Abstract
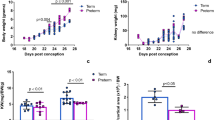
Recently, concern has been raised that corticosteroid treatment of preterm neonates might be associated with adverse effects later in life, including early development of hypertension. Here, we investigate the impact of neonatal dexamethasone (Dex) treatment on early renal cell proliferation and nephron number. We analyzed mitotic activity in renal cortex of rat pups neonatally treated with Dex. Nephron number was measured and possible renal damage was quantified by counting inflammatory foci, ED-1 positive cells (macrophages), and the desmin score (activated podocytes). Mitotic activity was 34 and 29% lower on d 2 and 4 in Dex-treated rats compared with saline-treated controls. The number of glomeruli was lower at 4 wk, but nephron size was unchanged after Dex treatment, as calculated from glomerular density and (lower) body- and kidney weight. At wk 50, the glomerular number was significantly lower in Dex-treated rats, whereas body and kidney weight were the same as in Sal controls. Dex rats also showed more kidney damage, manifested by a ∼3.5-fold increase in inflammation foci/mm2 and in ED-1 positive cells/mm2 and a ∼4.3-fold increased desmin score. Temporary suppression of mitotic activity during neonatal Dex treatment leads to reduction of nephron number and more kidney damage later in life.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- CLD:
-
chronic lung disease
- Dex:
-
dexamethasone
- Sal:
-
saline
References
Ehrenkranz RA, Walsh MC, Vohr BR, Jobe AH, Wright LL, Fanaroff AA, Wrage LA, Poole K 2005 Validation of the National Institutes of Health consensus definition of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatrics 116: 1353–1360
Coalson JJ 2003 Pathology of new bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Semin Neonatol 8: 73–81
Committee on Fetus and Newborn 2002 Postnatal corticosteroids to treat or prevent chronic lung disease in preterm infants. Pediatrics 109: 330–338
Kinsella JP, Greenough A, Abman SH 2006 Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Lancet 367: 1421–1431
Barrington KJ 2001 Postnatal steroids and neurodevelopmental outcomes: a problem in the making. Pediatrics 107: 1425–1426
Stark AR, Carlo WA, Tyson JE, Papile LA, Wright LL, Shankaran S, Donovan EF, Oh W, Bauer CR, Saha S, Poole WK, Stoll BJ 2001 Adverse effects of early dexamethasone in extremely-low-birth-weight infants. National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. N Engl J Med 344: 95–101
Yeh TF, Lin YJ, Lin HC, Huang CC, Hsieh WS, Lin CH, Tsai CH 2004 Outcomes at school age after postnatal dexamethasone therapy for lung disease of prematurity. N Engl J Med 350: 1304–1313
Jobe AH 2004 Postnatal corticosteroids for preterm infants—do what we say, not what we do. N Engl J Med 350: 1349–1351
Kamphuis PJ, Croiset G, Bakker JM, van Bel F, Van Ree JM, Wiegant VM 2004 Neonatal dexamethasone treatment affects social behaviour of rats in later life. Neuropharmacology 47: 461–474
Raff H 2004 Neonatal dexamethasone therapy: short-and long-term consequences. Trends Endocrinol Metab 15: 351–352
Shinwell ES, Eventov-Friedman S 2009 Impact of perinatal corticosteroids on neuromotor development and outcome: review of the literature and new meta-analysis. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 14: 164–170
Kamphuis PJ, de Vries WB, Bakker JM, Kavelaars A, van Dijk JE, Schipper ME, van Oosterhout MF, Croiset G, Heijnen CJ, van Bel F, Wiegant VM 2007 Reduced life expectancy in rats after neonatal dexamethasone treatment. Pediatr Res 61: 72–76
de Vries WB, van der Leij FR, Bakker JM, Kamphuis PJ, van Oosterhout MF, Schipper ME, Smid GB, Bartelds B, van Bel F 2002 Alterations in adult rat heart after neonatal dexamethasone therapy. Pediatr Res 52: 900–906
de Vries WB, Bal MP, Homoet-van der Kraak P, Kamphuis PJ, van der Leij FR, Baan J, Steendijk P, de Weger RA, van Bel F, van Oosterhout MF 2006 Suppression of physiological cardiomyocyte proliferation in the rat pup after neonatal glucocorticosteroid treatment. Basic Res Cardiol 101: 36–42
