Abstract
Introduction:
Objective biomarkers are needed to assess neuroprotective therapies after perinatal hypoxic–ischemic encephalopathy (HIE). We tested the hypothesis that, in infants who underwent therapeutic hypothermia after perinatal HIE, neurodevelopmental performance was predicted by fractional anisotropy (FA) values in the white matter (WM) on early diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) as assessed by means of tract-based spatial statistics (TBSS).
Methods:
We studied 43 term infants with HIE. Developmental assessments were carried out at a median (range) age of 24 (12–28) mo.
Results:
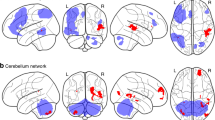
As compared with infants with favorable outcomes, those with unfavorable outcomes had significantly lower FA values (P < 0.05) in the centrum semiovale, corpus callosum (CC), anterior and posterior limbs of the internal capsule, external capsules, fornix, cingulum, cerebral peduncles, optic radiations, and inferior longitudinal fasciculus. In a second analysis in 32 assessable infants, the Griffiths Mental Development Scales (Revised) (GMDS-R) showed a significant linear correlation (P < 0.05) between FA values and developmental quotient (DQ) and all its component subscale scores.
Discussion:
DTI analyzed by TBSS provides a qualified biomarker that can be used to assess the efficacy of additional neuroprotective therapies after HIE.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Himmelmann K, Hagberg G, Beckung E, Hagberg B, Uvebrant P . The changing panorama of cerebral palsy in Sweden. IX. Prevalence and origin in the birth-year period 1995-1998. Acta Paediatr 2005;94:287–94.
Edwards AD, Brocklehurst P, Gunn AJ, et al. Neurological outcomes at 18 months of age after moderate hypothermia for perinatal hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy: synthesis and meta-analysis of trial data. BMJ 2010;340:c363.
Ma D, Hossain M, Chow A, et al. Xenon and hypothermia combine to provide neuroprotection from neonatal asphyxia. Ann Neurol 2005;58:182–93.
Martin JL, Ma D, Hossain M, et al. Asynchronous administration of xenon and hypothermia significantly reduces brain infarction in the neonatal rat. Br J Anaesth 2007;98:236–40.
Zhu C, Kang W, Xu F, et al. Erythropoietin improved neurologic outcomes in newborns with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatrics 2009;124:e218–26.
Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Johansen-Berg H, et al. Tract-based spatial statistics: voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. Neuroimage 2006;31:1487–505.
Porter EJ, Counsell SJ, Edwards AD, Allsop J, Azzopardi D . Tract-based spatial statistics of magnetic resonance images to assess disease and treatment effects in perinatal asphyxial encephalopathy. Pediatr Res 2010;68:205–9.
Thompson CM, Puterman AS, Linley LL, et al. The value of a scoring system for hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy in predicting neurodevelopmental outcome. Acta Paediatr 1997;86:757–61.
Rutherford M, Pennock J, Schwieso J, Cowan F, Dubowitz L . Hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy: early and late magnetic resonance imaging findings in relation to outcome. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 1996;75:F145–51.
Martinez-Biarge M, Diez-Sebastian J, Kapellou O, et al. Predicting motor outcome and death in term hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Neurology 2011;76:2055–61.
Rutherford M, Ramenghi LA, Edwards AD, et al. Assessment of brain tissue injury after moderate hypothermia in neonates with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy: a nested substudy of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 2010;9:39–45.
Gonzalez FF, Miller SP . Does perinatal asphyxia impair cognitive function without cerebral palsy? Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2006;91:F454–9.
de Vries LS, Jongmans MJ . Long-term outcome after neonatal hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2010;95:F220–4.
Robertson CM, Finer NN, Grace MG . School performance of survivors of neonatal encephalopathy associated with birth asphyxia at term. J Pediatr 1989;114:753–60.
Marlow N, Rose AS, Rands CE, Draper ES . Neuropsychological and educational problems at school age associated with neonatal encephalopathy. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2005;90:F380–7.
Gadian DG, Aicardi J, Watkins KE, Porter DA, Mishkin M, Vargha-Khadem F . Developmental amnesia associated with early hypoxic-ischaemic injury. Brain 2000;123:Pt 3:499–507.
Mañeru C, Junqué C, Botet F, Tallada M, Guardia J . Neuropsychological long-term sequelae of perinatal asphyxia. Brain Inj 2001;15:1029–39.
McKinstry RC, Miller JH, Snyder AZ, et al. A prospective, longitudinal diffusion tensor imaging study of brain injury in newborns. Neurology 2002;59:824–33.
Winter JD, Lee DS, Hung RM, et al. Apparent diffusion coefficient pseudonormalization time in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatr Neurol 2007;37:255–62.
Rutherford M, Counsell S, Allsop J, et al. Diffusion weighted MR imaging in term perinatal brain injury: a comparison with site of lesion and time from birth. J Pediatr 2004;114:1004–14.
Hunt RW, Neil JJ, Coleman LT, Kean MJ, Inder TE . Apparent diffusion coefficient in the posterior limb of the internal capsule predicts outcome after perinatal asphyxia. Pediatrics 2004;114:999–1003.
