factor receptor
- GMP:
-
good manufacturing process
- HB-EGF:
-
heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor
- NEC:
-
necrotizing enterocolitis
References
Schnabl KL, Van Aerde JE, Thomson AB, Clandinin MT 2008 Necrotizing enterocolitis: a multifactorial disease with no cure. World J Gastroenterol 14: 2142–2161
Kliegman RM, Fanaroff AA 1984 Necrotizing enterocolitis. N Engl J Med 310: 1093–1103
Lee JS, Polin RA 2003 Treatment and prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis. Semin Neonatol 8: 449–459
Caplan MS, Jilling T 2001 New concepts in necrotizing enterocolitis. Curr Opin Pediatr 13: 111–115
Feng J, El-Assal ON, Besner GE 2005 Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF) and necrotizing enterocolitis. Semin Pediatr Surg 14: 167–174
Besner G, Higashiyama S, Klagsbrun M 1990 Isolation and characterization of a macrophage-derived heparin-binding growth factor. Cell Regul 1: 811–819
Higashiyama S, Abraham JA, Miller J, Fiddes JC, Klagsbrun M 1991 A heparin-binding growth factor secreted by macrophage-like cells that is related to EGF. Science 251: 936–939
Junttila TT, Sundvall M, Määttä JA, Elenius K 2000 Erbb4 and its isoforms: selective regulation of growth factor responses by naturally occurring receptor variants. Trends Cardiovasc Med 10: 304–310
Nishi E, Prat A, Hospital V, Elenius K, Klagsbrun M 2001 N-arginine dibasic convertase is a specific receptor for heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor that mediates cell migration. EMBO J 20: 3342–3350
Feng J, El-Assal ON, Besner GE 2006 Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor decreases the incidence of necrotizing enterocolitis in neonatal rats. J Pediatr Surg 41: 144–149
El-Assal ON, Besner GE 2004 Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF) and intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Semin Pediatr Surg 13: 2–10
El-Assal ON, Radulescu A, Besner GE 2007 Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor preserves mesenteric microcirculatory blood flow and protects against intestinal injury in rats subjected to hemorrhagic shock and resuscitation. Surgery 142: 234–242
Barlow B, Santulli TV, Heird WC, Pitt J, Blanc WA, Schullinger JN 1974 An experimental study of acute neonatal enterocolitis—the importance of breast milk. J Pediatr Surg 9: 587–595
Davis KM, Brigstock DR, Johnson PR, Crissman-Combs MA, McCarthy DW, Downing MT, Besner GE 1996 Production of glycosylated heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor in HeLa cells using vaccinia virus. Protein Expr Purif 8: 57–67
Caplan MS, Hedlund E, Adler L, Hsueh W 1994 Role of asphyxia and feeding in a neonatal rat model of necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatr Pathol 14: 1017–1028
Martin AE, Luquette MH, Besner GE 2005 Timing, route, and dose of administration of heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor in protection against intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Pediatr Surg 40: 1741–1747
Michalsky MP, Lara-Marquez M, Chun L, Besner GE 2002 Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor is present in human amniotic fluid and breast milk. J Pediatr Surg 37: 1–6
Feng J, Mehta VB, El-Assal ON, Wu D, Besner GE 2006 Tissue distribution and plasma clearance of heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF) in adult and newborn rats. Peptides 27: 1589–1596
Shin CE, Falcone RA Jr, Stuart L, Erwin CR, Warner BW 2000 Diminished growth factor levels in infants with necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr Surg 35: 173–176
Warner BB, Ryan AL, Seeger K, Leonard AC, Erwin CR, Warner BW 2007 Ontogeny of salivary epidermal growth factor and necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr 150: 358–363
Warner BW, Warner BB 2005 Role of epidermal growth factor in the pathogenesis of neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Semin Pediatr Surg 14: 175–180
Miettinen PJ, Berger JE, Meneses J, Phung Y, Pedersen RA, Werb Z 1995 Epithelial immaturity and multiorgan failure in mice lacking epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature 376: 337–341
Dvorak B, Halpern MD, Holubec H, Williams CS, McWilliam DL, Dominguez JA, Stepankova R, Payne CM, McCuskey RS 2002 Epidermal growth factor reduces the development of necrotizing enterocolitis in a neonatal rat model. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 282: G156–G164
Vinter-Jensen L, Duch BU, Petersen JA, Ryslev A, Gregersen H 1996 Systemic treatment with epidermal growth factor in the rat. Biomechanical properties of the growing small intestine. Regul Pept 61: 135–142
Sigalet DL, Martin GR, Butzner JD, Buret A, Meddings JB 2005 A pilot study of the use of epidermal growth factor in pediatric short bowel syndrome. J Pediatr Surg 40: 763–768
Sullivan PB, Lewindon PJ, Cheng C, Lenehan PF, Kuo BS, Haskins JR, Goodlad RA, Wright NA, de la Iglesia FA 2007 Intestinal mucosa remodeling by recombinant human epidermal growth factor in neonates with severe necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr Surg 42: 462–469
Palomino A, Hernández-Bernal F, Haedo W, Franco S, Más JA, Fernández JA, Soto G, Alonso A, González T, López-Saura P 2000 A multicenter, randomized, double-blind clinical trial examining the effect of oral human recombinant epidermal growth factor on the healing of duodenal ulcers. Scand J Gastroenterol 35: 1016–1022
Dvorak B, Khailova L, Clark JA, Molla Hosseini D, Arganbright KM, Reynolds CA, Halpern MD 2008 Comparison of epidermal growth factor and heparin-binding epidermal growth factor–like growth factor for prevention of experimental necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 47: 11–18
2005 Guidance for industry: Estimating the maximum safe starting dose in initial clinical trials for therapeutics in adult healthy volunteers. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration, Center for Drug Evaluation. Available at: http://www.fda.gov/CDER/GUIDANCE/5541fnl.htm
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Gregory Young, M.S., Ohio State University Center for Biostatistics, for his helpful comments and his assistance with the statistical analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by Trillium Therapeutics, Inc. (Toronto, Ontario, Canada) (G.E.B., A.R.), NIH RO1 DK074611 (G.E.B.), NIHT32 RR-023260-02 (N.A.Z.), The Samuel J. Roessler Memorial Fellowship (N.A.Z.), and The Firefighters Endowment Fund of Nationwide Children's Hospital (X.Y.).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Radulescu, A., Zorko, N., Yu, X. et al. Preclinical Neonatal Rat Studies of Heparin-Binding EGF-Like Growth Factor in Protection of the Intestines From Necrotizing Enterocolitis. Pediatr Res 65, 437–442 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181994fa0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181994fa0
This article is cited by
-
A simple and effective method to remove pigments from heterologous secretory proteins expressed in Pichia pastoris
Advanced Biotechnology (2024)
-
New directions in necrotizing enterocolitis with early-stage investigators
Pediatric Research (2020)
-
ErbB receptors and their growth factor ligands in pediatric intestinal inflammation
Pediatric Research (2014)
-
Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor protects intestinal stem cells from injury in a rat model of necrotizing enterocolitis
Laboratory Investigation (2012)
-
P-glycoprotein induction by breast milk attenuates intestinal inflammation in experimental necrotizing enterocolitis
Laboratory Investigation (2011)