Abstract
Background:
Low birth weight (LBW) is associated with increased morbidity and mortality for the newborn and risk of chronic disease in adulthood. Choline plays an essential role in the integrity of cell membranes, methylation reactions, and memory development. We examined whether choline, betaine, and dimethylglycine (DMG) concentrations were associated with LBW in Dutch women.
Methods:
Blood was sampled from umbilical cords (UCs) at delivery in singleton pregnancies (n = 1,126). Maternal blood was sampled at 30–34 wk of gestational age (GA) (n = 366). We calculated birth weights standardized for GA and defined LBW as standardized birth weight ≤2,500 g.
Results:
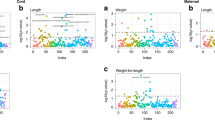
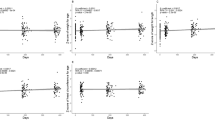
Maternal concentrations were lower as compared with UC concentrations and were not associated with birth weight. UC choline and betaine were inversely associated with birth weight (β = −60 (−89, −31) and β = −65 (−94, −36), respectively), whereas UC DMG was positively associated with birth weight (β = 35 (6.1, 63)). Odds ratios for LBW were 4.12 (1.15, 14.78), 5.68 (1.24, 25.91), and 0.48 (0.09, 2.65) for the highest UC choline, betaine, and DMG quartiles, respectively, as compared with the lowest quartiles.
Conclusion:
We observed an increased risk of LBW with increased umbilical choline and betaine in venous UC blood. These results might reflect a change in choline consumption or metabolism or a disturbed placental function.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Papageorgou A, Pelausa E, Kovacs L . The extremely low birth weight infant. In: MacDonald MG, Seshia MMK, eds. Avery’s Neonatology, 5th edn. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2009:978–1025.
Barker DJ . The fetal and infant origins of disease. Eur J Clin Invest 1995;25:457–63.
Buchman AL, Sohel M, Brown M, et al. Verbal and visual memory improve after choline supplementation in long-term total parenteral nutrition: a pilot study. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 2001;25:30–5.
Zeisel SH . Choline, homocysteine, and pregnancy. Am J Clin Nutr 2005;82:719–20.
Zeisel SH, Mar MH, Zhou Z, da Costa KA . Pregnancy and lactation are associated with diminished concentrations of choline and its metabolites in rat liver. J Nutr 1995;125:3049–54.
Zeisel SH . Choline: critical role during fetal development and dietary requirements in adults. Annu Rev Nutr 2006;26:229–50.
Sweiry JH, Page KR, Dacke CG, Abramovich DR, Yudilevich DL . Evidence of saturable uptake mechanisms at maternal and fetal sides of the perfused human placenta by rapid paired-tracer dilution: studies with calcium and choline. J Dev Physiol 1986;8:435–45.
McMahon KE, Farrell PM . Measurement of free choline concentrations in maternal and neonatal blood by micropyrolysis gas chromatography. Clin Chim Acta 1985;149:1–12.
Craciunescu CN, Wu R, Zeisel SH . Diethanolamine alters neurogenesis and induces apoptosis in fetal mouse hippocampus. FASEB J 2006;20:1635–40.
Zeisel SH, Niculescu MD . Perinatal choline influences brain structure and function. Nutr Rev 2006;64:197–203.
Thomas JD, Garrison M, O’Neill TM . Perinatal choline supplementation attenuates behavioral alterations associated with neonatal alcohol exposure in rats. Neurotoxicol Teratol 2004;26:35–45.
Shaw GM, Finnell RH, Blom HJ, et al. Choline and risk of neural tube defects in a folate-fortified population. Epidemiology 2009;20:714–9.
Shaw GM, Carmichael SL, Yang W, Selvin S, Schaffer DM . Periconceptional dietary intake of choline and betaine and neural tube defects in offspring. Am J Epidemiol 2004;160:102–9.
Ozarda Ilcol Y, Uncu G, Ulus IH . Free and phospholipid-bound choline concentrations in serum during pregnancy, after delivery and in newborns. Arch Physiol Biochem 2002;110:393–9.
