Abstract
Introduction:
The pathophysiology of necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is multifactorial, and gastrointestinal bacteria are thought to play an important role. In this study, the role of microflora in the gastrointestinal tract of neonates with NEC was assessed by comparing cases with controls.
Results:
Of the 163 neonates, 21 developed NEC. The risk of NEC decreased by 8% with each additional day of gestational age.
Discussion:
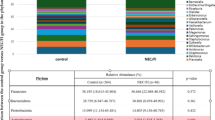
Typically, very few bacterial species could be cultured from the fecal specimens obtained. Gram-positive (G+) bacteria dominated the samples in the NEC group, whereas in the control group mixed flora of G+ and Gram-negative (G−) bacteria were isolated. Surprisingly, molecular analysis using PCR-DGGE profiles did not confirm these differences. Our data suggest that G+ bacteria in the intestine may play a role in the development of NEC in premature infants.
Methods:
One hundred and sixty three neonates born at <30 weeks of gestation were enrolled. Fecal samples taken during the first month of life were subjected to culture and PCR-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (PCR-DGGE). A total of 482 fecal samples were examined.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Lin PW, Stoll BJ . Necrotising enterocolitis. Lancet 2006; 368: 1271–83.
Blakely ML, Lally KP, McDonald S, et al.; NEC Subcommittee of the NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Postoperative outcomes of extremely low birth-weight infants with necrotizing enterocolitis or isolated intestinal perforation: a prospective cohort study by the NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Ann Surg 2005;241: 984–9; discussion 989–94.
McCracken VJ, Lorenz RG . The gastrointestinal ecosystem: a precarious alliance among epithelium, immunity and microbiota. Cell Microbiol 2001;3: 1–11.
Lin PW, Nasr TR, Stoll BJ . Necrotizing enterocolitis: recent scientific advances in pathophysiology and prevention. Semin Perinatol 2008;32: 70–82.
Neu J . Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis: an update. Acta Paediatr Suppl 2005;94: 100–5.
Schnabl KL, Van Aerde JE, Thomson AB, Clandinin MT . Necrotizing enterocolitis: a multifactorial disease with no cure. World J Gastroenterol 2008;14: 2142–61.
Updegrove K . Necrotizing enterocolitis: the evidence for use of human milk in prevention and treatment. J Hum Lact 2004;20: 335–9.
Peter CS, Feuerhahn M, Bohnhorst B, et al. Necrotising enterocolitis: is there a relationship to specific pathogens? Eur J Pediatr 1999;158: 67–70.
Westerbeek EA, van den Berg A, Lafeber HN, Knol J, Fetter WP, van Elburg RM . The intestinal bacterial colonisation in preterm infants: a review of the literature. Clin Nutr 2006;25: 361–8.
Palmer C, Bik EM, DiGiulio DB, Relman DA, Brown PO . Development of the human infant intestinal microbiota. PLoS Biol 2007;5: e177.
Blakey JL, Lubitz L, Campbell NT, Gillam GL, Bishop RF, Barnes GL . Enteric colonization in sporadic neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1985;4: 591–5.
Gewolb IH, Schwalbe RS, Taciak VL, Harrison TS, Panigrahi P . Stool microflora in extremely low birthweight infants. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 1999;80: F167–73.
Rotimi VO, Olowe SA, Ahmed I . The development of bacterial flora of premature neonates. J Hyg (Lond) 1985;94: 309–18.
Stark PL, Lee A . The microbial ecology of the large bowel of breast-fed and formula-fed infants during the first year of life. J Med Microbiol 1982;15: 189–203.
Björkstén B . The intrauterine and postnatal environments. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1999;104: 1119–27.
Dittmar E, Beyer P, Fischer D,et al. Necrotizing enterocolitis of the neonate with Clostridium perfringens: diagnosis, clinical course, and role of alpha toxin. Eur J Pediatr 2008;167: 891–5.
Duffy LC, Zielezny MA, Carrion V, et al. Concordance of bacterial cultures with endotoxin and interleukin-6 in necrotizing enterocolitis. Dig Dis Sci 1997;42: 359–65.