Liauw L, van Wezel-Meijler G, Veen S, van Buchem MA, van der Grond J . Do apparent diffusion coefficient measurements predict outcome in children with neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2009;30:264–70.
Wolf RL, Zimmerman RA, Clancy R, Haselgrove JH . Quantitative apparent diffusion coefficient measurements in term neonates for early detection of hypoxic-ischemic brain injury: initial experience. Radiology 2001;218:825–33.
Vermeulen RJ, van Schie PE, Hendrikx L, et al. Diffusion-weighted and conventional MR imaging in neonatal hypoxic ischemia: two-year follow-up study. Radiology 2008;249:631–9.
Twomey E, Twomey A, Ryan S, Murphy J, Donoghue VB . MR imaging of term infants with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy as a predictor of neurodevelopmental outcome and late MRI appearances. Pediatr Radiol 2010;40:1526–35.
Brissaud O, Amirault M, Villega F, Periot O, Chateil JF, Allard M . Efficiency of fractional anisotropy and apparent diffusion coefficient on diffusion tensor imaging in prognosis of neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: a methodologic prospective pilot study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2010;31:282–7.
Thayyil S, Chandrasekaran M, Taylor A, et al. Cerebral magnetic resonance biomarkers in neonatal encephalopathy: a meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2010;125:e382–95.
Ward P, Counsell S, Allsop J, et al. Reduced fractional anisotropy on diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging after hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatrics 2006;117:e619–30.
Malik GK, Trivedi R, Gupta RK, et al. Serial quantitative diffusion tensor MRI of the term neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE). Neuropediatrics 2006;37:337–43.
Aralasmak A, Ulmer JL, Kocak M, Salvan CV, Hillis AE, Yousem DM . Association, commissural, and projection pathways and their functional deficit reported in literature. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2006;30:695–715.
Nagy Z, Lindström K, Westerberg H, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging on teenagers, born at term with moderate hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatr Res 2005;58:936–40.
Ramaswamy V, Miller SP, Barkovich AJ, Partridge JC, Ferriero DM . Perinatal stroke in term infants with neonatal encephalopathy. Neurology 2004;62:2088–91.
Schulzke SM, Rao S, Patole SK . A systematic review of cooling for neuroprotection in neonates with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy – are we there yet? BMC Pediatr 2007;7:30.
Jacobs S, Hunt R, Tarnow-Mordi W, Inder T, Davis P . Cooling for newborns with hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2007:CD003311.
Azzopardi D, Edwards AD . Magnetic resonance biomarkers of neuroprotective effects in infants with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 2010;15:261–9.
Azzopardi DV, Strohm B, Edwards AD, et al. Moderate hypothermia to treat perinatal asphyxial encephalopathy. N Engl J Med 2009;361:1349–58.
Haataja L, Mercuri E, Regev R, et al. Optimality score for the neurologic examination of the infant at 12 and 18 months of age. J Pediatr 1999;135:2 Pt 1:153–61.
Haataja L, Mercuri E, Guzzetta A, et al. Neurologic examination in infants with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy at age 9 to 14 months: use of optimality scores and correlation with magnetic resonance imaging findings. J Pediatr 2001;138:332–7.
Huntley M . The Griffiths Mental Development Scales: From Birth to 2 years. Association for Research in Infant and Child Development (ARICD). Oxford, UK: The Test Agency, 1996:5–39.
Cans C . Surveillance of Cerebral Palsy in Europe: a collaboration of cerebral palsy surveys and registers. Dev Med Child Neurol 2000;42:816–24.
Gorter JW, Ketelaar M, Rosenbaum P, Helders PJ, Palisano R . Use of the GMFCS in infants with CP: the need for reclassification at age 2 years or older. Dev Med Child Neurol 2009;51:46–52.
Ball G, Counsell SJ, Anjari M, et al. An optimised tract-based spatial statistics protocol for neonates: applications to prematurity and chronic lung disease. Neuroimage 2010;53:94–102.
Acknowledgements
We thank the families who took part in the study and our colleagues in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit and the Children’s Ambulatory Unit at the Hammersmith Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tusor, N., Wusthoff, C., Smee, N. et al. Prediction of neurodevelopmental outcome after hypoxic–ischemic encephalopathy treated with hypothermia by diffusion tensor imaging analyzed using tract-based spatial statistics. Pediatr Res 72, 63–69 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2012.40
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2012.40
This article is cited by
-
Diffusion kurtosis imaging and diffusion weighted imaging comparison in diagnosis of early hypoxic–ischemic brain edema
European Journal of Medical Research (2023)
-
Cerebral injuries in neonatal encephalopathy treated with hypothermia: French LyTONEPAL cohort
Pediatric Research (2022)
-
Communication skills in children aged 6–8 years, without cerebral palsy cooled for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Neonatal encephalopathy prediction of poor outcome with diffusion-weighted imaging connectome and fixel-based analysis
Pediatric Research (2022)
-
Diffusion restriction in the corticospinal tract and the corpus callosum of term neonates with hypoxic–ischemic encephalopathy
Pediatric Radiology (2022)