Abstract
Background:
Sepsis continues to be a leading cause of death in infants and children. Natural killer (NK) cells serve as a bridge between innate and adaptive immunity, yet their role in pediatric sepsis has not been well characterized.
Methods:
We tested the hypothesis that decreased NK cell cytotoxicity is a common feature of pediatric systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS)/sepsis patients by measuring, using flow cytometry, NK cell cytotoxicity and cell surface phenotype in the peripheral blood of 38 pediatric intensive care patients who demonstrated signs and symptoms of SIRS and/or sepsis.
Results:
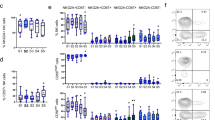
NK cell cytotoxicity was significantly reduced in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of pediatric SIRS/sepsis patients as compared with healthy controls, and the percentage of CD56dim CD16+ cytotoxic NK cells in PBMCs was lower in patients with SIRS/sepsis than in normal donors. However, on a per cell basis, CD56dim CD16+ NK cells in patients mediated cytotoxicity as well as those in normal donors.
Conclusion:
The NK cell dysfunction in pediatric SIRS/sepsis patients reflects a quantitative rather than a qualitative difference from healthy controls.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Watson RS, Carcillo JA . Scope and epidemiology of pediatric sepsis. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2005;6:Suppl 3:S3–5.
Rittirsch D, Flierl MA, Ward PA . Harmful molecular mechanisms in sepsis. Nat Rev Immunol 2008;8:776–87.
Kiessling R, Klein E, Wigzell H . “Natural” killer cells in the mouse. I. Cytotoxic cells with specificity for mouse Moloney leukemia cells. Specificity and distribution according to genotype. Eur J Immunol 1975;5:112–7.
Paust S, von Andrian UH . Natural killer cell memory. Nat Immunol 2011;12:500–8.
Cooper MA, Fehniger TA, Caligiuri MA . The biology of human natural killer-cell subsets. Trends Immunol 2001;22:633–40.
Mavilio D, Lombardo G, Benjamin J, et al. Characterization of CD56-/CD16+ natural killer (NK) cells: a highly dysfunctional NK subset expanded in HIV-infected viremic individuals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005;102:2886–91.
Alter G, Teigen N, Davis BT, et al. Sequential deregulation of NK cell subset distribution and function starting in acute HIV-1 infection. Blood 2005;106:3366–9.
Björkström NK, Ljunggren HG, Sandberg JK . CD56 negative NK cells: origin, function, and role in chronic viral disease. Trends Immunol 2010;31:401–6.
Blazar BA, Rodrick ML, O’Mahony JB, et al. Suppression of natural killer-cell function in humans following thermal and traumatic injury. J Clin Immunol 1986;6:26–36.
Villanueva J, Lee S, Giannini EH, et al. Natural killer cell dysfunction is a distinguishing feature of systemic onset juvenile rheumatoid arthritis and macrophage activation syndrome. Arthritis Res Ther 2005;7:R30–7.
Grom AA, Villanueva J, Lee S, Goldmuntz EA, Passo MH, Filipovich A . Natural killer cell dysfunction in patients with systemic-onset juvenile rheumatoid arthritis and macrophage activation syndrome. J Pediatr 2003;142:292–6.
von Muller L, Klemm A, Durmus N, et al. Cellular immunity and active human cytomegalovirus infection in patients with septic shock. J Infect Dis 2007;196:1288–95.
el-Sameea ER, Metwally SS, Mashhour E, et al. Evaluation of natural killer cells as diagnostic markers of early onset neonatal sepsis: comparison with C-reactive protein and interleukin-8. Egypt J Immunol 2004;11:91–102.
Goldstein B, Giroir B, Randolph A ; International Consensus Conference on Pediatric Sepsis. International pediatric sepsis consensus conference: definitions for sepsis and organ dysfunction in pediatrics. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2005;6:2–8.
Gonzalez VD, Falconer K, Björkström NK, et al. Expansion of functionally skewed CD56-negative NK cells in chronic hepatitis C virus infection: correlation with outcome of pegylated IFN-alpha and ribavirin treatment. J Immunol 2009;183:6612–8.
Reeves RK, Gillis J, Wong FE, Yu Y, Connole M, Johnson RP . CD16- natural killer cells: enrichment in mucosal and secondary lymphoid tissues and altered function during chronic SIV infection. Blood 2010;115:4439–46.
Björkström NK, Lindgren T, Stoltz M, et al. Rapid expansion and long-term persistence of elevated NK cell numbers in humans infected with hantavirus. J Exp Med 2011;208:13–21.
Sieni E, Cetica V, Mastrodicasa E, et al. Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a model for understanding the human machinery of cellular cytotoxicity. Cell Mol Life Sci 2012;69:29–40.
Stepp SE, Dufourcq-Lagelouse R, Le Deist F, et al. Perforin gene defects in familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Science 1999;286:1957–9.
Aricò M, Allen M, Brusa S, et al. Haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: proposal of a diagnostic algorithm based on perforin expression. Br J Haematol 2002;119:180–8.
Marcenaro S, Gallo F, Martini S, et al. Analysis of natural killer-cell function in familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (FHL): defective CD107a surface expression heralds Munc13-4 defect and discriminates between genetic subtypes of the disease. Blood 2006;108:2316–23.
Kim GG, Donnenberg VS, Donnenberg AD, Gooding W, Whiteside TL . A novel multiparametric flow cytometry-based cytotoxicity assay simultaneously immunophenotypes effector cells: comparisons to a 4 h 51Cr-release assay. J Immunol Methods 2007;325:51–66.
Bryant J, Day R, Whiteside TL, Herberman RB . Calculation of lytic units for the expression of cell-mediated cytotoxicity. J Immunol Methods 1992;146:91–103.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Halstead, E., Carcillo, J., Schilling, B. et al. Reduced frequency of CD56dim CD16pos natural killer cells in pediatric systemic inflammatory response syndrome/sepsis patients. Pediatr Res 74, 427–432 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2013.121
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2013.121
This article is cited by
-
Sepsis with liver dysfunction and coagulopathy predicts an inflammatory pattern of macrophage activation
Intensive Care Medicine Experimental (2022)
-
Pathological alteration and therapeutic implications of sepsis-induced immune cell apoptosis
Cell Death & Disease (2019)
-
Occurrence of marked sepsis-induced immunosuppression in pediatric septic shock: a pilot study
Annals of Intensive Care (2018)