Buchman AL, Sohel M, Moukarzel A, et al. Plasma choline in normal newborns, infants, toddlers, and in very-low-birth-weight neonates requiring total parenteral nutrition. Nutrition 2001;17:18–21.
Zeisel SH, Epstein MF, Wurtman RJ . Elevated choline concentration in neonatal plasma. Life Sci 1980;26:1827–31.
Yudilevich DL, Sweiry JH . Membrane carriers and receptors at maternal and fetal sides of the placenta by single circulation paired-tracer dilution: evidence for a choline transport system. Contrib Gynecol Obstet 1985;13:158–61.
Velzing-Aarts FV, Holm PI, Fokkema MR, van der Dijs FP, Ueland PM, Muskiet FA . Plasma choline and betaine and their relation to plasma homocysteine in normal pregnancy. Am J Clin Nutr 2005;81:1383–9.
Wallace JM, Bonham MP, Strain J, et al. Homocysteine concentration, related B vitamins, and betaine in pregnant women recruited to the Seychelles Child Development Study. Am J Clin Nutr 2008;87:391–7.
Braekke K, Ueland PM, Harsem NK, Karlsen A, Blomhoff R, Staff AC . Homocysteine, cysteine, and related metabolites in maternal and fetal plasma in preeclampsia. Pediatr Res 2007;62:319–24.
Molloy AM, Mills JL, Cox C, et al. Choline and homocysteine interrelations in umbilical cord and maternal plasma at delivery. Am J Clin Nutr 2005;82:836–42.
Friesen RW, Novak EM, Hasman D, Innis SM . Relationship of dimethylglycine, choline, and betaine with oxoproline in plasma of pregnant women and their newborn infants. J Nutr 2007;137:2641–6.
Ilcol YO, Ozbek R, Hamurtekin E, Ulus IH . Choline status in newborns, infants, children, breast-feeding women, breast-fed infants and human breast milk. J Nutr Biochem 2005;16:489–99.
Cogswell ME, Yip R . The influence of fetal and maternal factors on the distribution of birthweight. Semin Perinatol 1995;19:222–40.
Solanky N, Requena Jimenez A, D’Souza SW, Sibley CP, Glazier JD . Expression of folate transporters in human placenta and implications for homocysteine metabolism. Placenta 2010;31:134–43.
Zeisel SH . Dietary choline: biochemistry, physiology, and pharmacology. Annu Rev Nutr 1981;1:95–121.
Hogeveen M, Blom HJ, van der Heijden EH, et al. Maternal homocysteine and related B vitamins as risk factors for low birthweight. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2010;202:572.e1–6.
Ueland PM, Midttun O, Windelberg A, Svardal A, Skålevik R, Hustad S . Quantitative profiling of folate and one-carbon metabolism in large-scale epidemiological studies by mass spectrometry. Clin Chem Lab Med 2007;45:1737–45.
Hastie T, Tibshirani R . Generalized additive models for medical research. Stat Methods Med Res 1995;4:187–96.
Acknowledgements
We thank Gry Kvalheim and Arno van Rooij for their expert technical assistance contributing to the laboratory results.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hogeveen, M., den Heijer, M., Semmekrot, B. et al. Umbilical choline and related methylamines betaine and dimethylglycine in relation to birth weight. Pediatr Res 73, 783–787 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2013.54
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2013.54
This article is cited by
-
Serum choline in extremely preterm infants declines with increasing parenteral nutrition
European Journal of Nutrition (2021)
-
Choline and polyunsaturated fatty acids in preterm infants’ maternal milk
European Journal of Nutrition (2017)
-
Validation of a Food Frequency Questionnaire for Estimating Micronutrient Intakes in an Urban US Sample of Multi-Ethnic Pregnant Women
Maternal and Child Health Journal (2016)
-
An isotope dilution capillary electrophoresis/tandem mass spectrometry (CE-MS/MS) method for the simultaneous measurement of choline, betaine, and dimethylglycine concentrations in human plasma
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry (2016)
-
1H-NMR metabolite profiling of abalone digestive gland in response to short-term starvation
Aquaculture International (2016)