Abstract
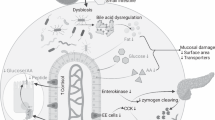
Tropical enteropathy and zinc deficiency are major public health problems worldwide. Tropical enteropathy is characterized by reduced mannitol absorption with normal or increased lactulose absorption when a dual sugar absorption test is administered, the results of which are reported as the lactulose:mannitol ratio (L:M). Zinc homeostasis is quantified with a dual stable isotope test. This study tested the hypothesis that endogenous fecal zinc (EFZ) was correlated with the L:M. A dual sugar absorption test and dual stable isotope test were performed on 25 asymptomatic Malawian children aged 3–5 y at risk for tropical enteropathy and zinc deficiency. EFZ and net zinc retention were estimated and correlated with the L:M. Twenty-two children (88%) had an abnormal L:M (L:M >0.10), and the L:M was 0.24 ± 0.10 (mean ± SD). EFZ was 1.68 ± 1.06 mg/d, a quantity greater than is seen in healthy populations from the developed world. EFZ was positively correlated with the L:M (r = 0.62, p < 0.001). Net zinc retention (0.67 ± 1.6 mg/d) was negatively correlated with the L:M (r = −0.47, p = 0.02). This suggests that perturbed zinc homeostasis is associated with subclinical enteropathy in these children.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- EFZ:
-
endogenous fecal zinc
- FAZ:
-
fractional absorbed zinc
- L:M:
-
lactulose-to-mannitol ratio
- NZR:
-
net zinc retention
- TAZ:
-
total dietary absorbed zinc
References
Black RE, Allen LH, Bhutta ZA, Caulfield LE, de Onis M, Ezzati M, Mathers C, Rivera J 2008 Maternal and child undernutrition: global and regional exposures and health consequences. Lancet 371: 243–260
Sian L, Mingyan X, Miller LV, Tong L, Krebs NF, Hambidge KM 1996 Zinc absorption and intestinal losses of endogenous zinc in young Chinese women with marginal zinc intakes. Am J Clin Nutr 63: 348–353
Griffin IJ, Lynch MF, Hawthorne KM, Chen Z, Hamzo M, Abrams SA 2007 Zinc homeostasis in 1–4 year olds consuming diets typical of US children. Br J Nutr 98: 358–363
Hambidge KM, Mazariegos M, Solomons NW, Westcott JE, Lei S, Raboy V, Grunwald G, Miller LV, Sheng X, Krebs NF 2007 Intestinal excretion of endogenous zinc in Guatemalan school children. 137: 1747–1749
Sheng XY, Hambidge KM, Zhu XX, Ni JX, Bailey KB, Gibson RS, Krebs NF 2006 Major variables of zinc homeostasis in Chinese toddlers. Am J Clin Nutr 84: 389–394
Griffin IJ, Hicks PD, Liang LK, Abrams SA 2004 Metabolic adaptations to low zinc intakes in premenarcheal girls. Am J Clin Nutr 80: 385–390
Campbell DI, Murch SH, Elia M, Sullivan PB, Sanyang MS, Jobareth B, Lunn PG 2003 Chronic T cell-mediated enteropathy in rural west African children: relationship with nutritional status and small bowel function. Pediatr Res 54: 306–311
Kelly P, Menzies I, Crane R, Zulu I, Nickols C, Feakins R, Mwansa J, Mudenda V, Katubulushi M, Greenwald S, Farthing M 2004 Responses of small intestinal architecture and function over time to environmental factors in a tropical population. Am J Trop Med Hyg 70: 412–419
Lunn PG, Northrop-Clewes CA, Downes RM 1991 Intestinal permeability, mucosal injury and growth faltering in Gambian infants. Lancet 338: 907–910
Brown KH, Khatun M, Ahmed G 1981 Relationship of the xylose absorption status of children in Bangladesh to their absorption of macronutrients from local diets. Am J Clin Nutr 34: 1540–1547
Menzies IS, Zuckerman MJ, Nukajam WS, Somasundaram S, Murphy B, Jenkins A, Crane R, Gregory G 1999 Geography of intestinal permeability and absorption. Gut 44: 483–489
Shulman RJ, Eakin MN, Czyzewski DI, Jarrett M, Ou CN 2008 Increased gastrointestinal permeability and gut inflammation in children with functional abdominal pain and irritable bowel syndrome. J Pediatr 153: 646–650
