Abstract
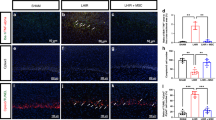
Little is known about roles of inflammation and hypoxic ischemia (HI) in the generation of neuroinflammation and damage of blood-brain barrier (BBB) in the white matter (WM) that displays regional vulnerability in preterm infants. We investigated whether low-dose lipopolysaccharide (LPS) sensitizes HI-induced WM injury in postpartum (P) day 2 rat pups by selectively increasing neuroinflammation and BBB damage in the WM. Pups received LPS (0.05 mg/kg) (LPS + HI) or normal saline (NS + HI) followed by 90-min HI. LPS and NS group were the pups that had LPS or NS only. Myelin basic protein immunohistochemistry on P11 showed WM injury in LPS + HI group, but not in NS + HI, LPS, and NS groups. In contrast, no gray matter injury was found in the four groups. LPS + HI group also showed decreased number of oligodendrocytes in the WM 72-h postinsult. In the same brain region, increases of activated microglia, TNF-α expression, BBB leakage, and cleaved caspase-3 positive cells were much more prominent in LPS + HI group than in the other three groups 24-h postinsult. The oligodendrocytes were the major cells with cleaved caspase-3 expression. We concluded that low-dose LPS sensitized HI-induced WM injury in the immature brain by selectively up-regulating neuroinflammation and BBB damage in the WM.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- BBB:
-
blood-brain barrier
- HI:
-
hypoxic ischemia
- IOD:
-
integrated optical density
- LPS:
-
lipopolysaccharide
- MBP:
-
myelin basic protein
- NS:
-
normal saline
- VLBW:
-
very-low-birth-weight
- WM:
-
white matter
References
Volpe JJ 2008 Neurology of the Newborn. 5th ed. W.B. Saunders Co, Philadelphia, pp 370–379, 433-436
Vincer MJ, Allen AC, Joseph KS, Stinson DA, Scot H, Wood E 2006 Increasing prevalence of cerebral palsy among very preterm infants: a population-based study. Pediatrics 118: e1621–e1626
Tsuji M, Saul JP, Plessis A, Eichenwald E, Sobh J, Crocker R, Volpe JJ 2000 Cerebral intravascular oxygenation correlates with mean arterial pressure in critically ill premature infants. Pediatrics 106: 625–632
Stoll BJ, Hansen NI, Adams-Chapman I, Fanaroff AA, Hintz SR, Vohr B, Higgins RD, for the National Institute of Child Health and Human development Neonatal Research Network 2004 Neurodevelopmental and growth impairment among extremely low-birth-weight infants with neonatal infection. JAMA 292: 2357–2365
Yanowitz TD, Jordan JA, Gilmour CH, Towbin R, Bowen A, Roberts JM, Brozanski BS 2002 Hemodynamic disturbances in premature infants born after chorioamnionitis: association with cord blood cytokine concentrations. Pediatr Res 51: 310–316
Kaukola T, Herva R, Perhomma M, Paakko E, Kingsmore S, Vainionpaa L, Hallman M 2006 Population cohort associating chorioamnionitis, cord inflammatory cytokines and neurological outcome in very preterm, extremely low birth weight infants. Pediatr Res 59: 478–483
Lehnardt S, Massillon L, Follett P, Jensen FE, Ratan R, Rosenberg PA, Volpe JJ, Vartanian T 2003 Activation of innate immunity in the CNS triggers neurodegeneration through a Toll-like receptor 4-dependent pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 8514–8519
Eklind S, Mallard C, Leverin AL, Gilland E, Blomgren K, Mattsby-Baltzer I, Hagberg H 2001 Bacterial endotoxin sensitizes the immature brain to hypoxic-ischemic injury. Eur J Neurosci 13: 1101–1106
Wang X, Svedin P, Nie C, Lapatto R, Zhu C, Gustavsson M, Sandberg M, Karlsson JO, Romero R, Hagberg H, Mallard C 2007 N-acetylcysteine reduces lipopolysaccharide-sensitized hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Ann Neurol 61: 263–271
Rousset CI, Chalon S, Cantagrel S, Bodard S, Andres C, Gressens P, Saliba E 2006 Maternal exposure to LPS induces hypomyelination in the internal capsule and programmed cell death in the deep gray matter in newborn rats. Pediatr Res 59: 428–433
Paintlia MK, Paintlia AS, Barbosa E, Singh I, Singh AK 2004 N-acetylcysteine prevents endotoxin-induced degeneration of oligodendrocyte progenitors and hypomyelination in developing rat brain. J Neurosci Res 78: 347–361
Svedin P, Hagberg H, Savman K, Zhu C, Mallard C 2007 Matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene knock-out protects the immature brain after cerebral hypoxia-ischemia. J Neurosci 27: 1511–1518
Back SA, Han BH, Luo NL, Chricton CA, Xanthoudakis S, Tam J, Arvin KL, Holtzman 2002 Selective vulnerability of late oligodendrocyte progenitors to hypoxia-ischemia. J Neurosci 22: 455–463
Back SA, Luo NL, Borenstein NS, Levin JM, Volpe JJ, Kinney HC 2001 Late oligodendrocyte progenitors coincide with the developmental window of vulnerability for human perinatal white matter injury. J Neurosci 21: 1302–1312
Craig A, Luo NL, Beardsley DJ, Wingate-Pearse N, Walker DW, Hohimer AR, Back SA 2003 Quantitative analysis of perinatal rodent oligodendrocyte lineage progression and its correlation with human. Exp Neurol 181: 231–240
