Abstract
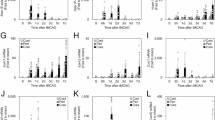
Periventricular leukomalacia (PVL) is a major form of brain damage in premature infants. This study was to test whether IGF-1 can prevent PVL-like brain damage induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in the neonatal rat. Intraventricular delivery of LPS resulted in an acute brain inflammatory response, i.e., rapid recruitment of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs), activation of microglia and astrocytes, and induction of IL-1β (IL1β) expression. Brain inflammation was associated with the loss of O4+ preoligodendrocytes (preOLs), a decrease of myelin basic protein (MBP) in the white matter and an increase of pyknotic cells in the cortex. IGF-1 at a low dose significantly prevented LPS-induced deleterious effects without alteration of IL-1β expression and microglia/astrocytes activation. On the other hand, the low dose of IGF-1 enhanced LPS-induced PMNs recruitment and blood-brain barrier (BBB) permeability, and caused intracerebral hemorrhage. At higher doses, co-application of IGF-1 with LPS resulted in a high mortality rate. Brains from the surviving rats showed massive PMN infiltration and intracerebral hemorrhage. However, these adverse effects were not found in rats treated with IGF-1 alone. This study provides the alarming evidence that in an acute inflammatory condition, IGF-1 may have severe, harmful effects on the developing brain.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- BBB:
-
blood-brain barrier
- GFAP:
-
glial fibrillary acidic protein
- H&E:
-
hematoxylin and eosin
- IGF-1:
-
insulin-like growth factor-1
- LPS:
-
lipopolysaccharide
- MBP:
-
myelin basic protein
- PMN:
-
polymorphonuclear leukocyte
- Pre-OLs:
-
pre-oligodendrocyte
- PVL:
-
periventricular leukomalacia
- TUNEL:
-
terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling
References
Volpe JJ 2003 Cerebral white matter injury of the premature infant-more common than you think. Pediatrics 112: 176–180
Khwaja O, Volpe JJ 2008 Pathogenesis of cerebral white matter injury of prematurity. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 93: F153–F161
Leviton A, Dammann O 2004 Coagulation, inflammation, and the risk of neonatal white matter damage. Pediatr Res 55: 541–545
Pang Y, Cai Z, Rhodes PG 2003 Disturbance of oligodendrocyte development, hypomyelination and white matter injury in the neonatal rat brain after intracerebral injection of lipopolysaccharide. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 140: 205–214
McQuillen PS, Ferriero DM 2004 Selective vulnerability in the developing central nervous system. Pediatr Neurol 30: 227–235
Pang Y, Zheng B, Fan LW, Rhodes PG, Cai Z 2007 IGF-1 protects oligodendrocyte progenitors against TNFalpha-induced damage by activation of PI3K/Akt and interruption of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Glia 55: 1099–1107
Cui QL, Zheng WH, Quirion R, Almazan G 2005 Inhibition of Src-like kinases reveals Akt-dependent and -independent pathways in insulin-like growth factor I-mediated oligodendrocyte progenitor survival. J Biol Chem 280: 8918–8928
Ness JK, Scaduto RC Jr, Wood TL 2004 IGF-I prevents glutamate-mediated bax translocation and cytochrome C release in O4+ oligodendrocyte progenitors. Glia 46: 183–194
Brywe KG, Mallard C, Gustavsson M, Hedtjärn M, Leverin AL, Wang X, Blomgren K, Isgaard J, Hagberg H 2005 IGF-I neuroprotection in the immature brain after hypoxia-ischemia, involvement of Akt and GSK3beta?. Eur J Neurosci 21: 1489–1502
Wood TL, Loladze V, Altieri S, Gangoli N, Levison SW, Brywe KG, Mallard C, Hagberg H 2007 Delayed IGF-1 administration rescues oligodendrocyte progenitors from glutamate-induced cell death and hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Dev Neurosci 29: 302–310
Zhong J, Zhao L, Du Y, Wei G, Yao WG, Lee WH 2009 Delayed IGF-1 treatment reduced long-term hypoxia-ischemia-induced brain damage and improved behavior recovery of immature rats. Neurol Res 31: 483–489
Johnston MV, Hagberg H 2007 Sex and the pathogenesis of cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol 49: 74–78
Lin S, Fan LW, Pang Y, Rhodes PG, Mitchell HJ, Cai Z 2005 IGF-1 protects oligodendrocyte progenitor cells and improves neurological functions following cerebral hypoxia-ischemia in the neonatal rat. Brain Res 1063: 15–26
