Abstract
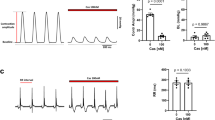
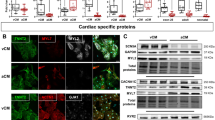
The novel Cav1.3 (α1D) L-type Ca2+ channel plays a significant role in sinoatrial (SA) and atrioventricular (AV) nodes function and in atrial fibrillation. However, the characterization of α1D Ca2+ channel during heart development is very limited. We used real-time RT-PCR, Western blotting, and indirect immunostaining to characterize the developmental expression and localization of α1D Ca2+ channel in rat hearts. Both protein and mRNA levels of α1D Ca2+ channel decreased postnatally. Two forms of α1D Ca2+ channel protein (250 and 190 kD) were observed, with the full-length (250 kD) channel protein being predominant in the prenatal stages. Both Western blots and confocal imaging demonstrated that α1D Ca2+ channel protein was expressed in both atria and ventricles at fetal and neonatal stages but was absent in the adult ventricles. Interestingly, α1D Ca2+ channel was also found at the nucleus/perinucleus of immature but not adult atrial cells. Furthermore, the nuclear staining was reproduced in adult atrial cell line, HL-1 cells, which possess immature properties. The data are first to show that α1D Ca2+ channel has unique age-dependent expression profile and subcellular localization in the heart, suggesting a developmental stage-dependent specific function.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- ICa-L:
-
L-type Ca2+ current
REFERENCES
Catterall WA, Perez-Reyes E, Snutch TP, Striessnig J 2005 International Union of Pharmacology. XLVIII. Nomenclature and structure-function relationships of voltage-gated calcium channels. Pharmacol Rev 57: 411–425
Ertel EA, Campbell KP, Harpold MM, Hofmann F, Mori Y, Perez-Reyes E, Schwartz A, Snutch TP, Tanabe T, Birnbaumer L, Tsien RW, Catterall WA 2000 Nomenclature of voltage-gated calcium channels. Neuron 25: 533–535
Hell JW, Westenbroek RE, Warner C, Ahlijanian MK, Prystay W, Gilbert MM, Snutch TP, Catterall WA 1993 Identification and differential subcellular localization of the neuronal class C and class D L-type calcium channel alpha 1 subunits. J Cell Biol 123: 949–962
Seino S, Chen L, Seino M, Blondel O, Takeda J, Johnson JH, Bell GI 1992 Cloning of the alpha 1 subunit of a voltage-dependent calcium channel expressed in pancreatic beta cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 584–588
Mangoni ME, Couette B, Bourinet E, Platzer J, Reimer D, Striessnig J, Nargeot J 2003 Functional role of L-type Cav1.3 Ca2+ channels in cardiac pacemaker activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 5543–5548
Matthes J, Yildirim L, Wietzorrek G, Reimer D, Striessnig J, Herzig S 2004 Disturbed atrio-ventricular conduction and normal contractile function in isolated hearts from Cav1.3-knockout mice. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 369: 554–562
Zhang Z, He Y, Tuteja D, Xu D, Timofeyev V, Zhang Q, Glatter KA, Xu Y, Shin HS, Low R, Chiamvimonvat N 2005 Functional roles of Cav1.3(alpha1D) calcium channels in atria: insights gained from gene-targeted null mutant mice. Circulation 112: 1936–1944
Mancarella S, Yue Y, Karnabi E, Qu Y, El Sherif N, Boutjdir M 2008 Impaired calcium homeostasis is associated with atrial fibrillation in the {alpha}1D L-type Ca2+ channel KO mouse. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2008 295: H2017–H2024
Bell DC, Butcher AJ, Berrow NS, Page KM, Brust PF, Nesterova A, Stauderman KA, Seabrook GR, Nurnberg B, Dolphin AC 2001 Biophysical properties, pharmacology, and modulation of human, neuronal L-type (alpha(1D), Ca(V)1.3) voltage-dependent calcium currents. J Neurophysiol 85: 816–827
