Abstract
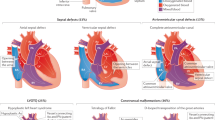
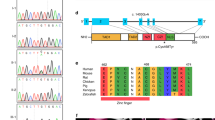
Although the etiology for the majority of congenital heart disease (CHD) remains poorly understood, the known genetic causes are often the result of mutations in cardiac developmental genes. GATA6 encodes for a cardiac transcription factor, which is broadly expressed in the developing heart and is critical for normal cardiac morphogenesis, making it a candidate gene for congenital heart defects in humans. The objective of this study was to determine the frequency of GATA6 sequence variants in a population of individuals with a spectrum of cardiac malformations. The coding regions of GATA6 were sequenced in 310 individuals with CHD. We identified two novel sequence variations in GATA6 that altered highly conserved amino acid residues (A178V and L198V) and were not found in a control population. These variants were identified in two individuals (one with tetralogy of Fallot and the other with an atrioventricular septal defect in the setting of complex CHD). Biochemical studies demonstrate that the GATA6 A178V mutant protein results in increased transactivation ability when compared with wild-type GATA6. These data suggest that nonsynonymous GATA6 sequence variants are infrequently found in individuals with CHD.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- α-MHC:
-
alpha-myosin heavy chain
- ANF:
-
atrial natriuretic factor
- CHD:
-
congenital heart disease
References
Hoffman JI, Kaplan S 2002 The incidence of congenital heart disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 39: 1890–1900
Garg V 2006 Insights into the genetic basis of congenital heart disease. Cell Mol Life Sci 63: 1141–1148
Ransom J, Srivastava D 2007 The genetics of cardiac birth defects. Semin Cell Dev Biol 18: 132–139
Garg V, Kathiriya IS, Barnes R, Schluterman MK, King IN, Butler CA, Rothrock CR, Eapen RS, Hirayama-Yamada K, Joo K, Matsuoka R, Cohen JC, Srivastava D 2003 GATA4 mutations cause human congenital heart defects and reveal an interaction with TBX5. Nature 424: 443–447
Tomita-Mitchell A, Maslen CL, Morris CD, Garg V, Goldmuntz E 2007 GATA4 sequence variants in patients with congenital heart disease. J Med Genet 44: 779–783
Rajagopal SK, Ma Q, Obler D, Shen J, Manichaikul A, Tomita-Mitchell A, Boardman K, Briggs C, Garg V, Srivastava D, Goldmuntz E, Broman KW, Benson DW, Smoot LB, Pu WT 2007 Spectrum of heart disease associated with murine and human GATA4 mutation. J Mol Cell Cardiol 43: 677–685
Morrisey EE, Ip HS, Lu MM, Paramacek MS 1996 GATA6: a zinc finger transcription factor that is expressed in multiple cell lineages derived from lateral mesoderm. Dev Biol 177: 309–322
Molkentin JD 2000 The zinc finger-containing transcription factors GATA-4, -5, and -6. Ubiquitously expressed regulators of tissue-specific gene expression. J Biol Chem 275: 38949–38952
Morrisey EE, Ip HS, Tang Z, Parmacek MS 1997 GATA-4 activates transcription via two novel domains that are conserved within the GATA-4/5/6 subfamily. J Biol Chem 272: 8515–8524
Watt AJ, Battle MA, Li J, Duncan SA 2004 GATA4 is essential for formation of the proepicardium and regulates cardiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101: 12573–12578
Zhao R, Watt AJ, Battle MA, Li J, Bondow BJ, Duncan SA 2008 Loss of both GATA4 and GATA6 blocks cardiac myocyte differentiation and results in acardia in mice. Dev Biol 317: 614–619
Molkentin JD, Lin Q, Duncan SA, Olson EN 1997 Requirement of the transcription factor GATA4 for heart tube formation and ventral morphogenesis. Genes Dev 11: 1061–1072
Kuo CT, Morrisey EE, Anandappa R, Sigrist K, Lu MM, Parmacek MS, Soudais C, Leiden JM 1997 GATA4 transcription factor is required for ventral morphogenesis and heart tube formation. Genes Dev 11: 1048–1060
Koutsourakis M, Langeveld A, Patient R, Beddington R, Grosveld F 1999 The transcription factor GATA6 is essential for early extraembryonic development. Development 126: 723–732
Lepore JJ, Mericko PA, Cheng L, Lu MM, Morrisey EE, Parmacek MS 2006 GATA-6 regulates semaphorin 3C and is required in cardiac neural crest for cardiovascular morphogenesis. J Clin Invest 116: 929–939
Kodo K, Nishizawa T, Furutani M, Arai S, Yamamura E, Joo K, Takahashi T, Matsuoka R, Yamagishi H 2009 GATA6 mutations cause human cardiac outflow tract defects by disrupting semaphorin-plexin signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106: 13933–13938
Xin M, Davis CA, Molkentin JD, Lien CL, Duncan SA, Richardson JA, Olson EN 2006 A threshold of GATA4 and GATA6 expression is required for cardiovascular development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103: 11189–11194
