Abstract
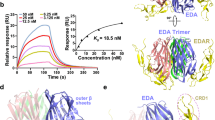
X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (XLHED), which is characterized by hypodontia, hypotrichosis, and hypohidrosis, is caused by mutations in ED1, the gene encoding ectodysplasin-A (EDA). This protein belongs to the tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily. We analyzed ED1 in two Japanese patients with XLHED. In patient 1, we identified a 4-nucleotide insertion, c.119-120insTGTG, in exon 1, which led to a frameshift mutation starting from that point (p.L40fsX100). The patient's mother was heterozygous for this mutation. In patient 2, we identified a novel missense mutation, c.1141G>C, in exon 9, which led to a substitution of glycine with arginine in the TNFL domain of EDA (p.G381R). This patient's mother and siblings showed neither symptoms nor ED1 mutations, so this mutation was believed to be a de novo mutation in maternal germline cells. According to molecular simulation analysis of protein structure and electrostatic surface, p.G381R increases the distance between K375 in monomer A and K327 in monomer B, which suggests an alteration of overall structure of EDA. Thus, we identified two novel mutations, p.L40fsX100 and p.G381R, in ED1 of two XLHED patients. Simulation analysis suggested that the p.G381R mutation hampers binding of EDA to its receptor via alteration of overall EDA structure.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- DHPLC:
-
denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography
- EDA:
-
ectodysplasin-A
- HED:
-
hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia
- TNFL:
-
tumor necrosis factor ligand
- XLHED:
-
X-linked HED
References
McKusick VA 1998 Mendelian Inheritance in Man, 12th Ed. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, pp 3307–3309
Monreal AW, Ferguson BM, Headon DJ, Street SL, Overbeek PA, Zonana J 1999 Mutations in the human homologue of mouse dl cause autosomal recessive and dominant hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Nat Genet 22: 366–369
Headon DJ, Emmal SA, Ferguson BM, Tucker AS, Justice MJ, Sharpe PT, Zonana J, Overbeek PA 2001 Gene defect in ectodermal dysplasia implicates a death domain adapter in development. Nature 414: 913–916
Kere J, Srivastava AK, Montonen O, Zonana J, Thomas N, Ferguson B, Munoz F, Morgan D, Clarke A, Baybayan P, Chen EY, Ezer S, Saarialho-Kere U, de la Chapelle A, Schlessinger D 1996 X-linked anhidrotic (hypohidrotic) ectodermal dysplasia is caused by mutation in a novel transmembrane protein. Nat Genet 13: 409–416
Bayés M, Hartung AJ, Ezer S, Pispa J, Thesleff I, Srivastava AK, Kere J 1998 The anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia gene (EDA) undergoes alternative splicing and encodes ectodysplasin-A with deletion mutations in collagenous repeats. Hum Mol Genet 7: 1661–1669
Monreal AW, Zonana J, Ferguson B 1998 Identification of a new splice form of the EDA1 gene permits detection of nearly all X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia mutations. Am J Hum Genet 63: 380–389
Ezer S, Bayés M, Elomaa O, Schlessinger D, Kere J 1999 Ectodysplasin is a collagenous trimeric type II membrane protein with a tumor necrosis factor-like domain and co-localizes with cytoskeletal structures at lateral and apical surfaces of cells. Hum Mol Genet 8: 2079–2086
Hymowitz SG, Compaan DM, Yan M, Wallweber HJ, Dixit VM, Starovasnik MA, de Vos AM 2003 The crystal structures of EDA-A1 and EDA-A2: splice variants with distinct receptor specificity. Structure 11: 1513–1520
Schneider P, Street SL, Gaide O, Hertig S, Tardivel A, Tschopp J, Runkel L, Alevizopoulos K, Ferguson BM, Zonana J 2001 Mutations leading to X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia affect three major functional domains in the tumor necrosis factor family member ectodysplasin-A. J Biol Chem 276: 18819–18827
Yan M, Wang LC, Hymowitz SG, Schilbach S, Lee J, Goddard A, de Vos AM, Gao WQ, Dixit VM 2000 Two-amino acid molecular switch in an epithelial morphogen that regulates binding to two distinct receptors. Science 290: 523–527
Yan M, Zhang Z, Brady JR, Schilbach S, Fairbrother WJ, Dixit VM 2002 Identification of a novel death domain-containing adaptor molecule for ectodysplasin-A receptor that is mutated in crinkled mice. Curr Biol 12: 409–413
Mikkola ML, Thesleff I 2003 Ectodysplasin signaling in development. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 14: 211–224
Bal E, Baala L, Cluzeau C, El Kerch F, Ouldim K, Hadj-Rabia S, Bodemer C, Munnich A, Courtois G, Sefiani A, Smahi A 2007 Autosomal dominant anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasias at the EDARADD locus. Hum Mutat 28: 703–709
Vincent MC, Biancalana V, Ginisty D, Mandel JL, Calvas P 2001 Mutational spectrum of the ED1 gene in X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Eur J Hum Genet 9: 355–363
