Abstract
Background:
Kawasaki disease (KD) is a systemic vasculitis of unknown etiology. Thymus and activation-regulated chemokine/chemokine ligand 17 (TARC/CCL17) is one of the Th2 chemokines and has been suggested as a candidate gene for conferring susceptibility to Th2 associated with allergy diseases. This study examined the correlation between gene polymorphisms and plasma levels of TARC/CCL17 in patients with KD and the outcomes of KD.
Methods:
A total of 381 KD patients and 564 controls were subjected to determination of five tagging single-nucleotide polymorphisms of TARC/CCL17. In addition, plasma TARC/CCL17 levels were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Results:
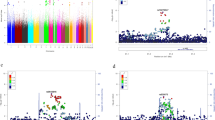
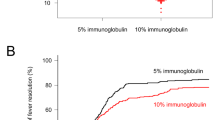
Polymorphisms of TARC/CCL17 were significantly different between normal children and patients with KD. A allele of rs4784805 has better intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) treatment response to KD. Furthermore, plasma TARC/CCL17 levels were higher in KD patients than that in controls before IVIG treatment. After IVIG treatment, plasma TARC/CCL17 levels decreased significantly.
Conclusion:
This study provides the first evidence supporting the association between TARC/CCL17 polymorphisms, susceptibility of KD, and IVIG responses in KD patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Kawasaki T, Kosaki F, Okawa S, Shigematsu I, Yanagawa H . A new infantile acute febrile mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome (MLNS) prevailing in Japan. Pediatrics 1974;54:271–6.
Wang CL, Wu YT, Liu CA, Kuo HC, Yang KD . Kawasaki disease: infection, immunity and genetics. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2005;24:998–1004.
Burns JC, Glodé MP . Kawasaki syndrome. Lancet 2004;364:533–44.
Liang CD, Kuo HC, Yang KD, Wang CL, Ko SF . Coronary artery fistula associated with Kawasaki disease. Am Heart J 2009;157:584–8.
Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Gerber MA, et al.; Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American Heart Association. Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: a statement for health professionals from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American Heart Association. Pediatrics 2004;114:1708–33.
Taubert KA, Rowley AH, Shulman ST . Nationwide survey of Kawasaki disease and acute rheumatic fever. J Pediatr 1991;119:279–82.
Imai T, Yoshida T, Baba M, Nishimura M, Kakizaki M, Yoshie O . Molecular cloning of a novel T cell-directed CC chemokine expressed in thymus by signal sequence trap using Epstein–Barr virus vector. J Biol Chem 1996;271:21514–21.
Imai T, Baba M, Nishimura M, Kakizaki M, Takagi S, Yoshie O . The T cell-directed CC chemokine TARC is a highly specific biological ligand for CC chemokine receptor 4. J Biol Chem 1997;272:15036–42.
Imai T, Nagira M, Takagi S, et al. Selective recruitment of CCR4-bearing Th2 cells toward antigen-presenting cells by the CC chemokines thymus and activation-regulated chemokine and macrophage-derived chemokine. Int Immunol 1999;11:81–8.
Tsunemi Y, Komine M, Sekiya T, et al. The -431C>T polymorphism of thymus and activation-regulated chemokine increases the promoter activity but is not associated with susceptibility to atopic dermatitis in Japanese patients. Exp Dermatol 2004;13:715–9.
Kakinuma T, Nakamura K, Wakugawa M, et al. Thymus and activation-regulated chemokine in atopic dermatitis: serum thymus and activation-regulated chemokine level is closely related with disease activity. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2001;107:535–41.
Sekiya T, Yamada H, Yamaguchi M, et al. Increased levels of a TH2-type CC chemokine thymus and activation-regulated chemokine (TARC) in serum and induced sputum of asthmatics. Allergy 2002;57:173–7.
Kuo HC, Wang CL, Liang CD, et al. Association of lower eosinophil-related T helper 2 (Th2) cytokines with coronary artery lesions in Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2009;20:266–72.
Brosius CL, Newburger JW, Burns JC, Hojnowski-Diaz P, Zierler S, Leung DY . Increased prevalence of atopic dermatitis in Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Infect Dis J 1988;7:863–6.
Webster RJ, Carter KW, Warrington NM, et al. Hospitalisation with infection, asthma and allergy in Kawasaki disease patients and their families: genealogical analysis using linked population data. PLoS ONE 2011;6:e28004.
Sekiya T, Tsunemi Y, Miyamasu M, et al. Variations in the human Th2-specific chemokine TARC gene. Immunogenetics 2003;54:742–5.
