Abstract
Background:
In preterm infants, low levels of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and IGF binding protein 3 (IGFBP-3) are associated with impaired brain growth and retinopathy of prematurity (ROP). Treatment with IGF-I/IGFBP-3 may be beneficial for brain development and may decrease the prevalence of ROP.
Methods:
In a phase II pharmacokinetics and safety study, five infants (three girls) with a median (range) gestational age (GA) of 26 wk + 6 d (26 wk + 0 d to 27 wk + 2 d) and birth weight of 990 (900–1,212) g received continuous intravenous infusion of recombinant human (rh)IGF-I/rhIGFBP-3. Treatment was initiated during the first postnatal day and continued for a median (range) duration of 168 (47–168) h in dosages between 21 and 111 µg/kg/24 h.
Results:
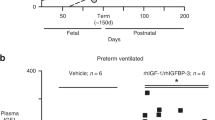
Treatment with rhIGF-I/rhIGFBP-3 was associated with higher serum IGF-I and IGFBP-3 concentrations (P < 0.001) than model-predicted endogenous levels. Of 74 IGF-I samples measured during study drug infusion, 37 (50%) were within the target range, 4 (5%) were above, and 33 (45%) were below. The predicted dose of rhIGF-I/rhIGFBP-3 required to establish circulating levels of IGF-I within the intrauterine range in a 1,000 g infant was 75–100 µg/kg/24 h. No hypoglycemia or other adverse effects were recorded.
Conclusion:
In this study, continuous intravenous infusion of rhIGF-I/rhIGFBP-3 was effective in increasing serum concentrations of IGF-I and IGFBP-3, and was found to be safe.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Gluckman PD . Clinical review 68: the endocrine regulation of fetal growth in late gestation: the role of insulin-like growth factors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1995;80:1047–50.
Netchine I, Azzi S, Le Bouc Y, Savage MO . IGF1 molecular anomalies demonstrate its critical role in fetal, postnatal growth and brain development. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2011;25:181–90.
Ashton IK, Zapf J, Einschenk I, MacKenzie IZ . Insulin-like growth factors (IGF) 1 and 2 in human foetal plasma and relationship to gestational age and foetal size during midpregnancy. Acta Endocrinol 1985;110:558–63.
Lassarre C, Hardouin S, Daffos F, Forestier F, Frankenne F, Binoux M . Serum insulin-like growth factors and insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in the human fetus. Relationships with growth in normal subjects and in subjects with intrauterine growth retardation. Pediatr Res 1991;29:219–25.
Hansen-Pupp I, Hellström-Westas L, Cilio CM, Andersson S, Fellman V, Ley D . Inflammation at birth and the insulin-like growth factor system in very preterm infants. Acta Paediatr 2007;96:830–6.
Langford K, Nicolaides K, Miell JP . Maternal and fetal insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins in the second and third trimesters of human pregnancy. Hum Reprod 1998;13:1389–93.
Hellström A, Engström E, Hård AL, et al. Postnatal serum insulin-like growth factor I deficiency is associated with retinopathy of prematurity and other complications of premature birth. Pediatrics 2003;112:1016–20.
Löfqvist C, Engström E, Sigurdsson J, et al. Postnatal head growth deficit among premature infants parallels retinopathy of prematurity and insulin-like growth factor-1 deficit. Pediatrics 2006;117:1930–8.
Holly J, Perks C . The role of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins. Neuroendocrinology 2006;83:154–60.
Lofqvist C, Chen J, Connor KM, et al. IGFBP3 suppresses retinopathy through suppression of oxygen-induced vessel loss and promotion of vascular regrowth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007;104:10589–94.
Hansen-Pupp I, Engström E, Niklasson A, et al. Fresh-frozen plasma as a source of exogenous insulin-like growth factor-I in the extremely preterm infant. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2009;94:477–82.
Löfqvist C, Niklasson A, Engström E, et al. A pharmacokinetic and dosing study of intravenous insulin-like growth factor-I and IGF-binding protein-3 complex to preterm infants. Pediatr Res 2009;65:574–9.
Mizuno N, Kato Y, Iwamoto M, et al. Kinetic analysis of the disposition of insulin-like growth factor 1 in healthy volunteers. Pharm Res 2001;18:1203–9.
Guler HP, Zapf J, Schmid C, Froesch ER . Insulin-like growth factors I and II in healthy man. Estimations of half-lives and production rates. Acta Endocrinol 1989;121:753–8.
Grahnén A, Kastrup K, Heinrich U, et al. Pharmacokinetics of recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I given subcutaneously to healthy volunteers and to patients with growth hormone receptor deficiency. Acta Paediatr Suppl 1993;82:suppl 391:9–13; discussion 14.
