Abstract
Introduction:
Cerebral white-matter (WM) abnormalities on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) correlate with neurodevelopmental disability in infants born prematurely.
Results:
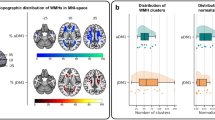
Quantitative histological measures of WM and ventricular volumes correlated with qualitative MRI scores of WM volume loss and ventriculomegaly. Diffuse astrocytosis was associated with signal abnormality on T2-weighted imaging and higher apparent diffusion coefficient in WM. Loss of oligodendrocytes was associated with lower relative anisotropy characterized by higher radial diffusivity values. The relationship between histopathology and MRI abnormalities was more pronounced in animals in the 28 d model, equivalent to the term human infant.
Discussion:
MRI reflects microstructural and anatomical abnormalities that are characteristic of WM injury in the preterm brain, and these changes are more evident on MRI at term-equivalent postmenstrual age.
Methods:
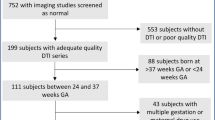
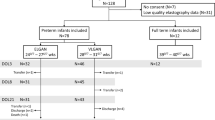
We assessed the histopathological correlates of MRI abnormalities in a baboon model of premature birth. Baboons were delivered at 125 d of gestation (dg, term ~185 dg) and maintained in an animal intensive care unit for 14 (n = 26) or 28 d (n = 17). Gestational control animals were delivered at 140 dg (n = 9) or 153 dg (n = 4). Cerebral WM in fixed brains was evaluated using MRI, diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), and histopathology.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Heron M, Sutton PD, Xu J, Ventura SJ, Strobino DM, Guyer B . Annual summary of vital statistics: 2007. Pediatrics 2010;125:4–15.
Moster D, Lie RT, Markestad T . Long-term medical and social consequences of preterm birth. N Engl J Med 2008;359:262–73.
Wilson-Costello D, Friedman H, Minich N, Fanaroff AA, Hack M . Improved survival rates with increased neurodevelopmental disability for extremely low birth weight infants in the 1990s. Pediatrics 2005;115:997–1003.
Drobyshevsky A, Bregman J, Storey P, et al. Serial diffusion tensor imaging detects white matter changes that correlate with motor outcome in premature infants. Dev Neurosci 2007;29:289–301.
Miller SP, Ferriero DM, Leonard C, et al. Early brain injury in premature newborns detected with magnetic resonance imaging is associated with adverse early neurodevelopmental outcome. J Pediatr 2005;147:609–16.
Woodward LJ, Anderson PJ, Austin NC, Howard K, Inder TE . Neonatal MRI to predict neurodevelopmental outcomes in preterm infants. N Engl J Med 2006;355:685–94.
Gilles FH, Murphy SF . Perinatal telencephalic leucoencephalopathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr 1969;32:404–13.
Haynes RL, Folkerth RD, Keefe RJ, et al. Nitrosative and oxidative injury to premyelinating oligodendrocytes in periventricular leukomalacia. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2003;62:441–50.
Marín-Padilla M . Developmental neuropathology and impact of perinatal brain damage. II: white matter lesions of the neocortex. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 1997;56:219–35.
Felderhoff-Mueser U, Rutherford MA, Squier WV, et al. Relationship between MR imaging and histopathologic findings of the brain in extremely sick preterm infants. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1999;20:1349–57.
Schouman-Claeys E, Henry-Feugeas MC, Roset F, et al. Periventricular leukomalacia: correlation between MR imaging and autopsy findings during the first 2 months of life. Radiology 1993;189:59–64.
Inder T, Huppi PS, Zientara GP, et al. Early detection of periventricular leukomalacia by diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging techniques. J Pediatr 1999;134:631–4.
Miller SP, Vigneron DB, Henry RG, et al. Serial quantitative diffusion tensor MRI of the premature brain: development in newborns with and without injury. J Magn Reson Imaging 2002;16:621–32.
Volpe JJ . Cerebral white matter injury of the premature infant-more common than you think. Pediatrics 2003;112(1 Pt 1):176–80.
Anjari M, Srinivasan L, Allsop JM, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging with tract-based spatial statistics reveals local white matter abnormalities in preterm infants. Neuroimage 2007;35:1021–7.
Cheong JL, Thompson DK, Wang HX, et al. Abnormal white matter signal on MR imaging is related to abnormal tissue microstructure. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2009;30:623–8.
Counsell SJ, Allsop JM, Harrison MC, et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging of the brain in preterm infants with focal and diffuse white matter abnormality. Pediatrics 2003;112(1 Pt 1):1–7.
Hüppi PS, Murphy B, Maier SE, et al. Microstructural brain development after perinatal cerebral white matter injury assessed by diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging. Pediatrics 2001;107:455–60.
Rose SE, Hatzigeorgiou X, Strudwick MW, Durbridge G, Davies PS, Colditz PB . Altered white matter diffusion anisotropy in normal and preterm infants at term-equivalent age. Magn Reson Med 2008;60:761–7.
Roelants-van Rijn AM, Nikkels PG, Groenendaal F, et al. Neonatal diffusion-weighted MR imaging: relation with histopathology or follow-up MR examination. Neuropediatrics 2001;32:286–94.
