Abstract
Introduction:
Protein intake in fetal life or infancy may play a key role in determining early growth rate, a determinant of later health and disease. Previous work has indicated that hair isotopic composition is influenced by diet and protein intake.
Methods:
This study analyzes the isotopic composition of hair obtained from 239 mother/newborn pairs randomly selected within a larger cohort enrolled in a study of pre- and postnatal determinants of the child’s development and health. The isotopic compositions in nitrogen (δ15N) and in carbon (δ13C) were determined by isotope ratio mass spectrometry.
Results:
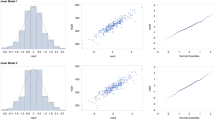
Mother and newborn hair δ15N were tightly correlated (Pearson r = 0.88). The mean δ15N and δ13C values of hair from newborn infants were significantly higher than those for the mothers: 9.7 ± 0.7 vs. 8.8 ± 0.6‰ (P < 0.0001) for δ15N and −20.0 ± 0.4 vs. −20.4 ± 0.4‰ (P < 0.0001) for δ13C. Maternal hair δ15N at parturition was slightly and positively correlated with estimates of protein intake (r = 0.14, P = 0.04).
Discussion:
Hair δ15N of the fetus is both highly dependent on and systematically higher than that of the mother. Whether quantitative and qualitative protein intake, disease, or hormonal status alter hair δ15N at birth remains to be determined.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Barker DJ, Winter PD, Osmond C, Margetts B, Simmonds SJ . Weight in infancy and death from ischaemicheart disease. Lancet 1989;2:577–80.
Barker DJ, Osmond C, Forsén TJ, Kajantie E, Eriksson JG . Trajectories of growth among children who have coronary events as adults. N Engl J Med 2005;353:1802–9.
Rolland-Cachera MF, Deheeger M, Akrout M, Bellisle F . Influence of macronutrients on adiposity development: a follow up study of nutrition and growth from 10 months to 8 years of age. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1995;19:573–8.
Günther AL, Buyken AE, Kroke A . The influence of habitual protein intake in early childhood on BMI and age at adiposity rebound: results from the DONALD Study. Int J Obes (Lond) 2006;30:1072–9.
Koletzko B, von Kries R, Closa R, et al.; European Childhood Obesity Trial Study Group. Lower protein in infant formula is associated with lower weight up to age 2 y: a randomized clinical trial. Am J Clin Nutr 2009;89:1836–45.
Ozanne SE, Hales CN . Lifespan: catch-up growth and obesity in male mice. Nature 2004;427:411–2.
Daenzer M, Ortmann S, Klaus S, Metges CC . Prenatal high protein exposure decreases energy expenditure and increases adiposity in young rats. J Nutr 2002;132:142–4.
Jansson N, Pettersson J, Haafiz A, et al. Down-regulation of placental transport of amino acids precedes the development of intrauterine growth restriction in rats fed a low protein diet. J Physiol (Lond) 2006;576(Pt 3):935–46.
Cetin I, Ronzoni S, Marconi AM, et al. Maternal concentrations and fetal-maternal concentration differences of plasma amino acids in normal and intrauterine growth-restricted pregnancies. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996;174:1575–83.
Paolini CL, Marconi AM, Ronzoni S, et al. Placental transport of leucine, phenylalanine, glycine, and proline in intrauterine growth-restricted pregnancies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001;86:5427–32.
Marconi AM, Paolini CL, Stramare L, et al. Steady state maternal-fetal leucine enrichments in normal and intrauterine growth-restricted pregnancies. Pediatr Res 1999;46:114–9.
Ravelli AC, van der Meulen JH, Michels RP, et al. Glucose tolerance in adults after prenatal exposure to famine. Lancet 1998;351:173–7.
Gluckman PD, Hanson MA, Cooper C, Thornburg KL . Effect of in utero and early-life conditions on adult health and disease. N Engl J Med 2008;359:61–73.
Lillycrop KA, Phillips ES, Jackson AA, Hanson MA, Burdge GC . Dietary protein restriction of pregnant rats induces and folic acid supplementation prevents epigenetic modification of hepatic gene expression in the offspring. J Nutr 2005;135:1382–6.
Petzke KJ, Boeing H, Klaus S, Metges CC . Carbon and nitrogen stable isotopic composition of hair protein and amino acids can be used as biomarkers for animal-derived dietary protein intake in humans. J Nutr 2005;135:1515–20.
Petzke KJ, Fuller BT, Metges CC . Advances in natural stable isotope ratio analysis of human hair to determine nutritional and metabolic status. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 2010;13:532–40.
Fuller BT, Fuller JL, Sage NE, Harris DA, O’Connell TC, Hedges RE . Nitrogen balance and delta15N: why you’re not what you eat during pregnancy. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 2004;18:2889–96.