Carvey PM, Zhao CH, Hendey B, Lum H, Trachtenberg J, Desai BS, Snyder J, Zhu YG, Ling ZD 2005 6-Hydroxydopamine-induced alterations in blood-brain barrier permeability. Eur J Neurosci 22: 1158–1168
Vig PJ, Subramony SH, D'Souza DR, Wei J, Lopez ME 2006 Intranasal administration of IGF-1 improves behavior and Purkinje cell pathology in SCA1 mice. Brain Res Bull 69: 573–579
Cao Y, Gunn AJ, Bennet L, Wu D, George S, Gluckman PD, Shao XM, Guan J 2003 Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1 suppresses oligodendrocyte caspase-3 activation and increases glial proliferation after ischemia in near-term fetal sheep. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 23: 739–747
Genoud S, Maricic I, Kumar V, Gage FH 2005 Targeted expression of IGF-1 in the central nervous system fails to protect mice from experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol 168: 40–45
Escartin C, Boyer F, Bemelmans AP, Hantraye P, Brouillet E 2007 IGF-1 exacerbates the neurotoxicity of the mitochondrial inhibitor 3NP in rats. Neurosci Lett 425: 167–172
Balaram SK, Agrawal DK, Edwards JD 1999 Insulin like growth factor-1 activates nuclear factor-kappaB and increases transcription of the intercellular adhesion molecule-1 gene in endothelial cells. Cardiovasc Surg 7: 91–97
Che W, Lerner-Marmarosh N, Huang Q, Osawa M, Ohta S, Yoshizumi M, Glassman M, Lee JD, Yan C, Berk BC, Abe J 2002 Insulin-like growth factor-1 enhances inflammatory responses in endothelial cells: role of Gab1 and MEKK3 in TNF-alpha-induced c-Jun and NF-kappaB activation and adhesion molecule expression. Circ Res 90: 1222–1230
Kooijman R, Coppens A, Hooghe-Peters E 2003 IGF-I stimulates IL-8 production in the promyelocytic cell line HL-60 through activation of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase. Cell Signal 15: 1091–1098
Vallée S, Fouchier F, Brémond P, Briand C, Marvaldi J, Champion S 2003 Insulin-like growth factor-1 downregulates nuclear factor kappa B activation and upregulates interleukin-8 gene expression induced by tumor necrosis factor alpha. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 305: 831–839
Mauro L, Bartucci M, Morelli C, Andò S, Surmacz E 2001 IGF-I receptor-induced cell-cell adhesion of MCF-7 breast cancer cells requires the expression of junction protein ZO-1. J Biol Chem 276: 39892–39897
Tonra JR, Mendell LM 1997 Rabbit IgG distribution in skin, spinal cord and DRG following systemic injection in rat. J Neuroimmunol 80: 97–105
Kovacs GT, Worgall S, Schwalbach P, Steichele T, Mehls O, Rosivall L 1999 Hypoglycemic effects of insulin-like growth factor-1 in experimental uremia: can concomitant growth hormone administration prevent this effect?. Horm Res 51: 193–200
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported in part by HD 35496 from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development; by NS 54278 from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke; and by funds from the Newborn Medicine Division and the Department of Pediatrics, University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, Mississippi.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pang, Y., Zheng, B., Campbell, L. et al. IGF-1 Can Either Protect Against or Increase LPS-Induced Damage in the Developing Rat Brain. Pediatr Res 67, 579–584 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181dc240f
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181dc240f
This article is cited by
-
Inhibition of lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 relieves PMN recruitment in CNS via LPA1/TSP1/CXCR2 pathway and alleviates disruption on blood-brain barrier following intracerebral haemorrhage in mice
Fluids and Barriers of the CNS (2023)
-
Growth Factors and Neuroglobin in Astrocyte Protection Against Neurodegeneration and Oxidative Stress
Molecular Neurobiology (2019)
-
Dietary proteins and IGF I levels in preterm infants: determinants of growth, body composition, and neurodevelopment
Pediatric Research (2015)
-
Intracerebral lipopolysaccharide induces neuroinflammatory change and augmented brain injury in growth-restricted neonatal rats
Pediatric Research (2012)