Abstract
Introduction:
The Coulter LH780 hematology analyzer can evaluate mean neutrophil volume (MNV), conductivity (MNC), scatter (MNS), and distribution width (DW). We sought to investigate the value of volume, conductivity, and scatter (VCS) parameters in diagnosis and treatment efficacy of neonatal sepsis.
Results:
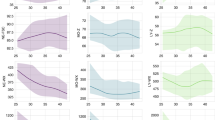
We observed significant increases in MNV, volume distribution width (VDW), conductivity distribution width (CDW), and significant decreases in MNC and MNS in septic newborns. There were significant decreases in MNV, VDW, and CDW, whereas MNC and MNS increased at the end of the treatment. Gram-negative sepsis caused higher MNV and VDW than Gram-positive sepsis.
Discussion:
This is the largest reported study seeking to determine cutoff levels of neutrophil VCS parameters in diagnosis of sepsis, and the first study in the evaluation of treatment efficacy and the effects of sepsis onset time and birth weight. We suggest that neutrophil VCS parameters and their DWs are useful both for early diagnosis and evaluation of treatment efficacy in neonatal sepsis without requirement for any extra blood collection.
Methods:
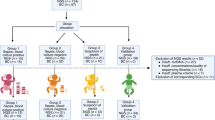
Peripheral blood samples from 304 newborns, 206 in group I (76 proven and 130 clinical sepsis) and 98 in group II (control group), were studied on diagnosis, 3rd day, and at the end of the treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Osrin D, Vergnano S, Costello A . Serious bacterial infections in newborn infants in developing countries. Curr Opin Infect Dis 2004;17: 217–24.
Gerdes JS . Diagnosis and management of bacterial infections in the neonate. Pediatr Clin North Am 2004;51: 939–59, viii–ix.
Khassawneh M, Hayajneh WA, Kofahi H, Khader Y, Amarin Z, Daoud A . Diagnostic markers for neonatal sepsis: comparing C-reactive protein, interleukin-6 and immunoglobulin M. Scand J Immunol 2007;65: 171–5.
Dilli D, Oguz SS, Dilmen U, Köker MY, Kizilgün M . Predictive values of neutrophil CD64 expression compared with interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein in early diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. J Clin Lab Anal 2010;24: 363–70.
Celik IH, Demirel FG, Uras N, et al. What are the cut-off levels for IL-6 and CRP in neonatal sepsis? J Clin Lab Anal 2010;24: 407–12.
Mathy KA, Koepke JA . The clinical usefulness of segmented vs. stab neutrophil criteria for differential leukocyte counts. Am J Clin Pathol 1974;61: 947–58.
Wenz B, Gennis P, Canova C, Burns ER . The clinical utility of the leukocyte differential in emergency medicine. Am J Clin Pathol 1986;86: 298–303.
Pierre RV . Peripheral blood film review. The demise of the eyecount leukocyte differential. Clin Lab Med 2002;22: 279–97.
Richardson-Jones A . An automated hematology instrument for comprehensive WBC, RBC, and platelet analysis. Am Clin Lab 1990;9: 18–22.
Krause JR . Automated differentials in the hematology laboratory. Am J Clin Pathol 1990;93(4 Suppl 1): S11–6.
Chaves F, Tierno B, Xu D . Quantitative determination of neutrophil VCS parameters by the Coulter automated hematology analyzer: new and reliable indicators for acute bacterial infection. Am J Clin Pathol 2005;124: 440–4.
Mardi D, Fwity B, Lobmann R, Ambrosch A . Mean cell volume of neutrophils and monocytes compared with C-reactive protein, interleukin-6 and white blood cell count for prediction of sepsis and nonsystemic bacterial infections. Int J Lab Hematol 2010;32: 410–8.
Raimondi F, Ferrara T, Capasso L, et al. Automated determination of neutrophil volume as screening test for late-onset sepsis in very low birth infants. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2010;29: 288.
Chaves F, Tierno B, Xu D . Neutrophil volume distribution width: a new automated hematologic parameter for acute infection. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2006;130: 378–80.
Lee JC, Ahern TP, Chaves FP, Quillen K . Utility of hematologic and volume, conductivity, and scatter parameters from umbilical cord blood in predicting chorioamnionitis. Int J Lab Hematol 2010;32: 351–9.
Koenig S, Quillen K . Using neutrophil and lymphocyte VCS indices in ambulatory pediatric patients presenting with fever. Int J Lab Hematol 2010;32: 449–51.
Abe R, Oda S, Sadahiro T, et al. Gram-negative bacteremia induces greater magnitude of inflammatory response than Gram-positive bacteremia. Crit Care 2010;14: R27.
Webb SA, Kahler CM . Bench-to-bedside review: bacterial virulence and subversion of host defences. Crit Care 2008;12: 234.
Haque KN . Definitions of bloodstream infection in the newborn. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2005;6(3 Suppl): S45–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
This study was accepted and presented as a poster presentation at the 24th International Society of Laboratory Hematology (ISLH) Congress, New Orleans, LA.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Celik, I., Demirel, G., Aksoy, H. et al. Automated determination of neutrophil VCS parameters in diagnosis and treatment efficacy of neonatal sepsis. Pediatr Res 71, 121–125 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2011.16
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2011.16
This article is cited by
-
Monocyte distribution width (MDW) and DECAF: two simple tools to determine the prognosis of severe COPD exacerbation
Internal and Emergency Medicine (2024)
-
Comparison of the diagnostic accuracy of monocyte distribution width and procalcitonin in sepsis cases in the emergency department: a prospective cohort study
BMC Infectious Diseases (2022)
-
Neutrophil Volume, conductivity and scatter (VCS) as a screening tool in neonatal sepsis
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Utility of neutrophil volume conductivity scatter (VCS) parameter changes as sepsis screen in neonates
Journal of Perinatology (2016)
-
Elevated mean neutrophil volume represents altered neutrophil composition and reflects damage after myocardial infarction
Basic Research in Cardiology (2015)