Camacho-Hübner C, Rose S, Preece MA, et al. Pharmacokinetic studies of recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I (rhIGF-I)/rhIGF-binding protein-3 complex administered to patients with growth hormone insensitivity syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006;91:1246–53.
Beardsall K, Vanhaesebrouck S, Ogilvy-Stuart AL, et al. A randomised controlled trial of early insulin therapy in very low birth weight infants, “NIRTURE” (neonatal insulin replacement therapy in Europe). BMC Pediatr 2007;7:29.
Boisclair YR, Rhoads RP, Ueki I, Wang J, Ooi GT . The acid-labile subunit (ALS) of the 150 kDa IGF-binding protein complex: an important but forgotten component of the circulating IGF system. J Endocrinol 2001;170:63–70.
Lewitt MS, Scott FP, Clarke NM, Baxter RC . Developmental regulation of circulating insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins in normal pregnancies and in pre-eclampsia. Prog Growth Factor Res 1995;6:475–80.
Herndon DN, Ramzy PI, DebRoy MA, et al. Muscle protein catabolism after severe burn: effects of IGF-1/IGFBP-3 treatment. Ann Surg 1999;229:713–20; discussion 720–2.
Beardsall K, Ogilvy-Stuart AL, Frystyk J, et al. Early elective insulin therapy can reduce hyperglycemia and increase insulin-like growth factor-I levels in very low birth weight infants. J Pediatr 2007;151:611–7, 617.e1.
Hikino S, Ihara K, Yamamoto J, et al. Physical growth and retinopathy in preterm infants: involvement of IGF-I and GH. Pediatr Res 2001;50:732–6.
Hansen-Pupp I, Löfqvist C, Polberger S, et al. Influence of insulin-like growth factor I and nutrition during phases of postnatal growth in very preterm infants. Pediatr Res 2011;69(5 Pt 1):448–53.
Fryburg DA, Jahn LA, Hill SA, Oliveras DM, Barrett EJ . Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I enhance human skeletal muscle protein anabolism during hyperaminoacidemia by different mechanisms. J Clin Invest 1995;96:1722–9.
Kaempf JW, Kaempf AJ, Wu Y, Stawarz M, Niemeyer J, Grunkemeier G . Hyperglycemia, insulin and slower growth velocity may increase the risk of retinopathy of prematurity. J Perinatol 2011;31:251–7.
Hansen-Pupp I, Hövel H, Hellström A, et al. Postnatal decrease in circulating insulin-like growth factor-I and low brain volumes in very preterm infants. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2011;96:1129–35.
Vanhaesebrouck S, Daniëls H, Moons L, Vanhole C, Carmeliet P, De Zegher F . Oxygen-induced retinopathy in mice: amplification by neonatal IGF-I deficit and attenuation by IGF-I administration. Pediatr Res 2009;65:307–10.
Marsál K, Persson PH, Larsen T, Lilja H, Selbing A, Sultan B . Intrauterine growth curves based on ultrasonically estimated foetal weights. Acta Paediatr 1996;85:843–8.
Niklasson A, Albertsson-Wikland K . Continuous growth reference from 24th week of gestation to 24 months by gender. BMC Pediatr 2008;8:8.
Blum WF, Breier BH . Radioimmunoassays for IGFs and IGFBPs. Growth Regul 1994;4:Suppl 1:11–9.
Beal S, Sheiner LB, Boeckmann, AJ . 1989–2006 NONMEM Users Guides. Ellicott City, Maryland: Icon Development Solutions, 1989–2006.
Anderson BJ, Holford NH . Mechanism-based concepts of size and maturity in pharmacokinetics. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2008;48:303–32.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Ann-Cathrine Berg and Eva Hammarstrand for their assistance in clinical data collection and Lisbeth Larsson for her assistance in analyzing the IGF-I and IGFBP-3 samples. Clinical trial registration number: NCT01096784.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ley, D., Hansen-Pupp, I., Niklasson, A. et al. Longitudinal infusion of a complex of insulin-like growth factor-I and IGF-binding protein-3 in five preterm infants: pharmacokinetics and short-term safety. Pediatr Res 73, 68–74 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2012.146
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2012.146
This article is cited by
-
Evaluation of recombinant human IGF-1/IGFBP-3 on intraventricular hemorrhage prevention and survival in the preterm rabbit pup model
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Short- and long-term effects of nutritional state on IGF-1 levels in nestlings of a wild passerine
Oecologia (2023)
-
Metabolic-endocrine disruption due to preterm birth impacts growth, body composition, and neonatal outcome
Pediatric Research (2022)
-
Preventing bronchopulmonary dysplasia: new tools for an old challenge
Pediatric Research (2019)
-
Development and verification of a pharmacokinetic model to optimize physiologic replacement of rhIGF-1/rhIGFBP-3 in preterm infants
Pediatric Research (2017)