Abstract
Introduction:
To examine the immune-modulatory effects of probiotics during early infancy, Bifidobacterium breve M-16V (B. breve) was administered to rat pups during the newborn or weaning period, and the expression of inflammatory genes was investigated using a cDNA microarray and real-time PCR.
Results:
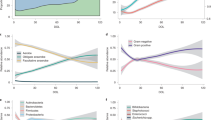
After B. breve administration, significant increases in the numbers of Bifidobacterium in both the cecum and colon were confirmed during the newborn period. The numbers of upregulated and downregulated genes were greater during the weaning period than in the newborn period and were greatest in the colon, with fewer genes altered in the small intestine and the fewest in the spleen. The expression of inflammation-related genes, including lipoprotein lipase (Lpl), glutathione peroxidase 2 (Gpx2), and lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (Lbp), was significantly reduced in the colon during the newborn period. In weaning rat pups, the expression of CD3d, a cell surface receptor–linked signaling molecule, was significantly enhanced in the colon; however, the expression of co-stimulatory molecules was not enhanced.
Discussion:
Our findings support a possible role for B. breve in mediating anti-inflammatory and antiallergic reactions by modulating the expression of inflammatory molecules during the newborn period and by regulating the expression of co-stimulatory molecules during the weaning period.
Methods:
Gene expression in the intestine was investigated after feeding 5×108 cfu of B. breve every day to the F344/Du rat from days 1 to 14 (newborn group) and from days 21 to 34 (weaning group). mRNA was extracted from intestine, and the expression of inflammatory gene was analyzed by microarray and real-time PCR.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Report of a Joint FAO/WHO Expert Consultation on Evaluation of Health and Nutritional Properties of Probiotics in Food Including Powder Milk with Live Lactic Acid Bacteria, 2001. (http://www.who.int/foodsafety/publications/fs_management/en/probiotics.pdf).
Yang YX, He M, Hu G, et al. Effect of a fermented milk containing Bifidobacterium lactis DN-173010 on Chinese constipated women. World J Gastroenterol 2008;14: 6237–43.
Coccorullo P, Strisciuglio C, Martinelli M, Miele E, Greco L, Staiano A . Lactobacillus reuteri (DSM 17938) in infants with functional chronic constipation: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. J Pediatr 2010;157: 598–602.
Kalliomäki M, Salminen S, Arvilommi H, Kero P, Koskinen P, Isolauri E . Probiotics in primary prevention of atopic disease: a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2001;357: 1076–9.
Xiao JZ, Kondo S, Yanagisawa N, et al. Probiotics in the treatment of Japanese cedar pollinosis: a double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Clin Exp Allergy 2006;36: 1425–35.
Inoue Y, Iwabuchi N, Xiao JZ, Yaeshima T, Iwatsuki K . Suppressive effects of bifidobacterium breve strain M-16V on T-helper type 2 immune responses in a murine model. Biol Pharm Bull 2009;32: 760–3.
Torii A, Torii S, Fujiwara S, Tanaka H, Inagaki N, Nagai H . Lactobacillus Acidophilus strain L-92 regulates the production of Th1 cytokine as well as Th2 cytokines. Allergol Int 2007;56: 293–301.
Nonaka Y, Izumo T, Izumi F, et al. Antiallergic effects of Lactobacillus pentosus strain S-PT84 mediated by modulation of Th1/Th2 immunobalance and induction of IL-10 production. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 2008;145: 249–57.
Schouten B, van Esch BC, Hofman GA, et al. Cow milk allergy symptoms are reduced in mice fed dietary synbiotics during oral sensitization with whey. J Nutr 2009;139: 1398–403.
Hougee S, Vriesema AJ, Wijering SC, et al. Oral treatment with probiotics reduces allergic symptoms in ovalbumin-sensitized mice: a bacterial strain comparative study. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 2010;151: 107–17.
Li Y, Shimizu T, Hosaka A, Kaneko N, Ohtsuka Y, Yamashiro Y . Effects of Bifidobacterium breve supplementation on intestinal flora of low birth weight infants. Pediatr Int 2004;46: 509–15.
Fujii T, Ohtsuka Y, Lee T, et al. Bifidobacterium breve enhances transforming growth factor beta1 signaling by regulating Smad7 expression in preterm infants. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2006;43: 83–8.
Abe F, Miyauchi H, Uchijima A, Yaeshima T, Iwatsuki K Stability of bifidobacteria in powdered formula. Int J Food Sci Tech 2009;44: 718–24.