Koschak A, Reimer D, Huber I, Grabner M, Glossmann H, Engel J, Striessnig J 2001 Alpha 1D (Cav1.3) subunits can form l-type Ca2+ channels activating at negative voltages. J Biol Chem 276: 22100–22106
Qu Y, Boutjdir M 2001 Gene expression of SERCA2a and L- and T-type Ca channels during human heart development. Pediatr Res 50: 569–574
Brillantes AM, Bezprozvannaya S, Marks AR 1994 Developmental and tissue-specific regulation of rabbit skeletal and cardiac muscle calcium channels involved in excitation-contraction coupling. Circ Res 75: 503–510
Liu L, O'Hara DS, Cala SE, Poornima I, Hines RN, Marsh JD 2000 Developmental regulation of the L-type calcium channel alpha1C subunit expression in heart. Mol Cell Biochem 205: 101–109
Qu Y, Karnabi E, Chahine M, Vassalle M, Boutjdir M 2007 Expression of skeletal muscle Na(V)1.4 Na channel isoform in canine cardiac Purkinje myocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 355: 28–33
Qu Y, Baroudi G, Yue Y, Boutjdir M 2005 Novel molecular mechanism involving alpha1D (Cav1.3) L-type calcium channel in autoimmune-associated sinus bradycardia. Circulation 111: 3034–3041
Boutjdir M, Chen L, Zhang ZH, Tseng CE, El-Sherif N, Buyon JP 1998 Serum and immunoglobulin G from the mother of a child with congenital heart block induce conduction abnormalities and inhibit L-type calcium channels in a rat heart model. Pediatr Res 44: 11–19
Ogawa E, Saito Y, Harada M, Kamitani S, Kuwahara K, Miyamoto Y, Ishikawa M, Hamanaka I, Kajiyama N, Takahashi N, Nakagawa O, Masuda I, Kishimoto I, Nakao K 2000 Outside-in signalling of fibronectin stimulates cardiomyocyte hypertrophy in cultured neonatal rat ventricular myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 32: 765–776
Qu Y, Baroudi G, Yue Y, El-Sherif N, Boutjdir M 2005 Localization and modulation of {alpha}1D (Cav1.3) L-type Ca channel by protein kinase A. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 288: H2123–H2130
Huynh TV, Chen F, Wetzel GT, Friedman WF, Klitzner TS 1992 Developmental changes in membrane Ca2+ and K+ currents in fetal, neonatal, and adult rabbit ventricular myocytes. Circ Res 70: 508–515
Draguhn A, Borner G, Beckmann R, Buchner K, Heinemann U, Hucho F 1997 Large-conductance cation channels in the envelope of nuclei from rat cerebral cortex. J Membr Biol 158: 159–166
Franco-Obregón A, Wang HW, Clapham DE 2000 Distinct ion channel classes are expressed on the outer nuclear envelope of T- and B-lymphocyte cell lines. Biophys J 79: 202–214
Stehno-Bittel L, Perez-Terzic C, Luckhoff A, Clapham DE 1996 Nuclear ion channels and regulation of the nuclear pore. Soc Gen Physiol Ser 51: 195–207
Stehno-Bittel L, Luckhoff A, Clapham DE 1995 Calcium release from the nucleus by InsP3 receptor channels. Neuron 14: 163–167
Maruyama Y, Shimada H, Taniguchi J 1995 Ca(2+)-activated K(+)-channels in the nuclear envelope isolated from single pancreatic acinar cells. Pflugers Arch 430: 148–150
Takemura H, Yasui K, Opthof T, Niwa N, Horiba M, Shimizu A, Lee JK, Honjo H, Kamiya K, Ueda Y, Kodama I 2005 Subtype switching of L-Type Ca2+ channel from Cav1.3 to Cav1.2 in embryonic murine ventricle. Circ J 69: 1405–1411
Nuss HB, Houser SR 1993 T-type Ca2+ current is expressed in hypertrophied adult feline left ventricular myocytes. Circ Res 73: 777–782
Martínez ML, Heredia MP, Delgado C 1999 Expression of T-type Ca(2+) channels in ventricular cells from hypertrophied rat hearts. J Mol Cell Cardiol 31: 1617–1625
Bas A, Forsberg G, Hammarstrom S, Hammarstrom ML 2004 Utility of the housekeeping genes 18S rRNA, beta-actin and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase for normalization in real-time quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction analysis of gene expression in human T lymphocytes. Scand J Immunol 59: 566–573