Gao HM, Hong JS 2008 Why neurodegenerative diseases are progressive: uncontrolled inflammation drives disease progression. Trends Immunol 29: 357–365
Fan LW, Mitchell HJ, Rhodes PG, Cai Z 2008 Alpha–phenyl-N-tert-butyl-nitrone attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced neuronal injury in the neonatal rat brain. Neuroscience 151: 737–744
Ivacko JA, Sun R, Silverstein FS 1996 Hypoxic-ischemic brain injury induces an acute microglial reaction in perinatal rats. Pediatr Res 39: 39–47
Fan LW, Pang Y, Lin S, Rhodes PG, Cai Z 2005 Minocycline attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced white matter injury in the neonatal rat brain. Neuroscience 133: 159–168
Bona E, Anderson AL, Blomgren K, Gilland E, Puka-Sundvall M, Gustafson K, Hagberg H 1999 Chemokine and inflammatory cell response to hypoxia-ischemia in immature rats. Pediatr Res 45: 500–509
Chang YC, Huang CC, Hung PL, Huang HM 2008 Rolipram, a phosphodiesterase type IV inhibitor, exacerbates periventricular white matter lesions in rat pups. Pediatr Res 64: 234–239
Paxinos G, Watson C 1986 The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, New York
Lee HT, Chang YC, Tu YF, Huang CC 2009 VEGF-A/VEGFR-2 signaling leading to cAMP response element-binding protein phosphorylation is a shared pathway underlying the protective effect of preconditioning on neurons and endothelial cells. J Neurosci 29: 4356–4368
Manning SM, Talos DM, Zhou C, Selip DB, Park HK, Park CJ, Volpe JJ, Jensen FE 2008 NMDA receptor blockade with memantine attenuates white matter injury in a rat model of periventricular leukomalacia. J Neurosci 28: 6670–6678
Lin HY, Huang CC, Chang KF 2009 Lipopolysaccharide preconditioning reduces neuroinflammation against hypoxic ischemia and provides long-term outcome of neuroprotection in neonatal rat. Pediatr Res 66: 254–259
Poets CF, Stebbens VA, Richard D, Southall DP 1995 Prolonged episodes of hypoxemia in preterm infants undetected by cardiorespiratory monitors. Pediatrics 95: 860–863
Mattia FR, deRegnier RA 1998 Chronic physiologic instability is associated with neurodevelopmental morbidity at one and two years in extremely premature infants. Pediatrics 102: e35
Billiards SS, Haynes RL, Folkerth RD, Trachtenberg FL, Liu LG, Volpe JJ, Kinney HC 2006 Development of microglia in the cerebral white matter of the human fetus and infant. J Comp Neurol 497: 199–208
Stolp HB, Dziegielewska KM, Ek CJ, Potter AM, Saunders NR 2005 Long-term changes in blood-brain barrier permeability and white matter following prolonged systemic inflammation in early development in the rat. Eur J Neurosci 22: 2805–2816
McColl BW, Rothwell NJ, Allan SM 2008 Systemic inflammation alters the kinetics of cerebrovascular tight junction disruption after experimental stroke in mice. J Neurosci 28: 9451–9462
Zoppo GJ, Milner R, Mabuchi T, Hung S, Wang X, Berg GI, Koziol JA 2007 Microglial activation and matrix protease generation during focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 38: 646–651
Dammann O, Durums S, Leviton A 2001 Do white cells matter in white matter damage?. Trends Neurosci 24: 320–324
Kadhim H, Tabarki B, Verellen G, De Prez C, Rona AM, Sebire G 2001 Inflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of periventricular leukomalacia. Neurology 56: 1278–1284
Acknowledgements
We thank Chien-Jung Ho for her skillful technical assistance with animal preparations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by grants from the Taiwan National Health Research Institute (NHRI-EX 97-9414NI), the National Science Counsel (NSC: 97-2811-B-006-014), Chi Mei Medical Center (CMNCKU 9802), and the Center for Gene Regulation and Signal Transduction Research, National Cheng Kung University.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, LW., Chang, YC., Lin, CY. et al. Low-Dose Lipopolysaccharide Selectively Sensitizes Hypoxic Ischemia-Induced White Matter Injury in the Immature Brain. Pediatr Res 68, 41–47 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181df5f6b
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181df5f6b
This article is cited by
-
Azithromycin reduces inflammation-amplified hypoxic–ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats
Pediatric Research (2022)
-
Effects of prenatal exposure to inflammation coupled with prepubertal stress on prefrontal white matter structure and related molecules in adult mouse offspring
Metabolic Brain Disease (2022)
-
Activation of GPR39 with TC-G 1008 attenuates neuroinflammation via SIRT1/PGC-1α/Nrf2 pathway post-neonatal hypoxic–ischemic injury in rats
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2021)
-
CXCL5 signaling is a shared pathway of neuroinflammation and blood–brain barrier injury contributing to white matter injury in the immature brain
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2016)
-
TNFR1-JNK signaling is the shared pathway of neuroinflammation and neurovascular damage after LPS-sensitized hypoxic-ischemic injury in the immature brain
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2014)