Abstract
Background:
Arterial spin labeling (ASL) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can evaluate brain perfusion in neonates noninvasively. The aim of this study was to investigate whether ASL MRI can demonstrate perfusion abnormalities in neonates diagnosed with perinatal arterial ischemic stroke (PAIS).
Methods:
Pulsed ASL perfusion MR images were acquired in the subacute stage (5–6 d after birth) and at follow-up (13 d to 16 wk after birth) in four PAIS patients. Images were visually evaluated for hypo- and hyperperfusion. In addition, cerebral oxygenation was monitored using near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS).
Results:
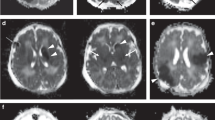
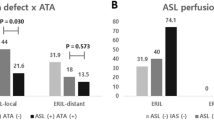
In three PAIS patients, ASL images showed hypoperfusion in the stroke area. In one of these, hyperperfusion was visualized in the periphery of the stroke area. In one PAIS patient, hyperperfusion was seen in the stroke area. In all infants, cerebral oxygenation was higher in the infarcted hemisphere as compared with the contralateral hemisphere. Follow-up ASL images showed partial recovery of perfusion in the stroke area.
Conclusion:
ASL perfusion MRI is able to reliably detect hypo- and hyperperfusion in PAIS patients and can be used to monitor the evolution of perfusion after an ischemic event.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Kirton A, deVeber G . Advances in perinatal ischemic stroke. Pediatr Neurol 2009;40:205–14.
Groenendaal F, Benders MJ, de Vries LS . Pre-wallerian degeneration in the neonatal brain following perinatal cerebral hypoxia-ischemia demonstrated with MRI. Semin Perinatol 2006;30:146–50.
Mercuri E, Barnett A, Rutherford M, et al. Neonatal cerebral infarction and neuromotor outcome at school age. Pediatrics 2004;113(1 Pt 1):95–100.
Bokkers RP, Hernandez DA, Merino JG, et al.; National Institutes of Health Stroke Natural History Investigators. Whole-brain arterial spin labeling perfusion MRI in patients with acute stroke. Stroke 2012;43:1290–4.
Chalela JA, Alsop DC, Gonzalez-Atavales JB, Maldjian JA, Kasner SE, Detre JA . Magnetic resonance perfusion imaging in acute ischemic stroke using continuous arterial spin labeling. Stroke 2000;31:680–7.
De Vis JB, Petersen ET, de Vries LS, et al. Regional changes in brain perfusion during brain maturation measured non-invasively with Arterial Spin Labeling MRI in neonates. Eur J Radiol 2013;82:538–43.
Licht DJ, Wang J, Silvestre DW, et al. Preoperative cerebral blood flow is diminished in neonates with severe congenital heart defects. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2004;128:841–9.
Miranda MJ, Olofsson K, Sidaros K . Noninvasive measurements of regional cerebral perfusion in preterm and term neonates by magnetic resonance arterial spin labeling. Pediatr Res 2006;60:359–63.
Wang J, Licht DJ, Silvestre DW, Detre JA . Why perfusion in neonates with congenital heart defects is negative–technical issues related to pulsed arterial spin labeling. Magn Reson Imaging 2006;24:249–54.
Wintermark P, Warfield S . New insights in perinatal arterial ischemic stroke by assessing brain perfusion. Transl Stroke Res 2012;2:255–62.
Wintermark P, Hansen A, Gregas MC, et al. Brain perfusion in asphyxiated newborns treated with therapeutic hypothermia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2011;32:2023–9.
Dullenkopf A, Kolarova A, Schulz G, Frey B, Baenziger O, Weiss M . Reproducibility of cerebral oxygenation measurement in neonates and infants in the clinical setting using the NIRO 300 oximeter. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2005;6:344–7.
van Bel F, Lemmers P, Naulaers G . Monitoring neonatal regional cerebral oxygen saturation in clinical practice: value and pitfalls. Neonatology 2008;94:237–44.
van der Aa NE, Porsius ED, Hendrikse J, et al. Changes in carotid blood flow after unilateral perinatal arterial ischemic stroke. Pediatr Res 2012;72:50–6.
Bivard A, Stanwell P, Levi C, Parsons M . Arterial spin labeling identifies tissue salvage and good clinical recovery after acute ischemic stroke. J Neuroimaging 2013;23:391–6.
Marchal G, Furlan M, Beaudouin V, et al. Early spontaneous hyperperfusion after stroke. A marker of favourable tissue outcome? Brain 1996;119 (Pt 2):409–19.
Toet MC, Lemmers PM, van Schelven LJ, van Bel F . Cerebral oxygenation and electrical activity after birth asphyxia: their relation to outcome. Pediatrics 2006;117:333–9.
Oishi M, Ishida G, Morii K, Hasegawa K, Sato M, Fujii Y . Ictal focal hyperperfusion demonstrated by arterial spin-labeling perfusion MRI in partial epilepsy status. Neuroradiology 2012;54:653–6.
Harteman JC, Groenendaal F, Kwee A, Welsing PM, Benders MJ, de Vries LS . Risk factors for perinatal arterial ischaemic stroke in full-term infants: a case-control study. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2012;97:F411–6.
Chiron C, Raynaud C, Mazière B, et al. Changes in regional cerebral blood flow during brain maturation in children and adolescents. J Nucl Med 1992;33:696–703.
Kinnala A, Suhonen-Polvi H, Aärimaa T, et al. Cerebral metabolic rate for glucose during the first six months of life: an FDG positron emission tomography study. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 1996;74:F153–7.
Varela M, Hajnal JV, Petersen ET, Golay X, Merchant N, Larkman DJ . A method for rapid in vivo measurement of blood T1. NMR Biomed 2011;24:80–8.
Wijbenga RG, Lemmers PM, van Bel F . Cerebral oxygenation during the first days of life in preterm and term neonates: differences between different brain regions. Pediatr Res 2011;70:389–94.
Golay X, Petersen ET, Hui F . Pulsed star labeling of arterial regions (PULSAR): a robust regional perfusion technique for high field imaging. Magn Reson Med 2005;53:15–21.
Luh WM, Wong EC, Bandettini PA, Hyde JS . QUIPSS II with thin-slice TI1 periodic saturation: a method for improving accuracy of quantitative perfusion imaging using pulsed arterial spin labeling. Magn Reson Med 1999;41:1246–54.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Vis, J., Petersen, E., Kersbergen, K. et al. Evaluation of perinatal arterial ischemic stroke using noninvasive arterial spin labeling perfusion MRI. Pediatr Res 74, 307–313 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2013.111
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2013.111
This article is cited by
-
Spontaneous recanalization and hyperperfusion are relatively common at presentation in pediatric arterial ischemic stroke
Neuroradiology (2019)
-
Magnetic resonance imaging based noninvasive measurements of brain hemodynamics in neonates: a review
Pediatric Research (2016)
-
A pilot cohort study of cerebral autoregulation and 2-year neurodevelopmental outcomes in neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy who received therapeutic hypothermia
BMC Neurology (2015)
-
Arterial spin-labelling perfusion MRI and outcome in neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
European Radiology (2015)