Visinoni AF, de Souza RL, Freire-Maia N, Gollop TR, Chautard-Freire-Maia EA 2003 X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia mutations in Brazilian families. Am J Med Genet A 122: 51–55
Zhao J, Hua R, Zhao X, Meng Y, Ao Y, Liu Q, Shang D, Sun M, Lo WH, Zhang X 2008 Three novel mutations of the EDA gene in Chinese patients with X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Br J Dermatol 158: 614–617
Lexner MO, Bardow A, Juncker I, Jensen LG, Almer L, Kreiborg S, Hertz JM 2008 X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Genetic and dental findings in 67 Danish patients from 19 families. Clin Genet 74: 252–259
Yotsumoto S, Fukumaru S, Matsushita S, Oku T, Kobayashi K, Saheki T, Kanzaki T 1998 A novel point mutation of the EDA gene in a Japanese family with anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. J Invest Dermatol 111: 1246–1247
Aoki N, Ito K, Tachibana T, Ito M 2000 A novel arginine → serine mutation in EDA1 in a Japanese family with X-linked anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. J Invest Dermatol 115: 329–330
Hashiguchi T, Yotsumoto S, Kanzaki T 2003 Mutations in the ED1 gene in Japanese families with X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Exp Dermatol 12: 518–522
RamaDevi AR, Reddy EC, Ranjan S, Bashyam MD 2008 Molecular genetic analysis of patients from India with hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia reveals novel mutations in the EDA and EDAR genes. Br J Dermatol 158: 163–167
Li S, Li J, Cheng J, Zhou B, Tong X, Dong X, Wang Z, Hu Q, Chen M, Hua ZC 2008 Non-syndromic tooth agenesis in two Chinese families associated with novel missense mutations in the TNF domain of EDA (ectodysplasin A). PLoS One 3: e2396
Sutomo R, Akutsu T, Takeshima Y, Nishio H, Sadewa AH, Harada Y, Matsuo M 2002 Rapid SMN1 deletion test using DHPLC to screen patients with spinal muscular atrophy. Am J Med Genet 113: 225–226
Sadewa AH, Sasongko TH, Gunadi Lee MJ, Daikoku K, Yamamoto A, Yamasaki T, Tanaka S, Matsuo M, Nishio H 2008 Germ-line mutation of KCNQ2, p.R213W, in a Japanese family with benign familial neonatal convulsion. Pediatr Int 50: 167–171
Ishihara H, Kanda F, Nishio H, Sumino K, Chihara K 2001 Clinical features and skewed X-chromosome inactivation in female carriers of X-linked recessive spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. J Neurol 248: 856–860
Lau AW, Brown CJ, Peñaherrera M, Langlois S, Kalousek DK, Robinson WP 1997 Skewed X-chromosome inactivation is common in fetuses or newborns associated with confined placental mosaicism. Am J Hum Genet 61: 1353–1361
DeLano WL 2002 The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System. Available at: http://www.pymol.org Accessed August 30, 2008
Guex N, Peitsch MC 1997 SWISS-MODEL and the Swiss-PdbViewer: an environment for comparative protein modeling. Electrophoresis 18: 2714–2723
Ren P, Ponder JW 2003 Polarizable atomic multipole water model for molecular mechanics simulation. J Phys Chem B 107: 5933–5947
Baker NA, Sept D, Joseph S, Holst MJ, McCammon JA 2001 Electrostatics of nanosystems: application to microtubules and the ribosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 10037–10041
Martínez F, Millán JM, Orellana C, Prieto F 1999 X-linked anhidrotic (hypohidrotic) ectodermal dysplasia caused by a novel mutation in EDA1 gene: 406T>G (Leu55Arg). J Invest Dermatol 113: 285–286
Vincent MC, Cossée M, Vabres P, Stewart F, Bonneau D, Calvas P 2002 Pitfalls in clinical diagnosis of female carriers of X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Arch Dermatol 138: 1256–1258
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Ahmad Hamim Sadewa and Dr. Teguh Haryo Sasongko (Kobe University Graduate School of Medicine) for their technical assistance and Drs. Surini Yusoff and Indra Sari Kusuma Harahap (Kobe University Graduate School of Medicine) for their helpful comments on interpretation of the data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by a Grant-Aid from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture of Japan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gunadi, Miura, K., Ohta, M. et al. Two Novel Mutations in the ED1 Gene in Japanese Families With X-Linked Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia. Pediatr Res 65, 453–457 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181991229
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181991229
This article is cited by
-
NRG1 variant effects in patients with Hirschsprung disease
BMC Pediatrics (2018)
-
Mutational spectrum in 101 patients with hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia and breakpoint mapping in independent cases of rare genomic rearrangements
Journal of Human Genetics (2016)
-
Orofacial Features of Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia
Head and Neck Pathology (2012)