Odamaki T, Xiao JZ, Iwabuchi N, et al. Fluctuation of fecal microbiota in individuals with Japanese cedar pollinosis during the pollen season and influence of probiotic intake. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol 2007;17: 92–100.
Bartosch S, Fite A, Macfarlane GT, McMurdo ME . Characterization of bacterial communities in feces from healthy elderly volunteers and hospitalized elderly patients by using real-time PCR and effects of antibiotic treatment on the fecal microbiota. Appl Environ Microbiol 2004;70: 3575–81.
Matsuki T, Watanabe K, Fujimoto J, et al. Quantitative PCR with 16S rRNA-gene-targeted species-specific primers for analysis of human intestinal bifidobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 2004;70: 167–73.
Delroisse JM, Boulvin AL, Parmentier I, Dauphin RD, Vandenbol M, Portetelle D . Quantification of Bifidobacterium spp. and Lactobacillus spp. in rat fecal samples by real-time PCR. Microbiol Res 2008;163: 663–70.
Karlsson A, Jägervall A, Pettersson M, Andersson AK, Gillberg PG, Melgar S . Dextran sulphate sodium induces acute colitis and alters hepatic function in hamsters. Int Immunopharmacol 2008;8: 20–27.
Ritzka M, Stanke F, Jansen S, et al. The CLCA gene locus as a modulator of the gastrointestinal basic defect in cystic fibrosis. Hum Genet 2004;115: 483–91.
Te Velde AA, Pronk I, de Kort F, Stokkers PC . Glutathione peroxidase 2 and aquaporin 8 as new markers for colonic inflammation in experimental colitis and inflammatory bowel diseases: an important role for H2O2? Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2008;20: 555–60.
Dincer Y, Erzin Y, Himmetoglu S, Gunes KN, Bal K, Akcay T . Oxidative DNA damage and antioxidant activity in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Dig Dis Sci 2007;52: 1636–41.
Kruidenier L, Kuiper I, Van Duijn W, et al. Imbalanced secondary mucosal antioxidant response in inflammatory bowel disease. J Pathol 2003;201: 17–27.
Van Overtvelt L, Moussu H, Horiot S, et al. Lactic acid bacteria as adjuvants for sublingual allergy vaccines. Vaccine 2010;28: 2986–92.
Wall R, Ross RP, Shanahan F, et al. Metabolic activity of the enteric microbiota influences the fatty acid composition of murine and porcine liver and adipose tissues. Am J Clin Nutr 2009;89: 1393–401.
Ruemmele FM, Bier D, Marteau P, et al. Clinical evidence for immunomodulatory effects of probiotic bacteria. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2009;48: 126–41.
Shima T, Fukushima K, Setoyama H, et al. Differential effects of two probiotic strains with different bacteriological properties on intestinal gene expression, with special reference to indigenous bacteria. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 2008;52: 69–77.
Hoarau C, Lagaraine C, Martin L, Velge-Roussel F, Lebranchu Y . Supernatant of Bifidobacterium breve induces dendritic cell maturation, activation, and survival through a Toll-like receptor 2 pathway. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006;117: 696–702.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Yumiko Sakurai for her extended technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
H.I. and M.N. are employed by Morinaga Milk Industry Co., Ltd.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohtsuka, Y., Ikegami, T., Izumi, H. et al. Effects of Bifidobacterium breve on inflammatory gene expression in neonatal and weaning rat intestine. Pediatr Res 71, 46–53 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2011.11
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2011.11
This article is cited by
-
Microbial and immune faecal determinants in infants hospitalized with COVID-19 reflect bifidobacterial dysbiosis and immature intestinal immunity
European Journal of Pediatrics (2023)
-
Evaluation of Porcine Intestinal Epitheliocytes as an In vitro Immunoassay System for the Selection of Probiotic Bifidobacteria to Alleviate Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins (2021)
-
Effect of probiotic Bifidobacterium bifidum G9-1 on the relationship between gut microbiota profile and stress sensitivity in maternally separated rats
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Gene expression profiling in the intestinal mucosa of obese rats administered probiotic bacteria
Scientific Data (2017)
-
Adamdec1, Ednrb and Ptgs1/Cox1, inflammation genes upregulated in the intestinal mucosa of obese rats, are downregulated by three probiotic strains
Scientific Reports (2017)