Abstract
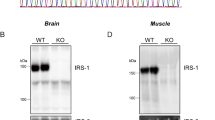
Intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR) has been linked to metabolic syndrome including insulin resistance, and overexpression of suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCSs) proteins is thought to be associated with increased whole-body insulin sensitivity. The insulin-resistant IUGR rat model was established by maternal food restriction (about 30% of the normal rats). The weight, length, and homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) of IUGR-born rats was higher than the control group. Insulin receptor substrate (IRS)-1 expression decreased, whereas SOCS-1 and SOCS-3 increased in the skeletal muscle of IUGR rats compared with the control group. The recombination plasmids PGPU6/GFP/Neo-SOCS-1small hairpin RNA (shRNA) and PGPU6/GFP/Neo-SOCS-3shRNA were transfected into skeletal muscle cells, and the shRNAs efficiently inhibited the expression of SOCS-1 and SOCS-3. Insulin-stimulated glucose transporter-4 (GLUT4) translocation was also dramatically increased. In conclusion, these data provide additional information on the mechanism of insulin resistance associated with IUGR. Down-regulation of SOCS-1 and SOCS-3 ameliorates the capacity of glucose transport and provides a potential gene therapy approach to managing metabolic syndrome.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- GLUT:
-
glucose transporter
- HOMA-IR:
-
homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance
- IRS-1:
-
insulin receptor substrate-1
- SOCS:
-
suppressors of cytokine signaling
- shRNA:
-
small hairpin RNAs
REFERENCES
Neitzke U, Harder T, Schellong K, Melchior K, Rodekamp E, Dudenhausen JW, Plagemann A 2008 Intrauterine growth restriction in a rodent model and developmental programming of the metabolic syndrome: a critical appraisal of the experimental evidence. Placenta 29: 246–254
Yajnik CS 2004 Early life origins of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes in India and other Asian countries. J Nutr 134: 205–210
Grundy SM, Brewer BH, Cleeman JI, Smith SC, Lenfant C 2004 Definition of metabolic syndrome. Circulation 109: 433–438
Virkamäki A, Ueki K, Kahn CR 1999 Protein-protein interaction in insulin signaling and the molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 103: 931–943
Ueki K, Kondo T, Kahn CR 2004 Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS-1) and SOCS-3 cause insulin resistance through inhibition of tyrosine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate proteins by discrete mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol 24: 5434–5446
Starr R, Metcalf D, Elefanty AG, Brysha M, Willson TA, Nicola NA, Hilton DJ, Alexander WS 1998 Liver degeneration and lymphoid deficiencies in mice lacking suppressor of cytokine signaling-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95: 14395–14399
Shahkhalili Y, Moulin J, Zbinden I, Aprikian O, Mace K 2010 Comparison of two models of intrauterine growth restriction for early catch-up growth and later development of glucose intolerance and obesity in rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 298: R141–R146
Frontini MG, Srinivasan SR, Xu J, Berenson GS 2004 Low birth weight and longitudinal trends of cardiovascular risk factor variables from childhood to adolescence:the bogalusa heart study. BMC Pediatr 4: 22–25
Lucas A 2005 Long-term programming effects of early nutrition—implications for the preterm infants. J Perinatol 25: S2–S6
Lebovitz HE 2006 Insulin resistance—a common link between type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Obes Metab 8: 237–249
Ozanne SE, Fermandez TD, Hales CN 2004 Fetal growth and adult disease. Semin Perinatol 28: 81–87
Hales CN, Barker DJ 1992 Type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus: the thrifty phenotype hypothesis. Diabetologia 35: 595–601
Barker DJ, Eriksson JG, Forsen T, Osmond C 2002 Fetal origins of adult disease: strength of effects and biological basis. Int J Epidemiol 31: 1235–1239