Manary MJ, Hotz C, Krebs NF, Gibson RS, Westcott JE, Arnold T, Broadhead RL, Hambidge KM 2000 Dietary phytate reduction improves zinc absorption in Malawian children recovering from tuberculosis but not in well children. J Nutr 130: 2959–2964
Galpin L, Manary MJ, Fleming K, Ou CN, Ashorn P, Shulman RJ 2005 Effect of Lactobacillus GG on intestinal integrity in Malawian children at risk of tropical enteropathy. Am J Clin Nutr 82: 1040–1045
Sullivan J, Ndekha M, Maker D, Hotz C, Manary MJ 2006 The quality of the diet in Malawian children with kwashiorkor and marasmus. Matern Child Nutr 2: 114–122
Hotz C, Gibson RS 2001 Complementary feeding practices and dietary intakes from complementary foods amongst weanlings in rural Malawi. Eur J Clin Nutr 55: 841–849
Yeudall F, Gibson RS, Cullinan TR, Mtimuni B 2005 Efficacy of a community-based dietary intervention to enhance micronutrient adequacy of high-phytate maize-based diets of rural Malawian children. Public Health Nutr 8: 826–836
Hambidge M 2003 Human zinc homeostasis: good but not perfect. J Nutr 133: 1438S–1442S
Chen P, Soares AM, Lima AA, Gamble MV, Schorling JB, Conway M, Barrett LJ, Blaner WS, Guerrant RL 2003 Association of vitamin A and zinc status with altered intestinal permeability: analyses of cohort data from northeastern Brazil. J Health Popul Nutr 21: 309–315
Hotz C, Peerson JM, Brown KH 2003 Suggested lower cutoffs of serum zinc concentrations for assessing zinc status: reanalysis of the second National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data (1976–1980). Am J Clin Nutr 78: 756–764
Krebs NE, Hambidge KM 2001 Zinc metabolism and homeostasis: the application of tracer techniques to human zinc physiology. Biometals 14: 397–412
Roy SK, Behrens RH, Haider R, Akramuzzaman SM, Mahalanabis D, Wahed MA, Tomkins AM 1992 Impact of zinc supplementation on intestinal permeability in Bangladeshi children with acute diarrhoea and persistent diarrhoea syndrome. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 15: 289–296
Koo SI, Turk DE 1977 Effect of zinc deficiency on the ultrastructure of the pancreatic acinar cell and intestinal epithelium in the rat. J Nutr 107: 896–908
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by Cooperative Agreement 58-6250-6001 from the US Department of Agriculture Agricultural Research Service and the International Atomic Energy Agency Contract 14586.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manary, M., Abrams, S., Griffin, I. et al. Perturbed Zinc Homeostasis in Rural 3–5-y-Old Malawian Children Is Associated With Abnormalities in Intestinal Permeability Attributed to Tropical Enteropathy. Pediatr Res 67, 671–675 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181da44dc
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181da44dc
This article is cited by
-
Infant diarrheal disease in rhesus macaques impedes microbiome maturation and is linked to uncultured Campylobacter species
Communications Biology (2024)
-
Limosilactobacillus mucosae-derived extracellular vesicles modulates macrophage phenotype and orchestrates gut homeostasis in a diarrheal piglet model
npj Biofilms and Microbiomes (2023)
-
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin drives enteropathic changes in small intestinal epithelia
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Correlation Between Zinc Nutritional Status with Serum Zonulin and Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Diarrhea-Predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Case–Control Study
Digestive Diseases and Sciences (2022)
-
Nutritional deficiency in an intestine-on-a-chip recapitulates injury hallmarks associated with environmental enteric dysfunction
Nature Biomedical Engineering (2022)