Fuller BT, Fuller JL, Harris DA, Hedges RE . Detection of breastfeeding and weaning in modern human infants with carbon and nitrogen stable isotope ratios. Am J Phys Anthropol 2006;129:279–93.
Macko SA, Fogel Estep ML, Engel MH, Hare PE . Kinetic fractionation of stable nitrogen isotopes during amino acid transamination. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 1986;50:2143–6.
Denne SC, Karn CA, Liechty EA . Leucine kinetics after a brief fast and in response to feeding in premature infants. Am J Clin Nutr 1992;56:899–904.
Beaufrere B, Putet G, Pachiaudi C, Salle B . Whole body protein turnover measured with 13C-leucine and energy expenditure in preterm infants. Pediatr Res 1990;28:147–52.
Hankard R, Goulet O, Ricour C, Rongier M, Colomb V, Darmaun D . Glutamine metabolism in children with short-bowel syndrome: a stable isotope study. Pediatr Res 1994;36:202–6.
des Robert C, Le Bacquer O, Piloquet H, Rozé JC, Darmaun D . Acute effects of intravenous glutamine supplementation on protein metabolism in very low birth weight infants: a stable isotope study. Pediatr Res 2002;51:87–93.
Hankard RG, Haymond MW, Darmaun D . Effect of glutamine on leucine metabolism in humans. Am J Physiol 1996;271(4 Pt 1):E748–54.
McClelland IS, Persaud C, Jackson AA . Urea kinetics in healthy women during normal pregnancy. Br J Nutr 1997;77:165–81.
Mojtahedi M, de Groot LC, Boekholt HA, van Raaij JM . Nitrogen balance of healthy Dutch women before and during pregnancy. Am J Clin Nutr 2002;75:1078–83.
Kalhan SC . Protein metabolism in pregnancy. Am J Clin Nutr 2000;71:Suppl 5:1249S–55S.
Hatch KA, Crawford MA, Kunz AW, et al. An objective means of diagnosing anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa using 15N/14N and 13C/12C ratios in hair. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 2006;20:3367–73.
Petzke KJ, Feist T, Fleig WE, Metges CC . Nitrogen isotopic composition in hair protein is different in liver cirrhotic patients. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 2006;20:2973–8.
Antonow-Schlorke I, Schwab M, Cox LA, et al. Vulnerability of the fetal primate brain to moderate reduction in maternal global nutrient availability. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011;108:3011–6.
Andreasyan K, Ponsonby AL, Dwyer T, et al. Higher maternal dietary protein intake in late pregnancy is associated with a lower infant ponderal index at birth. Eur J Clin Nutr 2007;61:498–508.
Mok E, Multon C, Piguel L, et al. Decreased full breastfeeding, altered practices, perceptions, and infant weight change of prepregnant obese women: a need for extra support. Pediatrics 2008;121:e1319–24.
de Lauzon B, Romon M, Deschamps V, et al.; Fleurbaix Laventie Ville Sante Study Group. The Three-Factor Eating Questionnaire-R18 is able to distinguish among different eating patterns in a general population. J Nutr 2004;134:2372–80.
Deschamps V, de Lauzon-Guillain B, Lafay L, Borys JM, Charles MA, Romon M . Reproducibility and relative validity of a food-frequency questionnaire among French adults and adolescents. Eur J Clin Nutr 2009;63:282–91.
Hercberg S, Galan P, Preziosi P, et al. Background and rationale behind the SU.VI.MAX Study, a prevention trial using nutritional doses of a combination of antioxidant vitamins and minerals to reduce cardiovascular diseases and cancers. SUpplementation en VItamines et Minéraux AntioXydants Study. Int J Vitam Nutr Res 1998;68:3–20.
Mamelle N, Munoz F, Grandjean H . [Fetal growth from the AUDIPOG study. I. Establishment of reference curves]. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris) 1996;25(1):61–70.
Acknowledgements
We thank all members of the EDEN mother–child study group for their invaluable input to this study. We give special thanks to Dominique Darmaun for his helpful and critical comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Luca, A., Boisseau, N., Tea, I. et al. δ15N and δ13C in hair from newborn infants and their mothers: a cohort study. Pediatr Res 71, 598–604 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2012.3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2012.3
This article is cited by
-
Isotopic analysis of formula milk reveals potential challenges in geolocating bottle-fed babies
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Early life histories at medieval Mikulčice (ninth–tenth centuries AD, Czechia) based on carbon and nitrogen profiles of tooth dentine
Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences (2024)
-
A multi-isotope analysis of Neolithic human groups in the Yonne valley, Northern France: insights into dietary patterns and social structure
Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences (2019)
-
A Multidisciplinary Approach to Neolithic Life Reconstruction
Journal of Archaeological Method and Theory (2019)
-
Isotopic evidence for the reconstruction of diet and mobility during village formation in the Early Middle Ages: Las Gobas (Burgos, northern Spain)
Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences (2018)