Bal MP, de Vries WB, Steendijk P, Homoet-van der Kraak P, van der Leij FR, Baan J, van Oosterhout MF, van Bel F 2009 Histopathological changes of the heart after neonatal dexamethasone treatment: studies in 4-, 8- and 50-week-old rats. Pediatr Res 66: 74–79
Martins JP, Monteiro JC, Paixao AD 2003 Renal function in adult rats subjected to prenatal dexamethasone. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 30: 32–37
Ortiz LA, Quan A, Weinberg A, Baum M 2001 Effect of prenatal dexamethasone on rat renal development. Kidney Int 59: 1663–1669
Liu Y, van Goor H, Havinga R, Baller JF, Bloks VW, van der Leij FR, Sauer PJ, Kuipers F, Navis G, de Borst MH 2008 Neonatal dexamethasone administration causes progressive renal damage due to induction of an early inflammatory response. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 294: F768–F776
Kamphuis PJ, Bakker JM, Broekhoven MH, Kunne C, Croiset G, Lentjes EG, Tilders FJ, van Bel F, Wiegant VM 2002 Enhanced glucocorticoid feedback inhibition of hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal responses to stress in adult rats neonatally treated with dexamethasone. Neuroendocrinology 76: 158–169
Tsuboi N, Kawamura T, Ishii T, Utsunomiya Y, Hosoya T 2009 Changes in the glomerular density and size in serial renal biopsies during the progression of IgA nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24: 892–899
Attia DM, Ni ZN, Boer P, Attia MA, Goldschmeding R, Koomans HA, Vaziri ND, Joles JA 2002 Proteinuria is preceded by decreased nitric oxide synthesis and prevented by a NO donor in cholesterol-fed rats. Kidney Int 61: 1776–1787
Luyckx VA, Brenner BM 2005 Low birth weight, nephron number, and kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl S68–S77
Moritz KM, Singh RR, Probyn ME, Denton KM 2009 Developmental programming of a reduced nephron endowment: more than just a baby's birth weight. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 296: F1–F9
Jahnukainen T, Chen M, Berg U, Celsi G 2001 Antenatal glucocorticoids and renal function after birth. Semin Neonatol 6: 351–355
Bladh LG, Liden J, Pazirandeh A, Rafter I, Dahlman-Wright K, Nilsson S, Okret S 2005 Identification of target genes involved in the antiproliferative effect of glucocorticoids reveals a role for nuclear factor-(kappa)B repression. Mol Endocrinol 19: 632–643
Cattarelli D, Chirico G, Simeoni U 2002 Renal effects of antenatally or postnatally administered steroids. Pediatr Med Chir 24: 157–162
Stubbe J, Madsen K, Nielsen FT, Skott O, Jensen BL 2006 Glucocorticoid impairs growth of kidney outer medulla and accelerates loop of Henle differentiation and urinary concentrating capacity in rat kidney development. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 291: F812–F822
Acknowledgements
We thank Ms. Dionne vd Giessen for expert technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by grants NHS 2001B081 (to M.P.B.) and NHS 2004T31 (to M.F.M.O.) from the Netherlands Heart Foundation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Vries, W., van den Borne, P., Goldschmeding, R. et al. Neonatal Dexamethasone Treatment in the Rat Leads to Kidney Damage in Adulthood. Pediatr Res 67, 72–76 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181bf570d
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181bf570d
This article is cited by
-
Neonatal Dexamethasone Treatment Suppresses Hippocampal Estrogen Receptor α Expression in Adolescent Female Rats
Molecular Neurobiology (2019)
-
Selective abdominal venous congestion induces adverse renal and hepatic morphological and functional alterations despite a preserved cardiac function
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Effect of perinatal glucocorticoids on vascular health and disease
Pediatric Research (2017)
-
Albuminuria is associated with too few glomeruli and too much testosterone
Kidney International (2013)