Guimiot F, Garel C, Fallet-Bianco C, et al. Contribution of diffusion-weighted imaging in the evaluation of diffuse white matter ischemic lesions in fetuses: correlations with fetopathologic findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2008;29:110–5.
Dieni S, Inder T, Yoder B, et al. The pattern of cerebral injury in a primate model of preterm birth and neonatal intensive care. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2004;63:1297–309.
Inder T, Neil J, Kroenke C, Dieni S, Yoder B, Rees S . Investigation of cerebral development and injury in the prematurely born primate by magnetic resonance imaging and histopathology. Dev Neurosci 2005;27:100–11.
Sun SW, Neil JJ, Song SK . Relative indices of water diffusion anisotropy are equivalent in live and formalin-fixed mouse brains. Magn Reson Med 2003;50:743–8.
Sun SW, Neil JJ, Liang HF, et al. Formalin fixation alters water diffusion coefficient magnitude but not anisotropy in infarcted brain. Magn Reson Med 2005;53:1447–51.
Inder TE, Wells SJ, Mogridge NB, Spencer C, Volpe JJ . Defining the nature of the cerebral abnormalities in the premature infant: a qualitative magnetic resonance imaging study. J Pediatr 2003;143:171–9.
Maalouf EF, Duggan PJ, Rutherford MA, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain in a cohort of extremely preterm infants. J Pediatr 1999;135:351–7.
Nguyen The Tich S, Anderson PJ, Shimony JS, Hunt RW, Doyle LW, Inder TE . A novel quantitative simple brain metric using MR imaging for preterm infants. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2009;30:125–31.
Loeliger M, Inder TE, Dalitz PA, et al. Developmental and neuropathological consequences of ductal ligation in the preterm baboon. Pediatr Res 2009;65:209–14.
Loeliger M, Inder TE, Shields A, et al. High-frequency oscillatory ventilation is not associated with increased risk of neuropathology compared with positive pressure ventilation: a preterm primate model. Pediatr Res 2009;66:545–50.
Rees SM, Camm EJ, Loeliger M, et al. Inhaled nitric oxide: effects on cerebral growth and injury in a baboon model of premature delivery. Pediatr Res 2007;61(5 Pt 1):552–8.
Budde MD, Kim JH, Liang HF, et al. Toward accurate diagnosis of white matter pathology using diffusion tensor imaging. Magn Reson Med 2007;57:688–95.
Back SA . Perinatal white matter injury: the changing spectrum of pathology and emerging insights into pathogenetic mechanisms. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev 2006;12:129–40.
Folkerth RD . The neuropathology of acquired pre- and perinatal brain injuries. Semin Diagn Pathol 2007;24:48–57.
McCurnin D, Seidner S, Chang LY, et al. Ibuprofen-induced patent ductus arteriosus closure: physiologic, histologic, and biochemical effects on the premature lung. Pediatrics 2008;121:945–56.
McCurnin DC, Pierce RA, Willis BC, et al. Postnatal estradiol up-regulates lung nitric oxide synthases and improves lung function in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2009;179:492–500.
Thomson MA, Yoder BA, Winter VT, Giavedoni L, Chang LY, Coalson JJ . Delayed extubation to nasal continuous positive airway pressure in the immature baboon model of bronchopulmonary dysplasia: lung clinical and pathological findings. Pediatrics 2006;118:2038–50.
Yoder BA, Siler-Khodr T, Winter VT, Coalson JJ . High-frequency oscillatory ventilation: effects on lung function, mechanics, and airway cytokines in the immature baboon model for neonatal chronic lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000;162:1867–76.
Loeliger M, Inder T, Cain S, et al. Cerebral outcomes in a preterm baboon model of early versus delayed nasal continuous positive airway pressure. Pediatrics 2006;118:1640–53.
Loeliger M, Shields A, McCurnin D, et al. Ibuprofen treatment for closure of patent ductus arteriosus is not associated with increased risk of neuropathology. Pediatr Res 2010;68:298–302.
Kroenke CD, Bretthorst GL, Inder TE, Neil JJ . Modeling water diffusion anisotropy within fixed newborn primate brain using Bayesian probability theory. Magn Reson Med 2006;55:187–97.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Michelle Loeliger and Chris Kroenke for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Griffith, J., Shimony, J., Cousins, S. et al. MR imaging correlates of white-matter pathology in a preterm baboon model. Pediatr Res 71, 185–191 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2011.33
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2011.33
This article is cited by
-
Early neuropathological and neurobehavioral consequences of preterm birth in a rabbit model
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
White matter injury in the preterm infant: pathology and mechanisms
Acta Neuropathologica (2017)
-
Moderate and late preterm infants exhibit widespread brain white matter microstructure alterations at term-equivalent age relative to term-born controls
Brain Imaging and Behavior (2016)
-
Differential vulnerability of white matter structures to experimental infantile hydrocephalus detected by diffusion tensor imaging
Child's Nervous System (2014)
-
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy markers of axons and astrogliosis in relation to specific features of white matter injury in preterm infants
Neuroradiology (2014)