Endo TA, Masuhara M, Yokouchi M, Suzuki R, Sakamoto H, Mitsui K, Matsumoto A, Tanimuna S, Ohtsubo M, Misawa H, Miyazaki T, Leonor N, Taniguchi T, Fujita T, Kanakura Y, Komiya S, Yoshimura A 1997 A new protein containing an SH2 domain that inhibits JAK kinases. Nature 387: 921–924
Peraldi P, Filloux C, Emanuelli B, Hilton DJ, Van Obberghen E 2001 Insulin induces suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 tyrosine phosphorylation through janus-activated kinase. J Biol Chem 276: 24614–24620
Ain R, Canham LN, Soares MJ 2005 Dexamethasone-induced intrauterine growth restriction impacts the placental prolactin family, insulin-like growth factor-II and the Akt signaling pathway. J Endocrinol 185: 253–263
Mooney RA, Senn J, Cameron S, Inamdar N, Boivin LM, Shang Y, Furlanetto RW 2001 Suppressors of cytokine signaling-1 and -6 associate with and inhibit the insulin receptor, a potential mechanism for cytokine-mediated insulin resistance. J Biol Chem 276: 25889–25893
Ueki K, Kadowaki T, Kahn CR 2005 Role of suppressors of cytokine signaling SOCS-1 and SOCS-3 in hepatic steatosis and the metabolic syndrome. Hepatol Res 33: 185–192
Garvey WT, Huecksteadt TP, Matthakt S, Olefsky JM 1988 Role of glucose transporters in the cellular insulin resistance of type 2 non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest 81: 1528–1536
Jaquet D, Vidal H, Hankard R, Czernichow P, Levy-Marchal C 2001 Impaired regulation of transporter 4 gene expression in insulin resistance associated with in utero undernutrition. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86: 3266–3271
Carvalho E, Schellhorn SE, Zabolotny JM 2004 GLUT4 overexpression or deficiency in adipocytes of transgenic mice alters the composition of GLUT4 vesicles and the subcellular localization of GLUT4 and IRAP. J Biol Chem 279: 21598–21605
Thamotharan M, Shin BC, Suddirikku DT 2005 GLUT4 expression and subcellular localization in the intrauterine growth-restricted adult rat female offspring. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 288: E935–E947
Holness MJ 2001 Enhanced glucose uptake into adipose tissue induced by early growth restriction augments excursions in plasma leptin response evoked by changes in insulin status. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 25: 1775–1781
Andersen PH, Lund S, Vestergaard H, Junker S, Kahn BB, Pedersen O 1993 Expression of the major insulin regulatable glucose transporter (GLUT 4) in skeletal muscle of non insulin dependent diabetic patients and healthy subjects before and after insulin infusion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 77: 27–32
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.30672262 and No.30772358) [X.L.], Eleventh Five-year National Science Supported Planning Project (No.2006BAI05A07) [X.L.], the Doctor Program of Higher Education from the Ministry of Education of China (No. 20060487062) [X.L.], and the 973 National Basic Research Project from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (No. 2007CB512900) [Q.N.].
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, L., Zheng, R., Wang, C. et al. The Influence of Down-Regulation of Suppressor of Cellular Signaling Proteins by RNAi on Glucose Transport of Intrauterine Growth Retardation Rats. Pediatr Res 69, 497–503 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e31821769bd
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e31821769bd
This article is cited by
-
LRP6 Bidirectionally Regulates Insulin Sensitivity through Insulin Receptor and S6K Signaling in Rats with CG-IUGR
Current Medical Science (2023)
-
Withania somnifera as a potential candidate to ameliorate high fat diet-induced anxiety and neuroinflammation
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2017)
-
IUGR with infantile overnutrition programs an insulin-resistant phenotype through DNA methylation of peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α in rats
Pediatric Research (2015)
-
Polymorphisms in the SOCS7 gene and glucose homeostasis traits
BMC Research Notes (2013)
-
Effects of SOCS 1/3 gene silencing on the expression of C/EBPα and PPARγ during differentiation and maturation of rat preadipocytes
Pediatric Research (2013)