Maitra M, Schluterman MK, Nichols HA, Richardson JA, Lo CW, Srivastava D, Garg V 2009 Interaction of Gata4 and Gata6 with Tbx5 is critical for normal cardiac development. Dev Biol 326: 368–377
Fluck CE, Miller WL 2004 GATA-4 and GATA-6 modulate tissue-specific transcription of the human gene for P450c17 by direct interaction with Sp1. Mol Endocrinol 18: 1144–1157
Schluterman MK, Krysiak AE, Kathiriya IS, Abate N, Chandalia M, Srivastava D, Garg V 2007 Screening and biochemical analysis of GATA4 sequence variations identified in patients with congenital heart disease. Am J Med Genet A 143A: 817–823
Srivastava D 2006 Making or breaking the heart: from lineage to determination to morphogenesis. Cell 126: 1037–1048
McElhinney DB, Geiger E, Clinder J, Benson DW, Goldmuntz E 2003 NKX2.5 mutations in patients with congenital heart disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 42: 1650–1655
McBride KL, Riley MF, Zender GA, Fitzgerald-Butt SM, Towbin JA, Belmont JW, Cole SE 2008 NOTCH1 mutations in individuals with left ventricular outflow tract malformations reduce ligand-induced signaling. Hum Mol Genet 17: 2886–2893
Bruneau BG 2008 The developmental genetics of congenital heart disease. Nature 451: 943–948
Zweier C, Sticht H, Aydin-Yaylagul I, Campbell CE, Rauch A 2007 Human TBX1 missense mutations cause gain of function resulting in the same phenotype as 22q11.2 deletions. Am J Hum Genet 80: 510–517
Postma AV, van de Meerakker JB, Mathijssen IB, Barnett P, Christoffels VM, Ilgun A, Lam J, Wilde AA, Lekanne Deprez RH, Moorman AF 2008 A gain-of-function TBX5 mutation is associated with atypical Holt-Oram syndrome and paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Circ Res 102: 1433–1442
Posch MG, Gramlich M, Sunde M, Schmitt K, Richter S, Perrot A, Panek AN, Al Khatib A, Nemer G, Megarbane A, Dietz R, Stiller B, Berger F, Harvey RP, Ozcelik C 2010 A gain-of-function TBX20 mutation causes congenital atrial septal defects, patent foramen ovale, and cardiac valve defects. J Med Genet 47: 230–235
Gelb BD, Tartaglia M 2006 Noonan syndrome and related disorders: dysregulated RAS-mitogen activated protein kinase signal transduction. Hum Mol Genet 15: R220–R226
Han K, Manley J 1993 Functional domains of the drosophila engrailed protein. EMBO J 12: 2723–2733
Gove C, Walmsley M, Nijjar S, Bertwistle D, Guille M, Partington G, Bomford A, Patient R 1997 1997 Over-expression of GATA-6 in xenopus embryos blocks differentiation of heart precursors. EMBO J 16: 355–368
Ching YH, Ghosh TK, Cross SJ, Packham EA, Honeyman L, Loughna S, Robinson TE, Dearlove AM, Ribas G, Bonser AJ, Thomas NR, Scotter AJ, Caves LS, Tyrrell GP, Newbury-Ecob RA, Munnich A, Bonnet D, Brook JD 2005 Mutation in myosin heavy chain 6 causes atrial septal defect. Nat Genet 37: 423–428
Acknowledgements
We thank the families for their participation; C. Rains, J. Neumann, and A. Winborn for research coordinator support; C. Turner for technical support; members of the McDermott Center for Human Growth and Development for assistance with sequencing; the Divisions of Pediatric Cardiology and Pediatric Cardiothoracic Surgery at Children's Medical Center of Dallas for assistance with clinical information and management; and Dr. K.L. McBride for critical review of the article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by Grants NIH/NHLBI (R01HL080592 and R01HL057181) and California Institute for Regenerative Medicine (to D.S.) and by Grants NIH/NHLBI (R01HL088965) and the Children's Heart Foundation (to V.G.).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maitra, M., Koenig, S., Srivastava, D. et al. Identification of GATA6 Sequence Variants in Patients With Congenital Heart Defects. Pediatr Res 68, 281–285 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181ed17e4
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181ed17e4
This article is cited by
-
Novel pathogenic GATA6 variant associated with congenital heart disease, diabetes mellitus and necrotizing enterocolitis
Pediatric Research (2024)
-
Gene expression and transcriptional regulation driven by transcription factors involved in congenital heart defects
Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -) (2023)
-
Case report: adult onset diabetes with partial pancreatic agenesis and congenital heart disease due to a de novo GATA6 mutation
BMC Medical Genetics (2020)
-
Zinc-finger proteins in health and disease
Cell Death Discovery (2017)