Patel P, Boyd CA, Johnston DG, Williamson C 2002 Analysis of GAPDH as a standard for gene expression quantification in human placenta. Placenta 23: 697–698
Mansur NR, Meyer-Siegler K, Wurzer JC, Sirover MA 1993 Cell cycle regulation of the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase/uracil DNA glycosylase gene in normal human cells. Nucleic Acids Res 21: 993–998
Oikarinen A, Makela J, Vuorio T, Vuorio E 1991 Comparison on collagen gene expression in the developing chick embryo tendon and heart. Tissue and development time-dependent action of dexamethasone. Biochim Biophys Acta 1089: 40–46
Boucek RJ Jr, Shelton M, Artman M, Mushlin PS, Starnes VA, Olson RD 1984 Comparative effects of verapamil, nifedipine, and diltiazem on contractile function in the isolated immature and adult rabbit heart. Pediatr Res 18: 948–952
Hoerter J, Mazet F, Vassort G 1981 Perinatal growth of the rabbit cardiac cell: possible implications for the mechanism of relaxation. J Mol Cell Cardiol 13: 725–740
Maylie JG 1982 Excitation-contraction coupling in neonatal and adult myocardium of cat. Am J Physiol 242: H834–H843
Xu M, Welling A, Paparisto S, Hofmann F, Klugbauer N 2003 Enhanced expression of L-type Cav1.3 calcium channels in murine embryonic hearts from Cav1.2-deficient mice. J Biol Chem 278: 40837–40841
Zhang Z, Xu Y, Song H, Rodriguez J, Tuteja D, Namkung Y, Shin HS, Chiamvimonvat N 2002 Functional Roles of Ca(v)1.3 (alpha(1D)) calcium channel in sinoatrial nodes: insight gained using gene-targeted null mutant mice. Circ Res 90: 981–987
Safa P, Boulter J, Hales TG 2001 Functional properties of Cav1.3 (alpha1D) L-type Ca2+ channel splice variants expressed by rat brain and neuroendocrine GH3 cells. J Biol Chem 276: 38727–38737
Scholze A, Plant TD, Dolphin AC, Nurnberg B 2001 Functional expression and characterization of a voltage-gated CaV1.3 (alpha1D) calcium channel subunit from an insulin-secreting cell line. Mol Endocrinol 15: 1211–1221
De Jongh KS, Colvin AA, Wang KK, Catterall WA 1994 Differential proteolysis of the full-length form of the L-type calcium channel alpha 1 subunit by calpain. J Neurochem 63: 1558–1564
Gerhardstein BL, Gao T, Bunemann M, Puri TS, Adair A, Ma H, Hosey MM 2000 Proteolytic processing of the C terminus of the alpha(1C) subunit of L-type calcium channels and the role of a proline-rich domain in membrane tethering of proteolytic fragments. J Biol Chem 275: 8556–8563
Gomez-Ospina N, Tsuruta F, Barreto-Chang O, Hu L, Dolmetsch R 2006 The C terminus of the L-type voltage-gated calcium channel Ca(V)1.2 encodes a transcription factor. Cell 127: 591–606
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Seino and Dr. Striessnig for providing the plasmids used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by National Institutes of Health [R01 HL-077494], Veterans Affairs MERIT grants [to M.B.], and Veteran Affairs MREP grant [to Y.Q.].
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, Y., Karnabi, E., Ramadan, O. et al. Perinatal and Postnatal Expression of Cav1.3 α1D Ca2+ Channel in the Rat Heart. Pediatr Res 69, 479–484 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e318217a0df
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e318217a0df
This article is cited by
-
Postnatal developmental changes in the sensitivity of L-type Ca2+ channel to inhibition by verapamil in a mouse heart model
Pediatric Research (2018)
-
NFAT5-mediated CACNA1C expression is critical for cardiac electrophysiological development and maturation
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2016)
-
Truncation of murine CaV1.2 at Asp 1904 increases CaV1.3 expression in embryonic atrial cardiomyocytes
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2013)