Liddiard K, Welch JS, Lozach J, Heinz S, Glass CK, Greaves DR . Interleukin-4 induction of the CC chemokine TARC (CCL17) in murine macrophages is mediated by multiple STAT6 sites in the TARC gene promoter. BMC Mol Biol 2006;7:45.
Wirnsberger G, Hebenstreit D, Posselt G, Horejs-Hoeck J, Duschl A . IL-4 induces expression of TARC/CCL17 via two STAT6 binding sites. Eur J Immunol 2006;36:1882–91.
Egwuagu CE, Yu CR, Zhang M, Mahdi RM, Kim SJ, Gery I . Suppressors of cytokine signaling proteins are differentially expressed in Th1 and Th2 cells: implications for Th cell lineage commitment and maintenance. J Immunol 2002;168:3181–7.
Nelms K, Keegan AD, Zamorano J, Ryan JJ, Paul WE . The IL-4 receptor: signaling mechanisms and biologic functions. Annu Rev Immunol 1999;17:701–38.
Kubo M, Hanada T, Yoshimura A . Suppressors of cytokine signaling and immunity. Nat Immunol 2003;4:1169–76.
Hijnen D, De Bruin-Weller M, Oosting B, et al. Serum thymus and activation-regulated chemokine (TARC) and cutaneous T cell- attracting chemokine (CTACK) levels in allergic diseases: TARC and CTACK are disease-specific markers for atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2004;113:334–40.
Wang GB, Li CR, Zu Y . [Change of MyD88-independent signal transduction of Toll-like receptor 4 in immunological pathogenesis of Kawasaki disease]. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi 2007;45:818–23.
Ogata S, Ogihara Y, Nomoto K, et al. Clinical score and transcript abundance patterns identify Kawasaki disease patients who may benefit from addition of methylprednisolone. Pediatr Res 2009;66:577–84.
Greaves DR, Häkkinen T, Lucas AD, et al. Linked chromosome 16q13 chemokines, macrophage-derived chemokine, fractalkine, and thymus- and activation-regulated chemokine, are expressed in human atherosclerotic lesions. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2001;21:923–9.
Kuo HC, Chang WC . Genetic polymorphisms in Kawasaki disease. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2011;32:1193–8.
Burgner D, Davila S, Breunis WB, et al.; International Kawasaki Disease Genetics Consortium. A genome-wide association study identifies novel and functionally related susceptibility Loci for Kawasaki disease. PLoS Genet 2009;5:e1000319.
Onouchi Y, Gunji T, Burns JC, et al. ITPKC functional polymorphism associated with Kawasaki disease susceptibility and formation of coronary artery aneurysms. Nat Genet 2008;40:35–42.
Kuo HC, Yang KD, Juo SH, et al. ITPKC single nucleotide polymorphism associated with the Kawasaki disease in a Taiwanese population. PLoS ONE 2011;6:e17370.
Kuo HC, Yu HR, Juo SH, et al. CASP3 gene single-nucleotide polymorphism (rs72689236) and Kawasaki disease in Taiwanese children. J Hum Genet 2011;56:161–5.
Kuo HC, Liang CD, Yu HR, et al. CTLA-4, position 49 A/G polymorphism associated with coronary artery lesions in Kawasaki disease. J Clin Immunol 2011;31:240–4.
Kuo HC, Onouchi Y, Hsu YW, et al. Polymorphisms of transforming growth factor-ß signaling pathway and Kawasaki disease in the Taiwanese population. J Hum Genet 2011;56:840–5.
Kuo HC, Liang CD, Wang CL, Yu HR, Hwang KP, Yang KD . Serum albumin level predicts initial intravenous immunoglobulin treatment failure in Kawasaki disease. Acta Paediatr 2010;99:1578–83.
Shulman ST, De Inocencio J, Hirsch R . Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Clin North Am 1995;42:1205–22.
Kuo HC, Yang KD, Liang CD, et al. The relationship of eosinophilia to intravenous immunoglobulin treatment failure in Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2007;18:354–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Table S1
(DOC 46 kb)
PowerPoint slides
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, CP., Huang, YH., Hsu, YW. et al. TARC/CCL17 gene polymorphisms and expression associated with susceptibility and coronary artery aneurysm formation in Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Res 74, 545–551 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2013.134
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2013.134
This article is cited by
-
CXCL13 polymorphism is associated with essential hypertension in Tatars from Russia
Molecular Biology Reports (2018)
-
Plasma levels of monokine induced by interferon-gamma/chemokine (C-X-X motif) ligand 9, thymus and activation-regulated chemokine/chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 17 in children with Kawasaki disease
BMC Pediatrics (2015)