Hällström M, Eerola E, Vuento R, Janas M, Tammela O . Effects of mode of delivery and necrotising enterocolitis on the intestinal microflora in preterm infants. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2004;23: 463–70.
Kosloske AM, Ulrich JA . A bacteriologic basis for the clinical presentations of necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr Surg 1980;15: 558–64.
Mshvildadze M, Neu J, Shuster J, Theriaque D, Li N, Mai V . Intestinal microbial ecology in premature infants assessed with non-culture-based techniques. J Pediatr 2010;156: 20–5.
Hoy CM, Wood CM, Hawkey PM, Puntis JW . Duodenal microflora in very-low-birth-weight neonates and relation to necrotizing enterocolitis. J Clin Microbiol 2000;38: 4539–47.
Millar MR, Linton CJ, Cade A, Glancy D, Hall M, Jalal H . Application of 16S rRNA gene PCR to study bowel flora of preterm infants with and without necrotizing enterocolitis. J Clin Microbiol 1996;34: 2506–10.
de la Cochetiere MF, Piloquet H, des Robert C, Darmaun D, Galmiche JP, Roze JC . Early intestinal bacterial colonization and necrotizing enterocolitis in premature infants: the putative role of Clostridium. Pediatr Res 2004; 56: 366–70.
Favier CF, Vaughan EE, De Vos WM, Akkermans AD . Molecular monitoring of succession of bacterial communities in human neonates. Appl Environ Microbiol 2002;68: 219–26.
Schwiertz A, Gruhl B, Löbnitz M, Michel P, Radke M, Blaut M . Development of the intestinal bacterial composition in hospitalized preterm infants in comparison with breast-fed, full-term infants. Pediatr Res 2003;54: 393–9.
Rougé C, Goldenberg O, Ferraris L, et al. Investigation of the intestinal microbiota in preterm infants using different methods. Anaerobe 2010;16: 362–70.
Zoetendal EG, Akkermans AD, De Vos WM . Temperature gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of 16S rRNA from human fecal samples reveals stable and host-specific communities of active bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 1998;64: 3854–9.
Smith B, Bodé S, Petersen BL, et al. Community analysis of bacteria colonizing intestinal tissue of neonates with necrotizing enterocolitis. BMC Microbiol 2011;11: 73.
Bell MJ, Ternberg JL, Feigin RD,et al. Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Therapeutic decisions based upon clinical staging. Ann Surg 1978;187: 1–7.
Smith B, Li N, Andersen AS, Slotved HC, Krogfelt KA . Optimising bacterial DNA extraction from faecal samples: comparison of three methods. Open Microbiol J 2011;5: 14–7.
Walter J, Tannock GW, Tilsala-Timisjarvi A,et al. Detection and identification of gastrointestinal Lactobacillus species by using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and species-specific PCR primers. Appl Environ Microbiol 2000;66: 297–303.
Muyzer G, de Waal EC, Uitterlinden AG . Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 1993;59: 695–700.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all the clinical staff at the Neonatal Department, Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen, Denmark, for their help with obtaining the samples, and Berit Jensen for her valuable technical assistance with laboratory analyses. We would like to pay our respects to our late colleague S. Bodé, Neonatal Department, Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen, who was a driving force during this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, B., Bodé, S., Skov, T. et al. Investigation of the early intestinal microflora in premature infants with/without necrotizing enterocolitis using two different methods. Pediatr Res 71, 115–120 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2011.1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2011.1
This article is cited by
-
The effect of probiotics on the clinical status of adult patients with atopic dermatitis: a systematic review
European Journal of Medical Research (2022)
-
Incomplete resection of necrotic bowel may increase mortality in infants with necrotizing enterocolitis
Pediatric Research (2021)
-
Intestinal dysbiosis and necrotizing enterocolitis: assessment for causality using Bradford Hill criteria
Pediatric Research (2020)
-
Clinical determinants of postoperative outcomes in surgical necrotizing enterocolitis
Journal of Perinatology (2020)
-
Using formalin fixed paraffin embedded tissue to characterize the preterm gut microbiota in necrotising enterocolitis and spontaneous isolated perforation using marginal and diseased tissue
BMC Microbiology (2019)