Abstract
Background:
Thyrosulfoconjugation appears to facilitate fetal-to-maternal transfer of 3,3′-diiodothyronine-sulfate (T2S). Elevated maternal levels of T2S cross-reactive material (compound W) are found in humans, with higher levels found in venous cord blood than in arterial samples. These findings are consistent with the postulate that the placenta plays an essential role in compound W production.
Methods:
Serum compound W levels were measured by a T2S-specific radioimmunoassay in 60 serum samples from newborns with hyperbilirubinemia, age 1–30 d. In addition, 59 maternal serum samples, from day 1 to day 7 after uneventful deliveries, were studied.
Results:
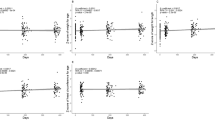
As compared with day 1, at day 5, the mean (±SE) compound W level fell to 43.5 ± 6.8% (decay half-life (t1/2) = 4.12 d) and to 33.7 ± 4.6% (decay t1/2 = 2.82 d) in the newborn and maternal groups, respectively. In the mothers, the level continued to decline along the same slope through day 7. In the newborns, however, the mean compound W level entered a slower phase of decay after the fifth day with a decay t1/2 = 10.9 d.
Conclusion:
Compound W is cleared at similar rates in newborn and postpartum maternal sera. This is consistent with the postulate that compound W is produced in the placenta.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Burrow GN, Fisher DA, Larsen PR . Maternal and fetal thyroid function. N Engl J Med 1994;331:1072–8.
Polk DH, Reviczky A, Wu SY, Huang WS, Fisher DA . Metabolism of sulfoconjugated thyroid hormone derivatives in developing sheep. Am J Physiol 1994;266(6 Pt 1):E892–6.
Wu SY, Green WL, Huang WS, Hays MT, Chopra IJ . Alternate pathways of thyroid hormone metabolism. Thyroid 2005;15:943–58.
Wu SY, Polk DH, Chen WL, Fisher DA, Huang WS, Yee B . A 3,3′-diiodothyronine sulfate cross-reactive compound in serum from pregnant women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1994;78:1505–9.
Wu SY, Huang WS, Ho E, Wu ES, Fisher DA . Compound W, a 3,3′-diiodothyronine sulfate cross-reactive substance in serum from pregnant women–a potential marker for fetal thyroid function. Pediatr Res 2007;61:307–12.
Wu SY, Fisher DA, Huang WS, Kuo SW, Chen WL . The changes of urinary compound W concentrations in pregnant women. Am J Obst Gynecol 1998;178:886–91.
Cortelazzi D, Morpurgo PS, Azmperini P, Fisher DA, Beck-Peccoz P, Wu SY . Fetal hypothyroidism: new diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Europ J Endocrinol 1999;141:570–8.
Haddow JE, Palomaki GE, Allan WC, et al. Maternal thyroid deficiency during pregnancy and subsequent neuropsychological development of the child. N Engl J Med 1999;341:549–55.
Casey BM, Dashe JS, Wells CE, et al. Subclinical hypothyroidism and pregnancy outcomes. Obstet Gynecol 2005;105:239–45.
Milanesi A, Brent GA . Management of hypothyroidism in pregnancy. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 2011;18:304–9.
Momotani N, Iwama S, Momotani K . Neurodevelopment in children born to hypothyroid mothers restored to normal thyroxine (T4) concentration by late pregnancy in Japan: no apparent influence of maternal T4 deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2012;97:1104–8.
Vanmiddlesworth L, Vanmiddlesworth NR, Egerman RS, et al. Thyroid function and 3,3’-diiodothyronine sulfate cross-reactive substance (compound W) in maternal hyperthyroidism with antithyroid treatment. Endocr Pract 2011;17:170–6.
Daffos F . Fetal blood sampling. Annu Rev Med 1989;40:319–29.
Luton D, Le Gac I, Vuillard E, et al. Management of Graves’ disease during pregnancy: the key role of fetal thyroid gland monitoring. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005;90:6093–8.
Eelkman Rooda SJ, Kaptein E, van Loon MA, Visser TJ . Development of a radioimmunoassay for triiodothyronine sulfate. J Immunoassay 1988;9:125–34.
Mol JA, Visser TJ . Synthesis and some properties of sulfate esters and sulfamates of iodothyronines. Endocrinology 1985;117:1–7.
Chen XX, Qin YF, Zhou XL, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of subclinical hypothyroidism detected by neonatal screening. World J Pediatr 2011;7:350–4.
Kirk RE . Experimental Design. Belmont, CA: Brooks/Cole, 1982:112–4.
Zar JH . Biostatistical Analysis. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1984:306–68.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, D., Yu, H., Bao, J. et al. 3,3′-Diiodothyronine sulfate cross-reactive material (compound W) in human newborns. Pediatr Res 72, 521–524 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2012.116
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2012.116